End-of-line tests evaluate the final product's quality by checking for defects after manufacturing, while inline tests monitor and ensure quality during the production process to catch issues early. Discover how understanding the differences between these testing methods can improve Your manufacturing outcomes by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
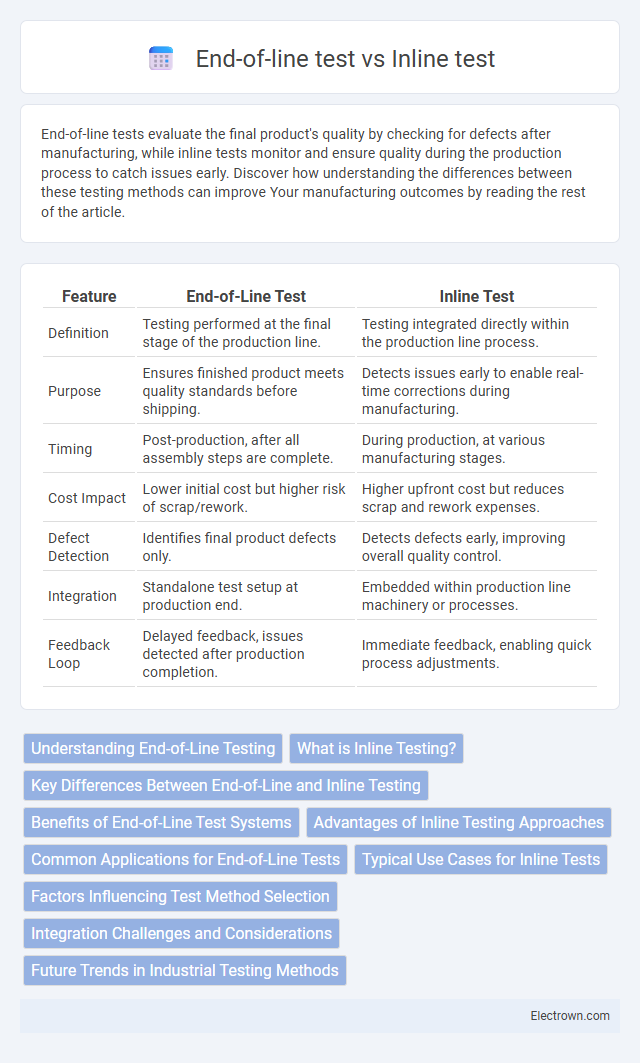
| Feature | End-of-Line Test | Inline Test |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Testing performed at the final stage of the production line. | Testing integrated directly within the production line process. |
| Purpose | Ensures finished product meets quality standards before shipping. | Detects issues early to enable real-time corrections during manufacturing. |
| Timing | Post-production, after all assembly steps are complete. | During production, at various manufacturing stages. |
| Cost Impact | Lower initial cost but higher risk of scrap/rework. | Higher upfront cost but reduces scrap and rework expenses. |
| Defect Detection | Identifies final product defects only. | Detects defects early, improving overall quality control. |
| Integration | Standalone test setup at production end. | Embedded within production line machinery or processes. |
| Feedback Loop | Delayed feedback, issues detected after production completion. | Immediate feedback, enabling quick process adjustments. |
Understanding End-of-Line Testing
End-of-line (EOL) testing is a critical quality control process performed on finished products to verify functionality, performance, and compliance with specifications before shipping. Unlike inline testing, which occurs during manufacturing to identify defects at intermediate stages, EOL testing ensures all system components work cohesively in real-world scenarios. This comprehensive assessment helps detect latent faults, ensuring reliability and customer satisfaction for complex electronic devices and automotive systems.
What is Inline Testing?
Inline testing refers to the process of evaluating electronic components or assemblies during the manufacturing line, allowing real-time defect detection and immediate feedback without halting production. This method improves efficiency by integrating test procedures directly into the assembly workflow, reducing the need for separate end-of-line testing phases. Inline testing uses automated equipment and sensors to identify faults early, facilitating quicker corrections and minimizing overall production downtime.
Key Differences Between End-of-Line and Inline Testing
End-of-line testing primarily occurs after the entire manufacturing process, assessing the final product's functionality and quality to ensure it meets specifications before shipment. Inline testing integrates test procedures during the manufacturing process, allowing for real-time detection and correction of defects, which reduces production downtime and improves yield. Key differences include timing of the test within the production cycle, impact on production flow, and ability to catch defects early versus verifying final product compliance.
Benefits of End-of-Line Test Systems
End-of-line test systems provide comprehensive quality assurance by verifying the complete functionality of electronic products before shipment, reducing the risk of defective units reaching customers. These systems enhance production efficiency through automated testing processes that minimize human error and accelerate throughput. Implementing end-of-line testing leads to improved product reliability, customer satisfaction, and lower warranty costs by ensuring that only fully validated products leave the manufacturing line.
Advantages of Inline Testing Approaches
Inline testing offers real-time detection of defects during the manufacturing process, significantly reducing downtime and rework costs compared to end-of-line testing. It enhances product quality by enabling immediate identification and correction of faults, ensuring higher yield rates and consistent output. Your production efficiency improves as inline testing integrates seamlessly into assembly lines, facilitating continuous monitoring without halting operations.
Common Applications for End-of-Line Tests
End-of-line tests are crucial in manufacturing environments where final quality assurance ensures products meet specifications before shipping. Common applications include automotive assembly, electronics manufacturing, and appliance production, where detecting functional defects, connectivity issues, or calibration errors is vital. Your production line benefits from these tests by reducing defects, improving reliability, and minimizing costly recalls.
Typical Use Cases for Inline Tests
Inline tests are commonly used during software development to verify the correctness of individual functions or methods as the code is written, ensuring immediate detection of errors. They are ideal for validating small units of code, supporting test-driven development (TDD) practices, and improving code quality by providing rapid feedback within integrated development environments (IDEs). Inline tests are particularly effective for continuous integration pipelines where quick, isolated testing helps maintain code stability before broader end-of-line testing.
Factors Influencing Test Method Selection
Factors influencing the selection between end-of-line (EOL) and inline testing methods include production volume, complexity of the product, and required test accuracy. Your choice depends on whether comprehensive data logging and final quality verification (EOL test) or real-time defect detection during manufacturing (inline test) are prioritized. Cost implications, testing speed, and integration with existing production systems also play crucial roles in determining the optimal test approach.
Integration Challenges and Considerations
End-of-line tests present integration challenges due to their placement at the final stage of the manufacturing process, making defect identification and correction more complex and costly. Inline tests enable real-time monitoring and quicker fault detection, but require seamless integration with production equipment and data systems to prevent workflow disruptions. Your testing strategy should balance these considerations to optimize quality control without compromising manufacturing efficiency.
Future Trends in Industrial Testing Methods
Future trends in industrial testing methods emphasize the integration of inline testing systems equipped with real-time data analytics and AI-driven defect detection, enhancing production efficiency and minimizing downtime. End-of-line testing remains crucial for final product validation but is increasingly supplemented by inline sensors and smart automation to detect defects earlier in the manufacturing process. The convergence of IoT technology and machine learning enables predictive maintenance and continuous quality monitoring, shaping a shift towards more adaptive and intelligent testing frameworks.
End-of-line test vs Inline test Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com