The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases back into the engine, while the PCV valve manages crankcase ventilation to prevent oil contamination and reduce harmful emissions. Understanding the differences between these valves can improve Your vehicle's performance and emissions control; continue reading to learn more about how each system works and their maintenance tips.
Table of Comparison
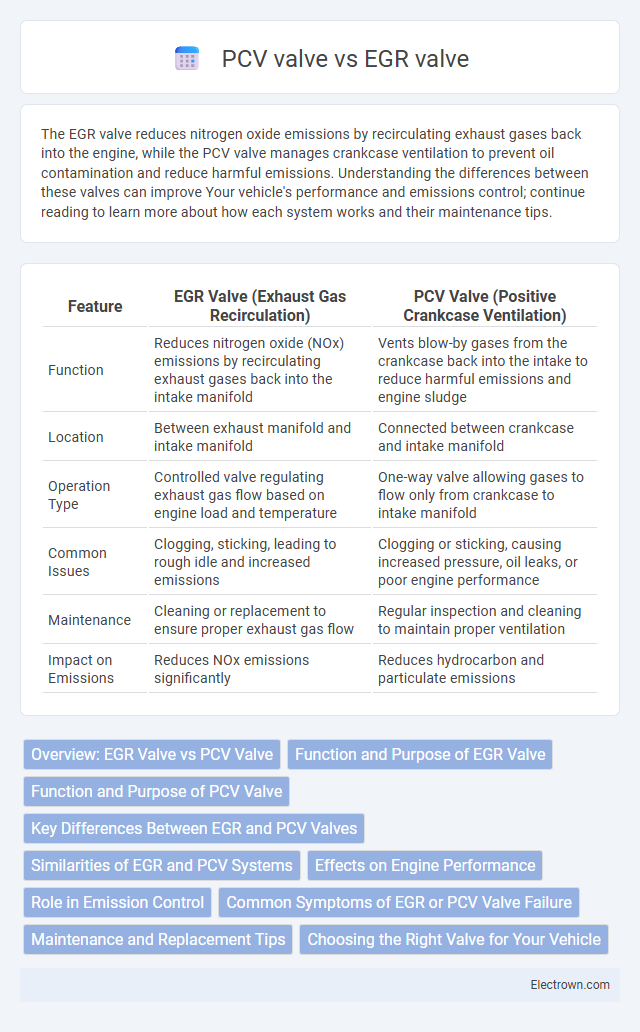
| Feature | EGR Valve (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) | PCV Valve (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by recirculating exhaust gases back into the intake manifold | Vents blow-by gases from the crankcase back into the intake to reduce harmful emissions and engine sludge |
| Location | Between exhaust manifold and intake manifold | Connected between crankcase and intake manifold |
| Operation Type | Controlled valve regulating exhaust gas flow based on engine load and temperature | One-way valve allowing gases to flow only from crankcase to intake manifold |
| Common Issues | Clogging, sticking, leading to rough idle and increased emissions | Clogging or sticking, causing increased pressure, oil leaks, or poor engine performance |
| Maintenance | Cleaning or replacement to ensure proper exhaust gas flow | Regular inspection and cleaning to maintain proper ventilation |
| Impact on Emissions | Reduces NOx emissions significantly | Reduces hydrocarbon and particulate emissions |
Overview: EGR Valve vs PCV Valve
EGR valves (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases back into the intake manifold, improving combustion efficiency and lowering engine temperatures. PCV valves (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) regulate and redirect blow-by gases from the crankcase to the intake manifold, preventing harmful emissions and maintaining engine pressure. Understanding the distinct roles of your vehicle's EGR and PCV valves helps ensure optimal emission control and engine performance.
Function and Purpose of EGR Valve
The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the engine intake, lowering combustion temperatures. It improves engine efficiency and helps meet environmental regulations by controlling harmful pollutants. Your vehicle relies on the EGR valve to maintain optimal emission control and smooth engine performance.
Function and Purpose of PCV Valve
The PCV valve regulates the flow of blow-by gases from the crankcase to the intake manifold, reducing emissions and preventing pressure buildup inside the engine. It plays a critical role in recycling unburned fuel vapors, thus improving engine efficiency and reducing harmful pollutants. Unlike the EGR valve, which recirculates exhaust gases for combustion temperature control, the PCV valve specifically manages crankcase ventilation to maintain optimal engine performance.
Key Differences Between EGR and PCV Valves
The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the engine cylinders, while the PCV valve manages crankcase pressure by redirecting blow-by gases into the intake manifold for combustion. You should understand that the EGR valve primarily controls emissions related to combustion temperature, whereas the PCV valve focuses on maintaining engine efficiency and preventing oil contamination. Both valves play distinct roles in emission control and engine performance but operate in different parts of the engine system.
Similarities of EGR and PCV Systems
Both EGR (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) and PCV (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) systems reduce harmful emissions by recirculating gases back into the engine for combustion. They improve engine efficiency by lowering combustion temperatures and minimizing the release of pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and hydrocarbons. Both systems play a crucial role in maintaining environmental compliance and enhancing overall engine performance.
Effects on Engine Performance
The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases into the intake manifold, which can improve fuel efficiency but may cause rough idling or decreased power if malfunctioning. The PCV valve regulates crankcase gases back into the combustion chamber, preventing engine oil contamination and maintaining optimal combustion, thus enhancing engine performance and longevity. Faulty PCV valves lead to increased emissions and engine sludge, while a malfunctioning EGR valve can result in knocking, reduced acceleration, and higher emissions.
Role in Emission Control
The EGR valve (Exhaust Gas Recirculation) reduces nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions by recirculating a portion of exhaust gases back into the combustion chamber, lowering combustion temperature. The PCV valve (Positive Crankcase Ventilation) prevents harmful blow-by gases from escaping into the atmosphere by redirecting them into the intake manifold for re-combustion. Both valves play crucial roles in emission control by minimizing pollutants and enhancing engine efficiency.
Common Symptoms of EGR or PCV Valve Failure
Common symptoms of EGR valve failure include rough idling, engine knocking, reduced fuel efficiency, and increased exhaust emissions due to improper recirculation of exhaust gases. PCV valve failure often results in rough engine performance, increased oil consumption, and sludge buildup caused by inadequate ventilation of crankcase gases. Both valve malfunctions may trigger the Check Engine Light and cause engine hesitation or stalling.
Maintenance and Replacement Tips
Regular maintenance of the EGR valve involves cleaning carbon deposits every 20,000 to 50,000 miles to ensure optimal engine performance and reduce emissions. The PCV valve should be checked and replaced every 30,000 to 50,000 miles to prevent oil leaks and maintain proper crankcase ventilation. Your vehicle's manual provides specific guidelines, but timely inspections and replacements of both valves can prevent costly engine repairs and improve fuel efficiency.
Choosing the Right Valve for Your Vehicle
Choosing the right valve for your vehicle depends on understanding the distinct roles of the EGR valve and PCV valve in engine performance and emissions control. The EGR valve reduces nitrogen oxide emissions by recirculating exhaust gases, improving fuel efficiency and preventing engine knocking, while the PCV valve manages crankcase ventilation to reduce harmful pollutants and maintain engine cleanliness. Evaluate your vehicle's specific needs, engine type, and manufacturer recommendations to determine whether the EGR or PCV valve replacement or maintenance will optimize your engine's performance and longevity.
EGR valve vs PCV valve Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com