High-voltage interlock systems are designed to prevent accidental access to energized components by automatically disconnecting power when access panels are opened, enhancing operator safety during maintenance. Understanding the key differences between high-voltage interlocks and safety disconnect switches can help you choose the right protection mechanism for your electrical setup; read on to explore their functions, applications, and benefits in detail.
Table of Comparison
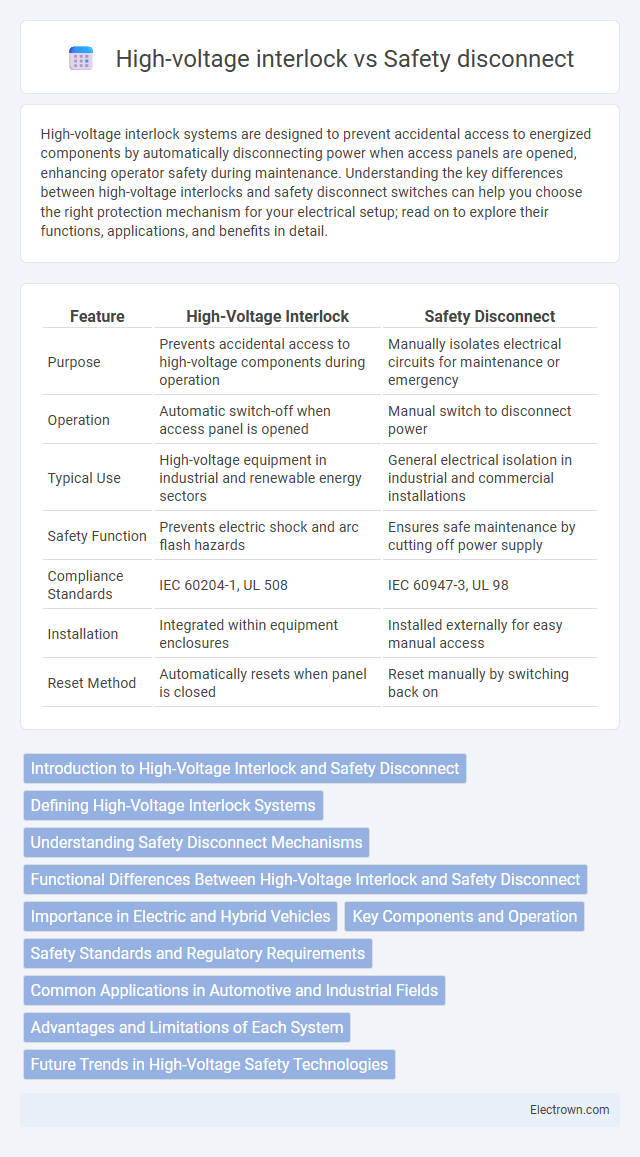
| Feature | High-Voltage Interlock | Safety Disconnect |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents accidental access to high-voltage components during operation | Manually isolates electrical circuits for maintenance or emergency |
| Operation | Automatic switch-off when access panel is opened | Manual switch to disconnect power |
| Typical Use | High-voltage equipment in industrial and renewable energy sectors | General electrical isolation in industrial and commercial installations |
| Safety Function | Prevents electric shock and arc flash hazards | Ensures safe maintenance by cutting off power supply |
| Compliance Standards | IEC 60204-1, UL 508 | IEC 60947-3, UL 98 |
| Installation | Integrated within equipment enclosures | Installed externally for easy manual access |
| Reset Method | Automatically resets when panel is closed | Reset manually by switching back on |
Introduction to High-Voltage Interlock and Safety Disconnect
High-voltage interlocks are essential safety devices designed to prevent accidental exposure to live electrical components by interrupting the circuit when access panels or doors are opened. Safety disconnects serve as manual switches that isolate electrical equipment from power sources, enabling safe maintenance and emergency shutdowns. Both devices play critical roles in electrical safety by ensuring controlled access and de-energization of high-voltage systems.
Defining High-Voltage Interlock Systems
High-voltage interlock systems (HVIL) are critical safety components designed to prevent accidental exposure to live electrical circuits by interrupting power when access to high-voltage parts is detected. These systems use sensors and switches to monitor enclosures, ensuring that vehicle or equipment operation ceases if covers or panels are opened. Unlike a safety disconnect, which provides a manual cutoff for electrical isolation, HVIL continuously monitors and automatically disables power to enhance operator safety in electric vehicles and industrial equipment.
Understanding Safety Disconnect Mechanisms
Safety disconnect mechanisms isolate electrical circuits by physically breaking the connection to prevent current flow, ensuring protection during maintenance or emergencies. High-voltage interlocks function by automatically interrupting power when access panels are opened, preventing exposure to live components and reducing the risk of electric shock or arc flash incidents. Both devices are critical for maintaining operational safety, with safety disconnects providing manual control and high-voltage interlocks offering automatic safeguard features in high-voltage systems.
Functional Differences Between High-Voltage Interlock and Safety Disconnect
High-voltage interlocks are designed to prevent access to live electrical components by interrupting power when a protective cover is removed, ensuring user safety during maintenance. Safety disconnects serve as manual switches that isolate electrical circuits by physically disconnecting power, allowing safe servicing and emergency shutdown. Your system's protection strategy benefits from combining high-voltage interlocks for automated prevention of hazardous exposure and safety disconnects for controlled circuit isolation.
Importance in Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
High-voltage interlock systems and safety disconnects are critical components in electric and hybrid vehicles for ensuring user and technician safety during maintenance and emergency situations. The high-voltage interlock prevents accidental exposure to dangerous electrical currents by interrupting power when access points are opened, while the safety disconnect allows the complete isolation of the high-voltage battery from the vehicle's electrical system. Your understanding of these safety features is essential to appreciate how they minimize the risk of electrical shock and support regulatory compliance in modern electric vehicle design.
Key Components and Operation
High-voltage interlocks typically consist of sensors, switches, and control circuits designed to prevent access to high-voltage areas unless the system is de-energized, ensuring operator safety by interrupting power flow when the interlock is engaged. Safety disconnect devices include a manually operated switch or breaker that physically isolates electrical equipment from the power source, providing a clear and reliable means to cut off electrical power for maintenance or emergency situations. The operation of high-voltage interlocks involves automatic detection and interruption of hazardous conditions, while safety disconnects require intentional human activation to disconnect power.
Safety Standards and Regulatory Requirements
High-voltage interlocks and safety disconnects must comply with stringent safety standards such as IEC 60947-3 and UL 508A to ensure proper protection against electrical hazards. Your equipment installation requires adherence to regulatory requirements like OSHA and NFPA 70E, which mandate appropriate lockout-tagout procedures and emergency disconnects for high-voltage systems. Understanding the distinctions between these devices helps maintain compliance and enhances operational safety within industrial environments.
Common Applications in Automotive and Industrial Fields
High-voltage interlocks are crucial in automotive electric vehicles, ensuring circuits are de-energized before maintenance, while safety disconnects are widely used in industrial machinery for emergency power isolation. Both devices enhance operational safety by preventing accidental energization, with interlocks primarily safeguarding high-voltage battery systems and disconnects securing heavy electrical equipment. Your understanding of these components is essential for maintaining compliance with safety standards in automotive manufacturing and industrial automation.
Advantages and Limitations of Each System
High-voltage interlock systems provide continuous monitoring and automatic shutdown features, enhancing safety by preventing access to energized components, but they may be complex to install and maintain. Safety disconnect switches offer a straightforward manual method to isolate electrical circuits for maintenance or emergency purposes, though they rely on proper operation by personnel and may not detect faults automatically. Your choice depends on balancing automated safety benefits with operational simplicity and maintenance capabilities.
Future Trends in High-Voltage Safety Technologies
Emerging advancements in high-voltage safety technologies emphasize enhanced integration of smart high-voltage interlock systems with real-time monitoring and automated diagnostics, surpassing traditional safety disconnect mechanisms. Your electrical infrastructure will benefit from predictive maintenance capabilities enabled by IoT connectivity and AI-driven data analysis, ensuring rapid fault detection and minimizing downtime. Future trends point toward increasingly reliable, user-centric solutions combining secure energy isolation with proactive safety management in high-voltage environments.
High-voltage interlock vs Safety disconnect Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com