LED resistors help regulate current flow to prevent LED burnout, while load equalizers mimic the resistance of standard bulbs to avoid error codes in vehicles with CAN bus systems. Discover which component best suits your automotive lighting needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
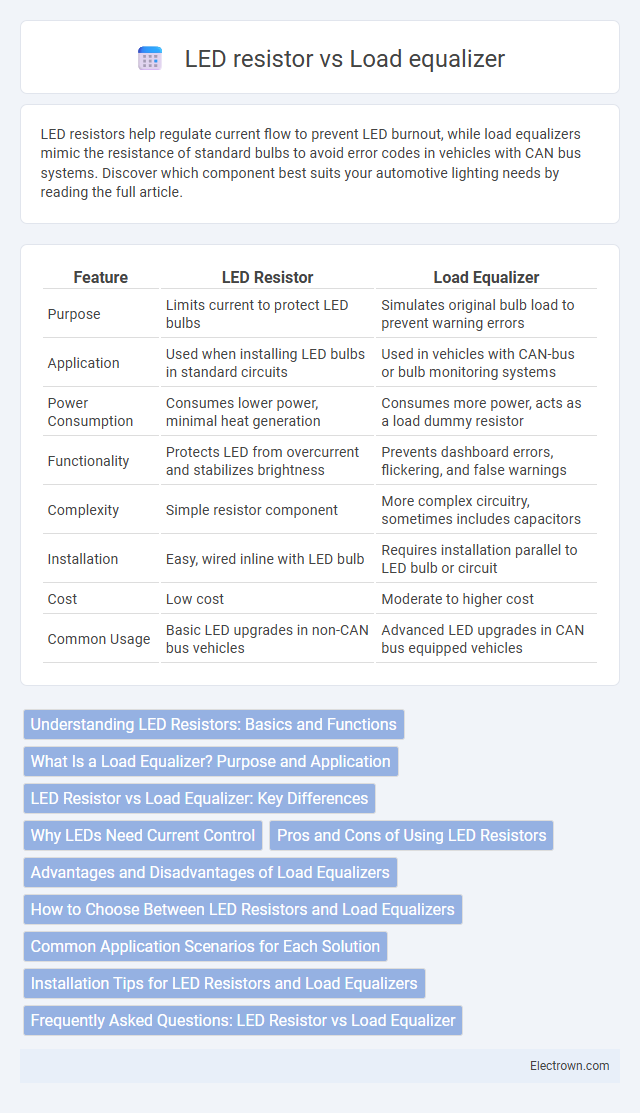
| Feature | LED Resistor | Load Equalizer |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Limits current to protect LED bulbs | Simulates original bulb load to prevent warning errors |
| Application | Used when installing LED bulbs in standard circuits | Used in vehicles with CAN-bus or bulb monitoring systems |
| Power Consumption | Consumes lower power, minimal heat generation | Consumes more power, acts as a load dummy resistor |
| Functionality | Protects LED from overcurrent and stabilizes brightness | Prevents dashboard errors, flickering, and false warnings |
| Complexity | Simple resistor component | More complex circuitry, sometimes includes capacitors |
| Installation | Easy, wired inline with LED bulb | Requires installation parallel to LED bulb or circuit |
| Cost | Low cost | Moderate to higher cost |
| Common Usage | Basic LED upgrades in non-CAN bus vehicles | Advanced LED upgrades in CAN bus equipped vehicles |
Understanding LED Resistors: Basics and Functions
LED resistors regulate current flow to protect LEDs from damage by limiting the amount of electricity passing through them, ensuring consistent brightness and prolonged lifespan. Load equalizers mimic the electrical load of standard bulbs, preventing error messages or hyper-flashing in vehicles when LED lights are installed. Understanding these components helps you choose the right solution for maintaining proper electrical function and protecting your LED lighting system.
What Is a Load Equalizer? Purpose and Application
A load equalizer is an electronic device designed to simulate the electrical load of a standard filament bulb in LED lighting circuits, preventing hyper-flashing, flickering, or error messages on your vehicle's dashboard. Its primary purpose is to balance the current flow and voltage in the circuit, ensuring compatibility between LED bulbs and the vehicle's original wiring system. Load equalizers are commonly applied in automotive lighting upgrades to maintain proper function and avoid codes generated by the car's monitoring system.
LED Resistor vs Load Equalizer: Key Differences
LED resistors primarily limit current to prevent LED burnout, ensuring stable operation in automotive lighting systems. Load equalizers mimic standard filament bulb resistance, preventing hyper-flashing or error codes in vehicles with LED replacement bulbs. While LED resistors dissipate heat to manage current, load equalizers integrate electronic components to simulate bulb load, making them essential for compatibility with vehicle CAN bus systems.
Why LEDs Need Current Control
LEDs require current control because they are current-driven devices, and without proper regulation, they can draw excessive current leading to overheating or failure. LED resistors provide a simple method to limit current by dropping voltage, but load equalizers are used to simulate the resistance of traditional incandescent bulbs, preventing hyper-flashing in vehicle lighting systems. Your choice between an LED resistor and a load equalizer depends on whether you need basic current limiting or to maintain proper signal behavior in automotive applications.
Pros and Cons of Using LED Resistors
LED resistors offer a simple and cost-effective solution for preventing hyper-flashing and ensuring proper current flow in LED lighting systems. They provide reliable heat dissipation and are easy to install but can generate excess heat, reducing energy efficiency and potentially shortening component lifespan. Compared to load equalizers, LED resistors do not mimic real bulb resistance as accurately, which may lead to less precise system compatibility in advanced vehicle electronics.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Load Equalizers
Load equalizers prevent hyper-flashing and error codes by simulating the resistance of traditional bulbs, making them ideal for LED turn signals. They offer the advantage of simple plug-and-play installation and compatibility with various vehicle models. However, load equalizers can generate heat, potentially draining battery power and causing electrical inefficiency compared to LED-specific resistors.
How to Choose Between LED Resistors and Load Equalizers
Choosing between LED resistors and load equalizers depends on the vehicle's electrical system and the type of LED lights installed. LED resistors dissipate excess current to prevent hyper-flashing in turn signals, best suited for simple setups without CAN bus systems. Load equalizers mimic the load of incandescent bulbs, ensuring compatibility with CAN bus and avoiding dashboard errors in modern vehicles.
Common Application Scenarios for Each Solution
LED resistors are commonly used in automotive lighting to prevent hyper-flashing and ensure consistent brightness in vehicles with LED turn signals, ideal for simple circuits requiring minimal modification. Load equalizers are preferred in complex setups where multiple LEDs are installed, such as aftermarket tail lights or interior lighting, providing stable current regulation and preventing error messages on advanced vehicle computer systems. You can choose LED resistors for straightforward applications, while load equalizers are suited for maintaining system compatibility in vehicles with sophisticated electronics.
Installation Tips for LED Resistors and Load Equalizers
When installing LED resistors, ensure the resistor value matches the LED specifications to prevent overcurrent and reduce flickering, and place it parallel to the LED circuit for stable voltage regulation. For load equalizers, position them close to the LED bulbs in the vehicle's wiring harness to mimic the resistance of traditional incandescent bulbs, preventing error codes and hyper-flashing in turn signals. Proper soldering, insulation, and secure mounting are essential for both components to guarantee reliable operation and longevity.
Frequently Asked Questions: LED Resistor vs Load Equalizer
LED resistors limit current in LED tail lights to prevent hyper-flashing, while load equalizers simulate the standard load of incandescent bulbs for proper vehicle signaling. Both devices address incompatibility issues in automotive lighting, but LED resistors dissipate power as heat, whereas load equalizers use electronic circuitry to mimic load without excessive energy loss. Choosing between them depends on vehicle wiring, budget, and installation complexity.
LED resistor vs Load equalizer Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com