X-by-wire technology replaces traditional mechanical and hydraulic controls with electronic systems, offering enhanced precision, reduced weight, and improved safety features. Discover how these innovations impact Your vehicle's performance and reliability by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
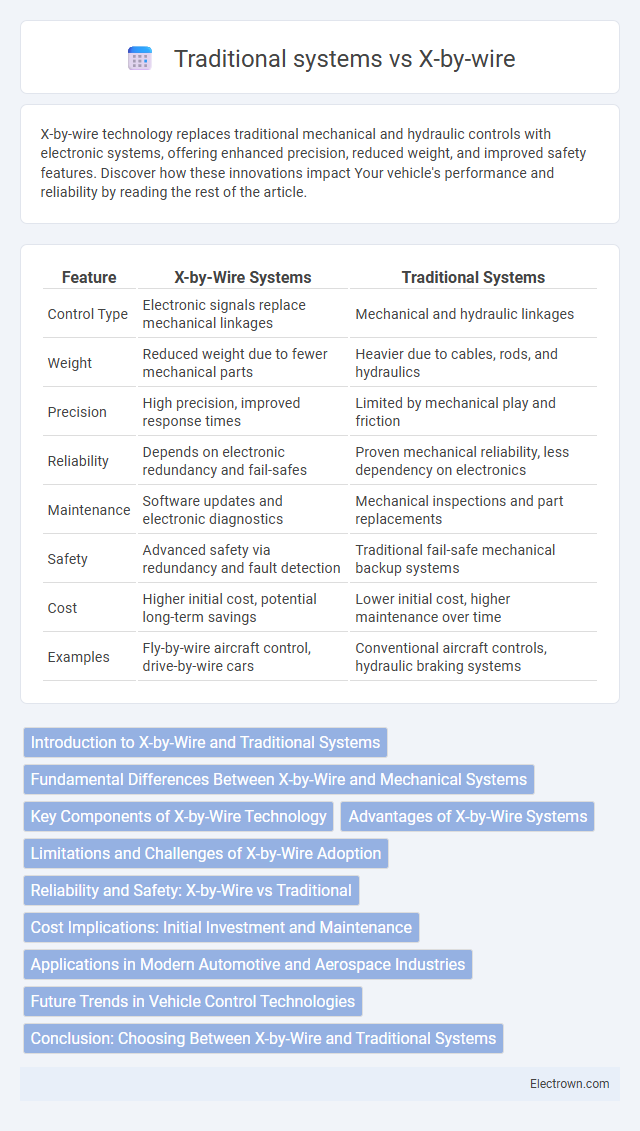
| Feature | X-by-Wire Systems | Traditional Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Control Type | Electronic signals replace mechanical linkages | Mechanical and hydraulic linkages |
| Weight | Reduced weight due to fewer mechanical parts | Heavier due to cables, rods, and hydraulics |
| Precision | High precision, improved response times | Limited by mechanical play and friction |
| Reliability | Depends on electronic redundancy and fail-safes | Proven mechanical reliability, less dependency on electronics |
| Maintenance | Software updates and electronic diagnostics | Mechanical inspections and part replacements |
| Safety | Advanced safety via redundancy and fault detection | Traditional fail-safe mechanical backup systems |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, potential long-term savings | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance over time |
| Examples | Fly-by-wire aircraft control, drive-by-wire cars | Conventional aircraft controls, hydraulic braking systems |
Introduction to X-by-Wire and Traditional Systems
X-by-wire systems replace mechanical and hydraulic controls with electronic signals for functions like steering, braking, and throttle, enhancing precision and enabling advanced driver assistance features. Traditional systems rely on physical linkages, cables, and hydraulic circuits to transmit driver inputs, offering direct mechanical feedback but limited flexibility for integration with modern technologies. The shift towards x-by-wire supports improved vehicle safety, weight reduction, and greater adaptability in autonomous and electric vehicle designs.
Fundamental Differences Between X-by-Wire and Mechanical Systems
X-by-wire systems replace traditional mechanical linkages with electronic controls, using sensors and actuators to transmit driver inputs. These systems eliminate physical connections such as steering columns or hydraulic lines, relying instead on digital signals for precise vehicle control. Traditional mechanical systems depend on direct mechanical or hydraulic pathways, resulting in simpler, but less adaptable, vehicle responsiveness and integration with advanced driver assistance technologies.
Key Components of X-by-Wire Technology
X-by-wire technology replaces mechanical linkages with electronic control systems, utilizing sensors, actuators, and control units as key components. Sensors detect driver inputs and vehicle conditions, transmitting signals to electronic control units (ECUs) that process data and command actuators to perform braking, steering, or throttle functions. This system enhances precision, reduces weight, and enables advanced driver assistance features compared to traditional mechanical and hydraulic systems.
Advantages of X-by-Wire Systems
X-by-wire systems offer increased precision and faster response times compared to traditional mechanical or hydraulic systems, enhancing overall vehicle control and safety. These systems reduce mechanical complexity and weight, leading to improved fuel efficiency and easier integration with advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Enhanced diagnostics and fault-tolerant features enable proactive maintenance and higher reliability in modern automotive applications.
Limitations and Challenges of X-by-Wire Adoption
X-by-wire systems face limitations including cybersecurity risks and reliance on electronic components that may fail under extreme conditions, unlike traditional mechanical or hydraulic systems which offer proven physical redundancy. Challenges in X-by-wire adoption involve the need for rigorous software validation, increased development costs, and ensuring real-time responsiveness to prevent latency issues. Your deployment must address these concerns through enhanced fault-tolerant designs and comprehensive safety certifications to ensure reliability comparable to traditional systems.
Reliability and Safety: X-by-Wire vs Traditional
X-by-wire systems enhance reliability by replacing mechanical and hydraulic linkages with electronic controls, reducing wear and failure points common in traditional systems. Safety improves through built-in redundancy and real-time diagnostics that detect faults early, unlike mechanical systems where issues might go unnoticed until failure. Traditional systems rely heavily on physical components prone to degradation, while x-by-wire enables faster, more precise responses critical for modern vehicle control and safety standards.
Cost Implications: Initial Investment and Maintenance
X-by-wire systems typically require a higher initial investment due to advanced sensors, actuators, and electronic control units compared to traditional mechanical or hydraulic systems. Maintenance costs may decrease over time as x-by-wire designs reduce wear-prone mechanical components, lowering parts replacement frequency and enabling easier diagnostics. Your overall cost efficiency improves by balancing upfront expenses with long-term savings in maintenance and system adaptability.
Applications in Modern Automotive and Aerospace Industries
X-by-wire technology replaces mechanical and hydraulic control systems with electronic controls, significantly enhancing precision and responsiveness in modern automotive and aerospace applications. In the automotive industry, drive-by-wire systems are widely used for throttle control, steering, and braking, enabling advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous driving capabilities. Aerospace applications utilize fly-by-wire systems to improve flight control accuracy, reduce weight, and increase safety by allowing rapid computer-mediated adjustments.
Future Trends in Vehicle Control Technologies
X-by-wire systems are rapidly replacing traditional hydraulic and mechanical controls, enabling enhanced precision, reduced weight, and increased integration with autonomous driving technologies. Future trends emphasize the development of advanced sensor fusion, real-time data processing, and cybersecurity measures to ensure reliable and safe vehicle control. Innovations in artificial intelligence and networked vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication will further optimize dynamic response and adaptability in next-generation automotive systems.
Conclusion: Choosing Between X-by-Wire and Traditional Systems
Choosing between x-by-wire and traditional systems depends on factors such as desired system responsiveness, safety requirements, and maintenance complexity. X-by-wire systems offer enhanced precision, reduced mechanical components, and potential for advanced automation but require robust electronic fail-safes. Traditional systems provide proven reliability and simpler diagnostics but are heavier and less adaptable to modern vehicle integration.
X-by-wire vs Traditional systems Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com