Wheel speed sensors measure the rotational speed of each wheel, providing critical data for anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and traction control, while vehicle speed sensors monitor the overall speed of the vehicle, informing engine control and transmission systems. Understanding the distinct roles of these sensors can help you diagnose speed-related issues more effectively; continue reading to explore their functions and differences in detail.
Table of Comparison
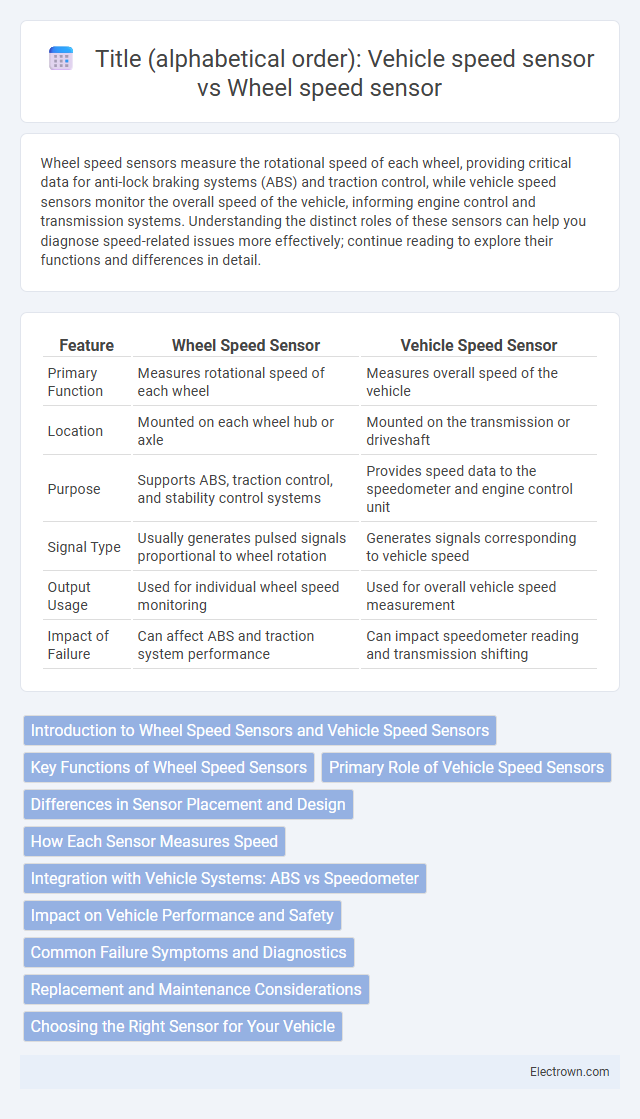
| Feature | Wheel Speed Sensor | Vehicle Speed Sensor |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Measures rotational speed of each wheel | Measures overall speed of the vehicle |
| Location | Mounted on each wheel hub or axle | Mounted on the transmission or driveshaft |
| Purpose | Supports ABS, traction control, and stability control systems | Provides speed data to the speedometer and engine control unit |
| Signal Type | Usually generates pulsed signals proportional to wheel rotation | Generates signals corresponding to vehicle speed |
| Output Usage | Used for individual wheel speed monitoring | Used for overall vehicle speed measurement |
| Impact of Failure | Can affect ABS and traction system performance | Can impact speedometer reading and transmission shifting |
Introduction to Wheel Speed Sensors and Vehicle Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors measure the rotational speed of each wheel to provide data essential for anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and traction control. Vehicle speed sensors monitor the overall speed of the vehicle by measuring the rotational speed of the transmission output shaft or driveshaft. Both sensors play critical roles in modern automotive safety and performance systems by delivering precise speed measurements for real-time adjustments.
Key Functions of Wheel Speed Sensors
Wheel speed sensors play a crucial role in monitoring the rotational speed of each wheel, providing real-time data that enhances anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and traction control. These sensors detect changes in wheel speed to prevent wheel lockup during braking and maintain vehicle stability. Your vehicle relies on accurate wheel speed data to optimize braking performance and ensure safe handling under various driving conditions.
Primary Role of Vehicle Speed Sensors
Vehicle speed sensors (VSS) primarily monitor the overall speed of a vehicle by measuring the rotational speed of the transmission or driveshaft, providing critical data to the engine control unit (ECU) for functions like speedometer display, transmission shifting, and anti-lock braking systems (ABS). In contrast, wheel speed sensors specifically detect the rotational speed of individual wheels to manage traction control and ABS more precisely, preventing wheel slip and enhancing vehicle stability. The vehicle speed sensor's integration into broader vehicle systems makes it essential for accurate speed measurement and smooth drivetrain operation.
Differences in Sensor Placement and Design
Wheel speed sensors are typically mounted directly on each wheel hub or axle to measure the rotational speed of individual wheels, using magnetic or Hall-effect components for precise, localized detection. Vehicle speed sensors, in contrast, are generally installed on the transmission or differential to gauge the overall speed of the vehicle by monitoring the output shaft rotation. The distinct placements reflect their design focus: wheel speed sensors prioritize detecting wheel slip or rotation for ABS and traction control systems, while vehicle speed sensors provide overall speed data for engine management and dashboard instrumentation.
How Each Sensor Measures Speed
Wheel speed sensors measure speed by detecting the rotational velocity of individual wheels through magnetic or Hall-effect signals generated by a toothed wheel or tone ring attached to the axle. Vehicle speed sensors typically measure the overall speed of the vehicle by monitoring the rotational speed of the transmission output shaft or driveshaft using similar electromagnetic or inductive technologies. The wheel speed sensor data is crucial for systems like ABS and traction control, while vehicle speed sensors provide input for speedometer readings and engine control units.
Integration with Vehicle Systems: ABS vs Speedometer
Wheel speed sensors provide real-time data to the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS), enabling precise control of brake pressure to prevent wheel lockup during braking. Vehicle speed sensors feed accurate velocity information to the speedometer and engine control unit, supporting functions like cruise control and transmission shifting. Both sensors integrate with vehicle electronics but serve distinct roles: wheel speed sensors focus on safety and braking performance, while vehicle speed sensors primarily enhance speed measurement and drivetrain management.
Impact on Vehicle Performance and Safety
Wheel speed sensors directly monitor the rotational speed of each wheel, providing critical data for anti-lock braking systems (ABS) and traction control, which enhance vehicle stability and safety during acceleration and braking. Vehicle speed sensors measure the overall speed of the vehicle, informing engine control units for optimal transmission shifting and cruise control accuracy, impacting fuel efficiency and smooth driving performance. Your vehicle's performance and safety heavily rely on the precise functioning of both sensors to ensure accurate speed detection and control under varying driving conditions.
Common Failure Symptoms and Diagnostics
Wheel speed sensors often fail due to debris buildup or wiring damage, causing erratic ABS warnings and inaccurate traction control. Vehicle speed sensors commonly exhibit symptoms like erratic speedometer readings and transmission shifting issues, indicating potential sensor faults. Your diagnostic approach should include scanning for error codes and inspecting sensor connections to accurately differentiate between these failures.
Replacement and Maintenance Considerations
Wheel speed sensors require frequent inspection and occasional replacement due to exposure to road debris and harsh conditions, making their maintenance critical for accurate ABS functionality. Vehicle speed sensors, typically more durable and located in protected areas like the transmission, often have longer intervals between replacements but still require diagnostic checks to prevent speedometer inaccuracies and transmission shifting issues. Understanding the differences in replacement complexity and maintenance needs helps you prioritize timely sensor servicing to ensure optimal vehicle safety and performance.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right sensor for your vehicle depends on the specific function needed: a wheel speed sensor measures the rotational speed of each wheel, critical for ABS and traction control systems, while a vehicle speed sensor monitors the overall speed of the vehicle, essential for transmission shifting and speedometer accuracy. Understanding the differences helps ensure you select a sensor that enhances safety and performance by providing accurate data for your vehicle's control systems. Proper sensor selection directly influences your vehicle's handling, braking efficiency, and overall driving experience.
Wheel speed sensor vs Vehicle speed sensor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com