Doppler blood pressure measurement uses ultrasonic waves to detect blood flow and provide precise readings, especially useful in patients with weak pulses or arrhythmias, while oscillometric methods rely on automated cuff inflation and detect vibrations in the artery wall to estimate blood pressure, offering ease of use and convenience. To understand which technique best suits your clinical needs or personal monitoring, read the rest of the article for detailed comparisons.
Table of Comparison
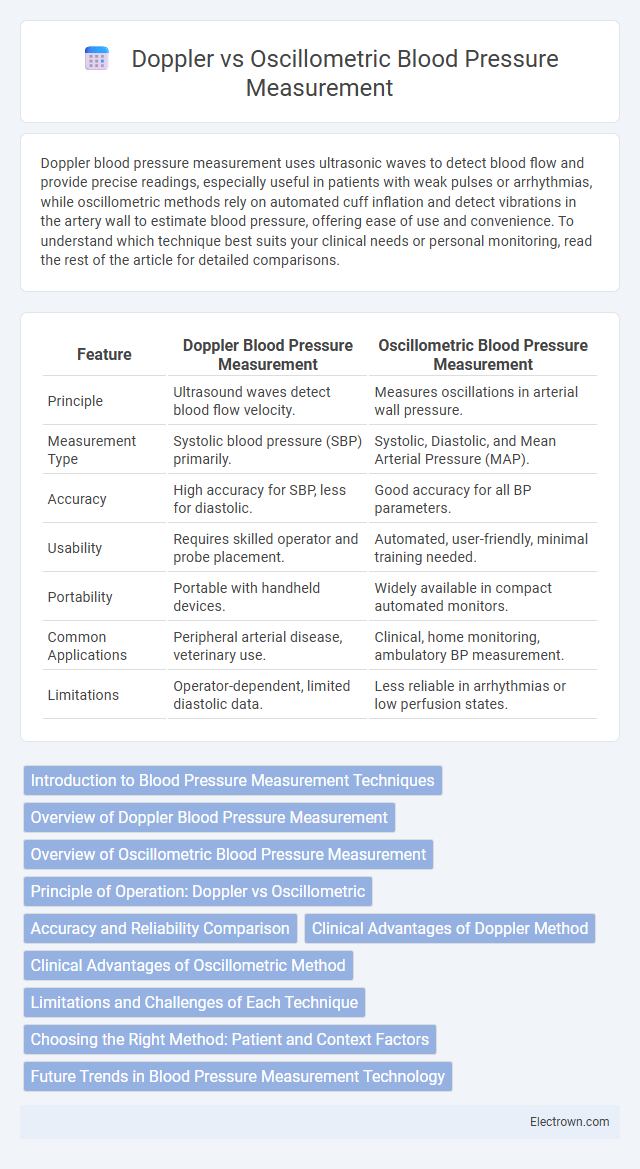
| Feature | Doppler Blood Pressure Measurement | Oscillometric Blood Pressure Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Ultrasound waves detect blood flow velocity. | Measures oscillations in arterial wall pressure. |
| Measurement Type | Systolic blood pressure (SBP) primarily. | Systolic, Diastolic, and Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP). |
| Accuracy | High accuracy for SBP, less for diastolic. | Good accuracy for all BP parameters. |
| Usability | Requires skilled operator and probe placement. | Automated, user-friendly, minimal training needed. |
| Portability | Portable with handheld devices. | Widely available in compact automated monitors. |
| Common Applications | Peripheral arterial disease, veterinary use. | Clinical, home monitoring, ambulatory BP measurement. |
| Limitations | Operator-dependent, limited diastolic data. | Less reliable in arrhythmias or low perfusion states. |
Introduction to Blood Pressure Measurement Techniques
Doppler and oscillometric methods represent two common techniques for non-invasive blood pressure measurement, each utilizing distinct principles to detect arterial pressure. Doppler measurement employs ultrasonic waves to capture blood flow sounds, providing accurate systolic readings especially in patients with weak pulses or arrhythmias. Oscillometric devices rely on pressure oscillations within an inflatable cuff to derive systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressures, offering user-friendly and automated monitoring widely used in clinical and home settings.
Overview of Doppler Blood Pressure Measurement
Doppler blood pressure measurement utilizes ultrasound waves to detect blood flow velocity within arteries, providing precise systolic blood pressure readings, especially in patients with weak pulses or vascular abnormalities. This method is highly sensitive and effective in detecting low arterial pressures that oscillometric devices may miss. Doppler technology is commonly used in clinical settings such as neonatal care and vascular assessments, where accuracy and early detection of circulatory issues are critical.
Overview of Oscillometric Blood Pressure Measurement
Oscillometric blood pressure measurement relies on an automated cuff that detects blood flow vibrations caused by arterial pulsations during cuff deflation, translating these oscillations into systolic and diastolic pressure readings. This non-invasive method uses an electronic pressure sensor and microprocessor to analyze oscillometric waveform amplitudes, providing consistent and user-independent results suitable for ambulatory and clinical settings. Compared to Doppler techniques, oscillometric devices offer ease of use, reduced need for operator skill, and the capability for continuous or repeated measurements without auditory interpretation.
Principle of Operation: Doppler vs Oscillometric
Doppler blood pressure measurement operates on the principle of detecting blood flow vibrations using ultrasound waves reflected by moving red blood cells, enabling identification of systolic pressure by auditory or visual signals. Oscillometric measurement relies on an automated cuff that inflates and deflates to sense oscillations in the arterial wall pressure, analyzing amplitude changes to estimate systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial pressures. The Doppler method provides direct flow-based detection, whereas oscillometric devices interpret pressure oscillations to determine blood pressure values.
Accuracy and Reliability Comparison
Doppler blood pressure measurement offers high accuracy in detecting systolic pressure by using ultrasound waves to capture arterial blood flow sounds, making it reliable especially in patients with weak or irregular pulses. Oscillometric devices estimate blood pressure by measuring oscillations in the arterial wall, providing convenience and automated readings but sometimes less precision in patients with arrhythmias or low perfusion. Your choice between Doppler and oscillometric methods should factor in the clinical context, prioritizing Doppler for precise systolic pressure detection and oscillometric for ease of use in routine monitoring.
Clinical Advantages of Doppler Method
Doppler blood pressure measurement offers superior accuracy in detecting low or weak arterial blood flow, making it highly effective in patients with conditions such as peripheral vascular disease or shock. Unlike oscillometric devices that rely on cuff pressure oscillations, the Doppler method continuously monitors blood flow using ultrasound, providing reliable readings even when pulse signals are faint or irregular. Your clinical assessments benefit from Doppler's ability to deliver precise systolic pressure values, crucial for managing critical care patients or those with compromised circulation.
Clinical Advantages of Oscillometric Method
The oscillometric blood pressure measurement method offers clinical advantages such as automated readings that reduce observer bias and improve consistency in patient monitoring. This technique is less dependent on operator skill compared to Doppler methods, enhancing accuracy in diverse clinical settings. Your practice benefits from faster, non-invasive measurements that are suitable for continuous blood pressure monitoring in critical care environments.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Technique
Doppler blood pressure measurement can be limited by operator skill and environmental noise, which affects accuracy, especially in patients with weak or irregular pulses. Oscillometric devices may struggle with accuracy in cases of arrhythmias, vascular stiffness, or low perfusion, leading to unreliable readings. Understanding these challenges helps you choose the most appropriate method for accurate blood pressure monitoring tailored to individual patient conditions.
Choosing the Right Method: Patient and Context Factors
Selecting between Doppler and oscillometric blood pressure measurement depends on patient-specific factors such as age, clinical condition, and mobility. Doppler methods provide more accurate readings in patients with weak pulses or arrhythmias, while oscillometric devices offer convenience and ease of use in routine monitoring and ambulatory settings. Understanding your clinical context ensures the optimal choice for reliable blood pressure assessment.
Future Trends in Blood Pressure Measurement Technology
Future trends in blood pressure measurement technology emphasize enhanced accuracy and user convenience, with wearable devices integrating Doppler and oscillometric sensors for continuous monitoring. Advances in artificial intelligence enable real-time data analysis, providing personalized health insights and early detection of cardiovascular issues. Your care can benefit from these innovations by allowing seamless, non-invasive tracking of blood pressure in everyday settings.
Doppler vs Oscillometric Blood Pressure Measurement Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com