Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) technology offers faster response times and better color accuracy by using thin-film transistors to control each pixel individually, while Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) relies on a simpler grid system, leading to lower resolution and slower refresh rates. Discover how these differences impact your device's display quality and battery life by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
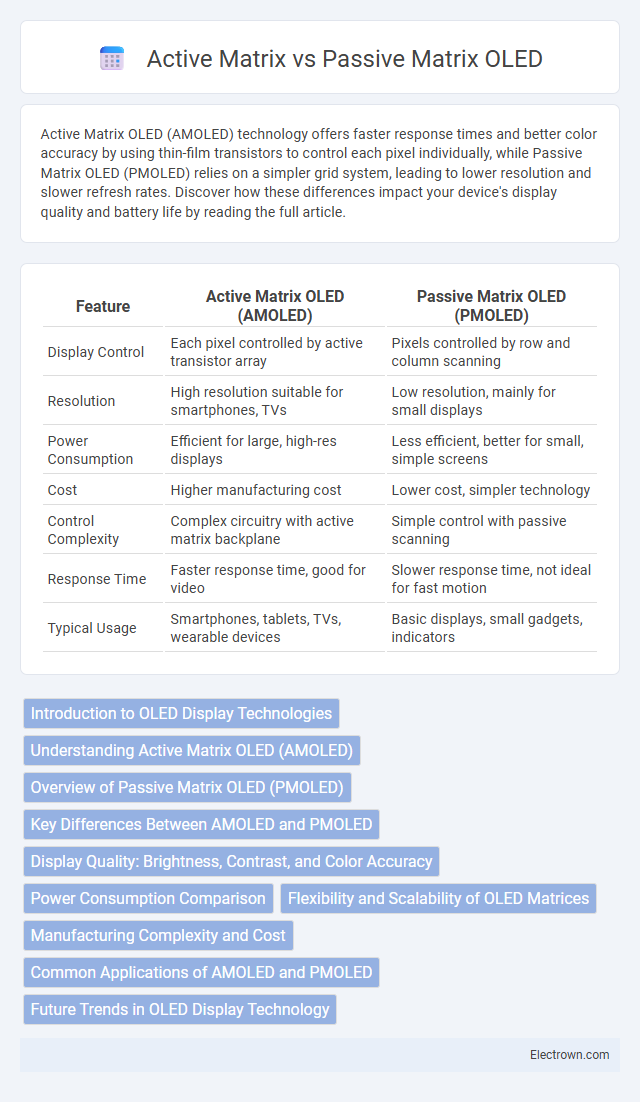
| Feature | Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) | Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) |
|---|---|---|
| Display Control | Each pixel controlled by active transistor array | Pixels controlled by row and column scanning |
| Resolution | High resolution suitable for smartphones, TVs | Low resolution, mainly for small displays |
| Power Consumption | Efficient for large, high-res displays | Less efficient, better for small, simple screens |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower cost, simpler technology |
| Control Complexity | Complex circuitry with active matrix backplane | Simple control with passive scanning |
| Response Time | Faster response time, good for video | Slower response time, not ideal for fast motion |
| Typical Usage | Smartphones, tablets, TVs, wearable devices | Basic displays, small gadgets, indicators |
Introduction to OLED Display Technologies
Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) displays use a thin-film transistor (TFT) array to control each pixel individually, delivering higher resolution, faster refresh rates, and superior image quality compared to Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) technology, which relies on simpler control schemes and is suitable for smaller screens with lower power consumption. AMOLED technology is ideal for smartphones, tablets, and high-end displays due to its vibrant color reproduction and energy efficiency, while PMOLED often serves applications like MP3 players and small wearable devices where cost and simplicity are prioritized. Understanding the differences between these OLED technologies helps you choose the best display solution based on performance, size, and power requirements.
Understanding Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED)
Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) technology uses a thin-film transistor (TFT) array to control individual pixels, allowing for faster refresh rates and higher resolution compared to Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED). AMOLED displays offer superior contrast, vibrant colors, and lower power consumption, making them ideal for smartphones, tablets, and wearable devices. The integrated transistor backplane enhances display response time and supports larger screen sizes with improved image quality.
Overview of Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED)
Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) displays use a simple control scheme where each row is activated sequentially, leading to lower power efficiency and limited resolution compared to Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED). PMOLED technology is commonly found in small, low-cost devices due to its straightforward design but struggles with larger screen sizes and faster refresh rates. Understanding the limitations of PMOLED helps you choose the appropriate display technology based on power consumption and display quality needs.
Key Differences Between AMOLED and PMOLED
AMOLED displays use an active matrix of thin-film transistors (TFTs) to control individual pixels, enabling faster response times, higher resolution, and better power efficiency compared to PMOLED. PMOLED screens rely on a passive matrix control system, which limits their size and resolution due to slower pixel switching and higher power consumption. AMOLED technology is ideal for smartphones and high-end devices, while PMOLED suits smaller, cost-effective applications like wearables and basic displays.
Display Quality: Brightness, Contrast, and Color Accuracy
Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) displays deliver superior brightness, contrast ratios, and color accuracy compared to Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) due to their individually controlled pixel transistors that enable precise light modulation. AMOLED screens achieve higher peak brightness levels and deeper blacks by dynamically adjusting each pixel, resulting in more vivid and true-to-life color reproduction. In contrast, PMOLEDs suffer from lower brightness and contrast because all pixels in a row or column are driven simultaneously, reducing image sharpness and color fidelity.
Power Consumption Comparison
Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) displays consume less power compared to Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) due to their efficient pixel control, enabling each pixel to be individually addressed and activated only when needed. PMOLED requires continuous refresh of the entire display, leading to higher power usage, especially in larger or high-resolution screens. AMOLED technology is preferred in battery-powered devices like smartphones and wearables for improved energy efficiency and longer battery life.
Flexibility and Scalability of OLED Matrices
Active Matrix OLEDs (AMOLEDs) offer superior flexibility and scalability compared to Passive Matrix OLEDs (PMOLEDs) due to their integrated thin-film transistor (TFT) backplane, enabling precise pixel control and high-resolution displays. AMOLED technology supports larger display sizes and curved or foldable form factors, making it ideal for smartphones, wearables, and televisions. In contrast, PMOLEDs are limited to smaller sizes and simpler designs, primarily used in compact devices with lower resolution requirements.
Manufacturing Complexity and Cost
Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) displays involve a more complex manufacturing process due to the integration of thin-film transistors (TFTs) on each pixel, resulting in higher production costs compared to Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED) panels. PMOLEDs are simpler to produce as they rely on a basic controlling method without individual pixel transistors, making them cheaper but less suitable for large, high-resolution screens. Your choice between AMOLED and PMOLED will impact device cost and display performance, especially in applications prioritizing size and image quality.
Common Applications of AMOLED and PMOLED
AMOLED displays are commonly used in smartphones, tablets, and high-end televisions due to their superior color accuracy, faster refresh rates, and energy efficiency. PMOLED technology is frequently found in small screens like fitness trackers, smartwatches, and simple display panels where lower cost and simpler manufacturing are advantageous. The use of AMOLED in devices requiring touch input and flexible displays contrasts with PMOLED's prevalence in applications with static or less interactive content.
Future Trends in OLED Display Technology
Active Matrix OLED (AMOLED) technology is increasingly favored for future OLED display advancements due to its superior response time, higher resolution, and energy efficiency compared to Passive Matrix OLED (PMOLED). Emerging trends indicate a strong shift towards flexible and foldable AMOLED panels, driven by innovations in thin-film transistor (TFT) backplanes and organic materials that enhance durability and color accuracy. Research in hybrid matrix structures aims to combine the low-cost benefits of PMOLED with the performance strengths of AMOLED, signaling a promising evolution in OLED display technology.
Active Matrix vs Passive Matrix OLED Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com