Wireless charging offers the convenience of cable-free power transfer, reducing wear on charging ports and enabling easy device placement on charging pads, while plug-in charging typically provides faster, more efficient energy transfer directly through cables for quicker battery replenishment. Explore the rest of the article to find out which charging method suits your lifestyle and device needs best.
Table of Comparison
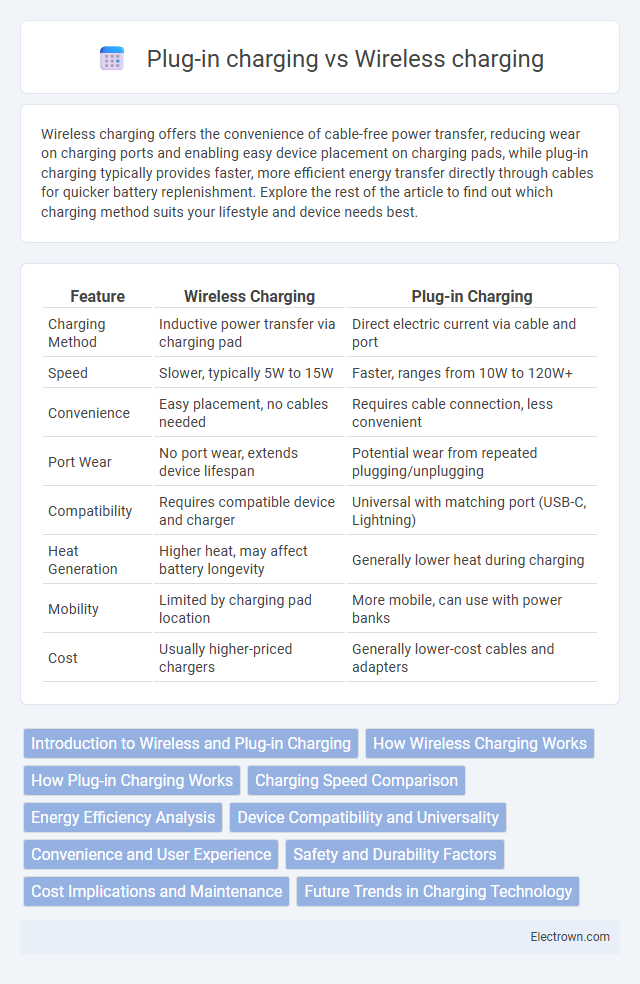
| Feature | Wireless Charging | Plug-in Charging |
|---|---|---|
| Charging Method | Inductive power transfer via charging pad | Direct electric current via cable and port |
| Speed | Slower, typically 5W to 15W | Faster, ranges from 10W to 120W+ |
| Convenience | Easy placement, no cables needed | Requires cable connection, less convenient |
| Port Wear | No port wear, extends device lifespan | Potential wear from repeated plugging/unplugging |
| Compatibility | Requires compatible device and charger | Universal with matching port (USB-C, Lightning) |
| Heat Generation | Higher heat, may affect battery longevity | Generally lower heat during charging |
| Mobility | Limited by charging pad location | More mobile, can use with power banks |
| Cost | Usually higher-priced chargers | Generally lower-cost cables and adapters |
Introduction to Wireless and Plug-in Charging
Wireless charging utilizes electromagnetic fields to transfer energy between a charging pad and a device without physical connectors, enabling convenience and reducing wear on ports. Plug-in charging relies on direct electrical contact through cables and connectors, typically offering faster power delivery and compatibility with a wide range of devices. Both methods serve essential roles in powering smartphones, wearables, and electric vehicles, with choices guided by speed, convenience, and device design considerations.
How Wireless Charging Works
Wireless charging operates through electromagnetic induction, where an alternating current in the charging pad creates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the receiver coil embedded in the device, converting it back into electrical energy to charge the battery. This technology relies on close proximity alignment between the transmitter and receiver coils to ensure efficient energy transfer, typically within a few millimeters. Advanced versions use resonant inductive coupling to extend the range and improve charging speed, making wireless charging convenient for smartphones, wearables, and electric vehicles.
How Plug-in Charging Works
Plug-in charging works by connecting your device directly to a power source through a cable, allowing electrical current to flow efficiently and rapidly into the battery. This direct electrical connection ensures faster charging speeds and better energy transfer compared to wireless methods. You benefit from higher charging efficiency and reduced energy loss, making it ideal for devices requiring quick power replenishment.
Charging Speed Comparison
Wireless charging typically offers slower charging speeds compared to plug-in charging, with wireless chargers delivering around 5 to 15 watts, while plug-in chargers can provide 20 watts or more, especially with fast-charging technologies. The efficiency of wireless charging is often reduced due to energy loss during transmission, resulting in longer charging times for your device. For the fastest charging experience, a plug-in charger remains the preferred choice, particularly when time is critical.
Energy Efficiency Analysis
Wireless charging typically exhibits lower energy efficiency compared to plug-in charging, with efficiency rates ranging from 60% to 80% due to energy loss in electromagnetic induction. Plug-in charging systems achieve higher energy efficiency, often exceeding 90%, by directly transferring electrical power through conductive connections. Analyzing energy consumption data reveals that wireless charging results in increased power waste and longer charging times compared to conventional plug-in methods.
Device Compatibility and Universality
Wireless charging offers broad compatibility with devices adhering to the Qi standard, including many smartphones, earbuds, and smartwatches, enabling cable-free power across multiple brands. Plug-in charging provides universal compatibility with virtually all devices, as it relies on wired connections like USB-C, Lightning, or micro-USB, making it essential for devices without wireless capabilities. Despite wireless charging's growing adoption, plug-in charging remains the most universally compatible method due to its direct power delivery and widespread connector support.
Convenience and User Experience
Wireless charging offers unparalleled convenience by eliminating the need for cables, allowing you to simply place your device on a charging pad, which enhances the overall user experience through effortless power replenishment. Plug-in charging, while requiring physical connection, typically delivers faster charging speeds and is more widely compatible with a variety of devices and accessories. Your choice between these methods depends on prioritizing ease of use versus charging efficiency and device versatility.
Safety and Durability Factors
Wireless charging reduces wear and tear on device ports, enhancing long-term durability by eliminating repeated cable insertion and removal. Plug-in charging, while generally faster, can cause physical damage to charging ports over time, posing safety risks such as short circuits or loose connections. Both methods incorporate safety features like overcharge protection and temperature regulation, but wireless charging offers a lower risk of electrical hazards due to its contactless design.
Cost Implications and Maintenance
Wireless charging systems typically incur higher initial costs due to advanced technology and specialized hardware requirements, whereas plug-in charging solutions are more affordable and widely available. Maintenance for wireless chargers tends to be minimal but may involve more expensive repairs if components fail, while plug-in chargers have simpler designs that are easier and cheaper to repair or replace. Cost-effectiveness over time favors plug-in charging for frequent use, although wireless charging offers convenience with potentially lower wear on device ports.
Future Trends in Charging Technology
Wireless charging technology is rapidly advancing with developments in longer range, higher efficiency, and faster power transfer, aiming to eliminate the need for physical connectors and enhance user convenience. Plug-in charging continues to evolve through innovations like ultra-fast charging protocols and improved cable durability, supporting higher wattages that reduce charging times significantly. Future trends suggest a hybrid approach combining wireless and plug-in methods, integrating smart charging systems and energy management for seamless, efficient device power solutions.
Wireless charging vs Plug-in charging Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com