Wet sump systems store engine oil in a pan beneath the engine, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness, while dry sump systems use an external reservoir to improve oil control and prevent starvation during high-performance driving. Discover how understanding the differences between wet sump vs dry sump can enhance Your engine's reliability and performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
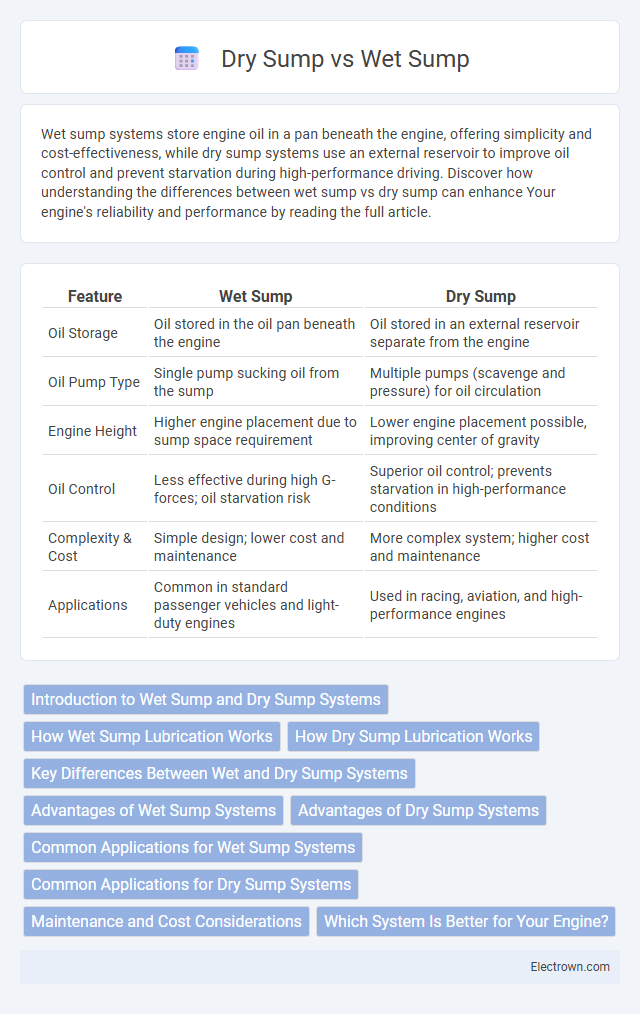
| Feature | Wet Sump | Dry Sump |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Storage | Oil stored in the oil pan beneath the engine | Oil stored in an external reservoir separate from the engine |
| Oil Pump Type | Single pump sucking oil from the sump | Multiple pumps (scavenge and pressure) for oil circulation |
| Engine Height | Higher engine placement due to sump space requirement | Lower engine placement possible, improving center of gravity |
| Oil Control | Less effective during high G-forces; oil starvation risk | Superior oil control; prevents starvation in high-performance conditions |
| Complexity & Cost | Simple design; lower cost and maintenance | More complex system; higher cost and maintenance |
| Applications | Common in standard passenger vehicles and light-duty engines | Used in racing, aviation, and high-performance engines |
Introduction to Wet Sump and Dry Sump Systems
Wet sump and dry sump systems are essential oil lubrication methods used in internal combustion engines. In a wet sump system, oil is stored in a pan beneath the engine, allowing gravity to return oil naturally, while a dry sump system uses an external reservoir and multiple scavenging pumps to manage oil flow, preventing oil starvation during high-performance or off-road driving. Understanding the differences in oil management and system design can help you choose the best lubrication system for your engine's performance and reliability needs.
How Wet Sump Lubrication Works
Wet sump lubrication circulates engine oil stored in a pan beneath the crankshaft, using an oil pump to deliver oil through passages to critical components like bearings and camshafts. The oil collects in the sump after lubricating the engine, cooling and protecting moving parts from friction and wear. This simple, cost-effective system is commonly used in everyday vehicles due to its reliability and ease of maintenance.
How Dry Sump Lubrication Works
Dry sump lubrication operates by utilizing an external reservoir and multiple scavenging pumps to remove oil from the engine crankcase quickly and efficiently, preventing oil starvation during high-performance driving. The system circulates oil through a series of filters and coolers before returning it to the engine, maintaining optimal oil pressure and temperature. This method reduces oil foaming and allows for a lower engine mounting position, enhancing vehicle stability and performance.
Key Differences Between Wet and Dry Sump Systems
Wet sump systems store engine oil in a pan beneath the engine, allowing gravity to return oil after circulation, which simplifies design and reduces cost. Dry sump systems use external reservoirs and multiple scavenge pumps to actively manage oil flow, providing improved lubrication under high-performance or extreme driving conditions. Key differences include oil storage location, complexity of components, and efficiency in oil control during rapid acceleration or cornering.
Advantages of Wet Sump Systems
Wet sump systems offer several advantages, including simpler design and lower cost due to fewer components compared to dry sump systems. These systems provide reliable lubrication by keeping oil in a reservoir at the bottom of the engine, ensuring consistent oil pressure during typical driving conditions. Your engine benefits from reduced complexity and easier maintenance when using a wet sump system.
Advantages of Dry Sump Systems
Dry sump systems offer superior oil control by preventing oil starvation and maintaining consistent oil pressure during high-performance driving or racing conditions. Their external reservoir increases oil capacity and improves cooling efficiency, which enhances engine durability and performance. You benefit from reduced engine height and improved ground clearance, enabling better vehicle handling and packaging flexibility.
Common Applications for Wet Sump Systems
Wet sump systems are widely used in everyday passenger vehicles, light trucks, and motorcycles due to their simple design and cost-effectiveness. These systems are ideal for applications where engine packaging space and manufacturing expenses need to be minimized. Commonly found in street cars and standard road-going motorcycles, wet sump setups provide reliable oil lubrication without the complexity of external reservoirs or pumps.
Common Applications for Dry Sump Systems
Dry sump systems are commonly used in high-performance and racing vehicles, offering superior oil control and preventing oil starvation during aggressive cornering or acceleration. You will also find dry sump systems in aircraft engines, where consistent oil pressure and reliability are critical under varying flight conditions. These systems excel in applications requiring precise lubrication in extreme environments and sustained high engine loads.
Maintenance and Cost Considerations
Wet sump oil systems generally have lower initial costs and simpler maintenance since they use standard engine components and require fewer specialized parts. Dry sump systems involve higher upfront expenses due to additional pumps, reservoirs, and plumbing, and their maintenance can be more complex and costly as a result. Your choice should weigh these factors against performance needs and long-term maintenance commitments.
Which System Is Better for Your Engine?
Wet sump systems are simpler, more cost-effective, and ideal for everyday driving and moderate performance engines due to their integrated oil reservoir in the oil pan. Dry sump systems offer superior oil control, enhanced cooling, and improved performance by storing oil in an external tank, making them the preferred choice for high-performance, racing, or off-road engines. Choosing the best system depends on your engine's power demands, operating conditions, and budget, with dry sump excelling in extreme environments while wet sump suits standard applications.
Wet sump vs Dry sump Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com