Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controls regulate power by varying the width of the pulses, providing precise control over devices like motors and LEDs through efficient energy use. Understanding the differences between PWM and Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) can enhance Your control system's performance; explore the rest of this article to discover how each method impacts your applications.
Table of Comparison
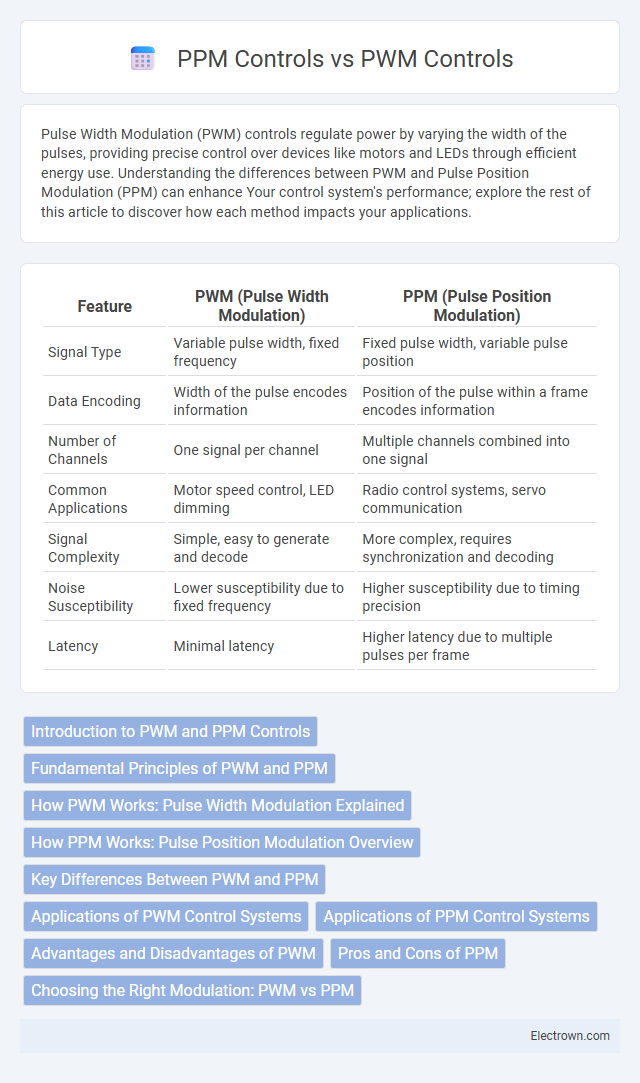
| Feature | PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) | PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Variable pulse width, fixed frequency | Fixed pulse width, variable pulse position |
| Data Encoding | Width of the pulse encodes information | Position of the pulse within a frame encodes information |
| Number of Channels | One signal per channel | Multiple channels combined into one signal |
| Common Applications | Motor speed control, LED dimming | Radio control systems, servo communication |
| Signal Complexity | Simple, easy to generate and decode | More complex, requires synchronization and decoding |
| Noise Susceptibility | Lower susceptibility due to fixed frequency | Higher susceptibility due to timing precision |
| Latency | Minimal latency | Higher latency due to multiple pulses per frame |
Introduction to PWM and PPM Controls
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controls regulate power by varying the duty cycle of a fixed-frequency signal, enabling precise control of motor speed and brightness in electronic devices. Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) controls encode information in the timing of signal pulses, commonly used in radio control systems for transmitting multiple channel data within a single signal frame. PWM offers high efficiency and smooth control for actuators, while PPM provides robust multi-channel communication essential for remote control applications.
Fundamental Principles of PWM and PPM
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controls motor speed by varying the duty cycle of a fixed-frequency signal, adjusting the proportion of 'on' time versus 'off' time to regulate power delivery. Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) varies the timing or position of pulses within a fixed frame period, encoding control signals through differences in pulse timing rather than width. PWM is widely used for precise power control in electric motors, while PPM finds applications in radio control systems where signal timing encodes multi-channel information.
How PWM Works: Pulse Width Modulation Explained
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controls the power delivered to devices by rapidly switching a signal on and off, varying the width of the "on" pulse within each cycle to adjust the effective voltage. This modulation of pulse duration allows precise control of motor speed, LED brightness, and other electronic components by changing the duty cycle between 0% and 100%. PWM signals maintain a constant frequency while varying pulse width, enabling efficient energy use and reducing heat generation in powered devices.
How PPM Works: Pulse Position Modulation Overview
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) controls operate by varying the timing of pulses within a fixed frame duration, where each pulse's position corresponds to a specific channel's signal value. Unlike Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), which adjusts the pulse width to encode information, PPM encodes multiple control channels into a single stream by sequentially shifting pulse locations. This timing-based encoding allows receivers to interpret several channels efficiently, making PPM popular in radio control systems for its reduced wiring demands and synchronized multi-channel transmission.
Key Differences Between PWM and PPM
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controls regulate the power delivered to devices by varying the width of the pulses in a fixed frequency signal, optimizing precision and efficiency in speed or brightness adjustments. PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) controls encode information by varying the position of each pulse within a time frame, commonly used in radio control systems to transmit multiple channels simultaneously. Understanding these key differences helps You select the appropriate control method for applications requiring either variable power output or multi-channel communication.
Applications of PWM Control Systems
PWM control systems are extensively used in motor speed regulation, LED dimming, and power delivery in electric vehicles due to their high efficiency and precise control capabilities. These systems optimize energy consumption in industrial automation and robotics by adjusting power signals without generating excessive heat. PWM is also critical in modern communication systems and audio amplification for delivering accurate signal modulation and noise reduction.
Applications of PPM Control Systems
PPM control systems are widely used in radio-controlled models, including drones, airplanes, and cars, due to their ability to transmit multiple channels of data over a single signal wire, reducing complexity and weight. These systems are preferred in applications requiring precise timing and synchronization, such as remote-controlled robotics and hobbyist projects. You can rely on PPM controls for efficient, multi-channel communication where space and signal integrity are critical.
Advantages and Disadvantages of PWM
PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controls offer precise speed and power regulation in motors, making them highly efficient and responsive for various applications. Their main advantage lies in fine-tuned control and reduced energy waste, but they can generate electrical noise and require more complex circuitry than simpler PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) controls. Your choice of PWM control impacts performance, especially when stable and efficient motor operation is critical.
Pros and Cons of PPM
PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) controls offer advantages such as reduced signal noise and improved resistance to interference compared to PWM (Pulse Width Modulation), making them ideal for complex radio control systems. However, PPM signals are more sensitive to timing errors and typically require more precise hardware synchronization, which can complicate implementation. Your choice between PPM and PWM should consider these trade-offs based on the application's reliability and precision requirements.
Choosing the Right Modulation: PWM vs PPM
Choosing the right modulation between PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) and PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) depends on the specific application requirements in remote control and signal processing systems. PWM is preferred for precise control of servos and motors due to its high resolution and straightforward implementation, while PPM is favored for transmitting multiple channels over a single signal line with reduced interference and synchronization advantages. Understanding the trade-offs in bandwidth, noise susceptibility, and channel count is essential for optimizing system performance in RC transmitters, drones, and communication protocols.
PWM vs PPM controls Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com