ECG gel offers superior conductivity and comfort compared to paste, ensuring clearer signal transmission during electrocardiogram procedures. Discover how choosing the right ECG medium can impact your diagnostic accuracy by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
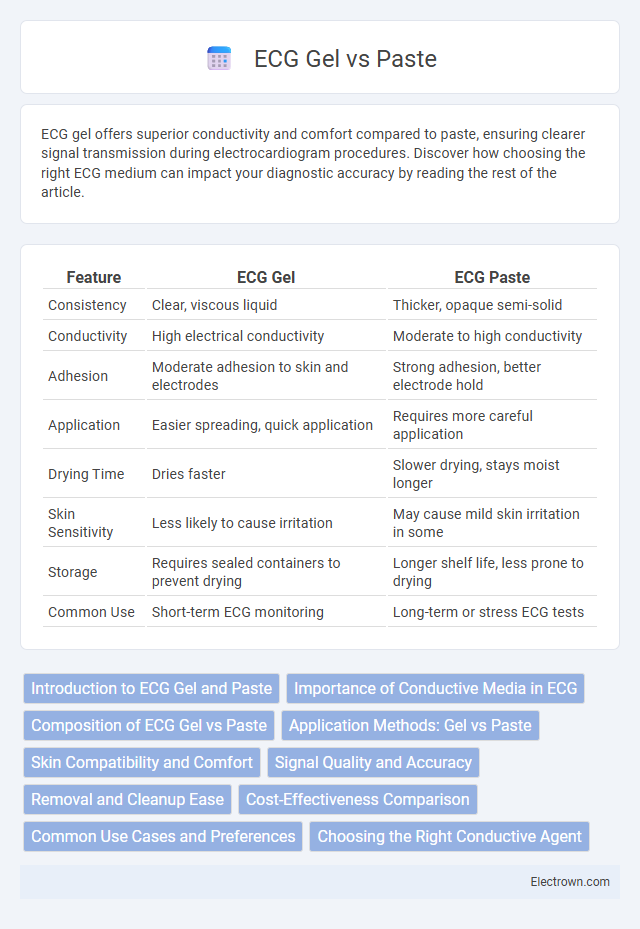
| Feature | ECG Gel | ECG Paste |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Clear, viscous liquid | Thicker, opaque semi-solid |
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity | Moderate to high conductivity |
| Adhesion | Moderate adhesion to skin and electrodes | Strong adhesion, better electrode hold |
| Application | Easier spreading, quick application | Requires more careful application |
| Drying Time | Dries faster | Slower drying, stays moist longer |
| Skin Sensitivity | Less likely to cause irritation | May cause mild skin irritation in some |
| Storage | Requires sealed containers to prevent drying | Longer shelf life, less prone to drying |
| Common Use | Short-term ECG monitoring | Long-term or stress ECG tests |
Introduction to ECG Gel and Paste
ECG gel and paste are conductive materials applied to the skin to enhance signal transmission during electrocardiogram procedures, ensuring accurate heart monitoring. Gel is typically water-based, providing a smooth, non-sticky texture that facilitates electrode adhesion and patient comfort, while paste is thicker and may offer longer-lasting conductivity in clinical settings. Understanding the differences in viscosity, drying time, and conductivity helps you select the right product for reliable ECG readings and patient care.
Importance of Conductive Media in ECG
Conductive media like ECG gel and paste are essential for ensuring accurate electrical signal transmission between the skin and electrodes during electrocardiography. ECG gel provides superior conductivity and reduces skin impedance, enhancing signal clarity and reducing motion artifacts. While paste offers longer adhesion for prolonged monitoring, gel remains favored for consistent signal quality in standard ECG procedures.
Composition of ECG Gel vs Paste
ECG gel typically contains water, conductive salts, and a thickening agent such as carbomer, designed to enhance electrical conductivity and improve electrode-skin contact during electrocardiography. In contrast, ECG paste often includes a higher concentration of conductive powders like silver or carbon combined with a viscous base, resulting in a more adhesive and stable medium ideal for extended monitoring sessions. The gel's water-based formula ensures easy application and removal, whereas the paste's dense composition provides prolonged adhesion and reliable signal quality in challenging conditions.
Application Methods: Gel vs Paste
ECG gel offers easy application with its smooth, non-sticky consistency that ensures optimal electrode-skin contact and quick drying time, reducing signal interference during monitoring. In contrast, ECG paste is thicker and more viscous, requiring careful spreading to avoid air bubbles, which can affect signal quality and patient comfort. Both forms aim to enhance electrode adhesion and conductivity, but gel is generally preferred for its ease of use and consistent performance in clinical settings.
Skin Compatibility and Comfort
ECG gel offers superior skin compatibility due to its water-based formulation, reducing irritation and allergic reactions compared to paste. The gel's smooth texture enhances patient comfort by preventing dryness and ensuring consistent electrode adhesion during monitoring. Your choice of gel can improve both the accuracy of ECG readings and the overall experience for sensitive skin.
Signal Quality and Accuracy
ECG gel provides superior signal quality by enhancing electrode-skin conductivity, reducing impedance, and minimizing motion artifacts, which results in more accurate heart rhythm detection. In contrast, ECG paste tends to dry out faster and may create uneven contact, leading to signal distortion and decreased diagnostic reliability. Choosing the right medium ensures your ECG readings are precise and consistent for optimal cardiac assessment.
Removal and Cleanup Ease
ECG gel offers superior ease of removal and cleanup compared to paste, leaving less residue on the skin and electrodes. Its water-soluble nature allows for quick rinsing with water, minimizing discomfort and saving time during electrode repositioning. You'll find that gel reduces the risk of skin irritation and simplifies maintenance of ECG equipment after use.
Cost-Effectiveness Comparison
ECG gel generally offers a more cost-effective solution compared to ECG paste due to its lower price per unit and ease of application, reducing the need for excess product usage. Gel's longer shelf life and consistent conductivity improve overall value by minimizing waste and repeat tests. Choosing the right product can enhance your budget efficiency without compromising signal quality during ECG procedures.
Common Use Cases and Preferences
ECG gel is commonly preferred for standard electrocardiogram procedures due to its smooth consistency and excellent conductivity, ensuring clear signal transmission and patient comfort during routine cardiac monitoring. In contrast, ECG paste is favored in situations requiring long-term electrode adherence or intense physical activity, as its thicker texture provides superior adhesive properties and reduces electrode displacement. Medical professionals often select gel for quick diagnostic tests and paste for extended monitoring, reflecting practical considerations based on application needs and patient mobility.
Choosing the Right Conductive Agent
Choosing the right conductive agent is essential for accurate ECG readings, where both gel and paste offer distinct advantages depending on clinical needs. ECG gel provides superior conductivity and quicker application, making it ideal for short-term monitoring and situations requiring rapid electrode placement. In contrast, ECG paste offers longer-lasting adhesion and stability, preferred for extended monitoring periods and patients with sensitive skin.
ECG Gel vs Paste Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com