Dry EMG sensors offer quick setup and greater comfort by eliminating the need for conductive gels, making them ideal for long-term and wearable applications. Gel-based EMG provides higher signal quality and accuracy, especially in clinical and research settings where precise muscle activity monitoring is crucial. Discover which EMG type best suits Your needs by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
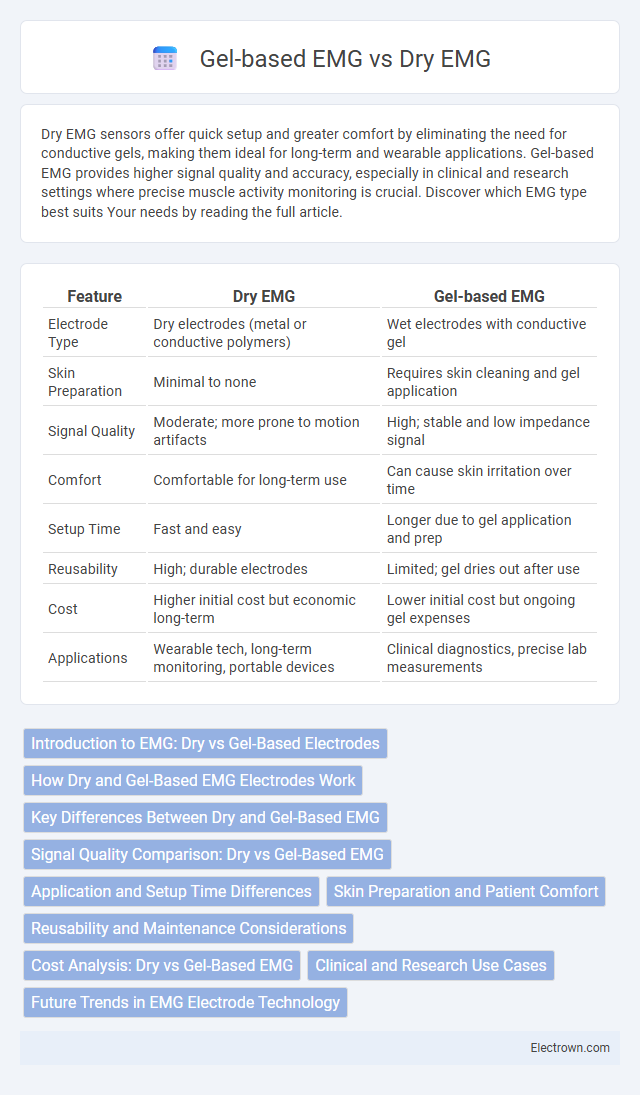
| Feature | Dry EMG | Gel-based EMG |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode Type | Dry electrodes (metal or conductive polymers) | Wet electrodes with conductive gel |
| Skin Preparation | Minimal to none | Requires skin cleaning and gel application |
| Signal Quality | Moderate; more prone to motion artifacts | High; stable and low impedance signal |
| Comfort | Comfortable for long-term use | Can cause skin irritation over time |
| Setup Time | Fast and easy | Longer due to gel application and prep |
| Reusability | High; durable electrodes | Limited; gel dries out after use |
| Cost | Higher initial cost but economic long-term | Lower initial cost but ongoing gel expenses |
| Applications | Wearable tech, long-term monitoring, portable devices | Clinical diagnostics, precise lab measurements |
Introduction to EMG: Dry vs Gel-Based Electrodes
Dry and gel-based electrodes are two primary types used in electromyography (EMG) to measure muscle electrical activity. Gel-based electrodes utilize conductive gels to enhance signal quality and skin contact, providing high accuracy but requiring preparation and maintenance. Dry electrodes offer convenience and reusability without the need for gels, making them ideal for wearable EMG devices while sometimes facing challenges with signal stability and skin impedance.
How Dry and Gel-Based EMG Electrodes Work
Dry EMG electrodes detect muscle electrical activity through direct skin contact using conductive materials without the need for conductive gels, relying on materials like silver/silver chloride or conductive polymers to pick up bioelectrical signals. Gel-based EMG electrodes utilize a hydrophilic gel to establish a low-impedance interface between the skin and electrode surface, enhancing signal conductivity and minimizing motion artifacts. Both types convert the muscle-generated ionic currents into measurable electrical signals, but gel-based electrodes typically provide higher signal quality due to improved skin-electrode contact.
Key Differences Between Dry and Gel-Based EMG
Dry EMG electrodes utilize solid conductive materials without the need for conductive gels, offering ease of application and reduced skin irritation compared to gel-based EMG, which relies on a wet gel interface for better signal conductivity. Gel-based EMG typically provides higher signal quality and lower impedance due to the conductive gel facilitating better skin-electrode contact, whereas dry EMG may experience higher impedance and signal noise. The choice between dry and gel-based EMG depends on factors such as measurement duration, patient comfort, and signal fidelity requirements in clinical or research settings.
Signal Quality Comparison: Dry vs Gel-Based EMG
Gel-based EMG electrodes typically provide superior signal quality due to lower skin-electrode impedance and better conductivity, resulting in clearer and more stable muscle activity readings. Dry EMG electrodes offer more convenience and quicker setup but often experience higher noise levels and signal variability, which can affect data accuracy. Your choice between dry and gel-based EMG should balance signal fidelity requirements with ease of use and the specific application environment.
Application and Setup Time Differences
Dry EMG sensors provide rapid setup with minimal skin preparation, making them ideal for applications requiring quick deployment such as real-time prosthetic control and wearable fitness devices. Gel-based EMG electrodes require extensive skin preparation and gel application, extending setup time but offering superior signal quality for clinical diagnostics and detailed muscle function analysis. The choice between dry and gel-based EMG depends on balancing convenience against the need for high-quality, noise-reduced data in specific applications.
Skin Preparation and Patient Comfort
Dry EMG electrodes typically require minimal skin preparation, such as cleaning with alcohol wipes, enhancing patient comfort by reducing setup time and skin irritation. Gel-based EMG electrodes demand thorough skin preparation, including shaving, abrasion, and applying conductive gel, which may cause discomfort or allergic reactions. Your choice between dry and gel-based EMG should consider the balance between ease of use and signal quality while prioritizing patient experience during the procedure.
Reusability and Maintenance Considerations
Dry EMG electrodes offer high reusability with minimal preparation, requiring only occasional cleaning to maintain signal quality, making them ideal for repeated measurements without consumable costs. Gel-based EMG electrodes, while providing superior initial signal conduction due to conductive gel, have limited reusability as the gel dries out, necessitating replacement after each use. Maintenance for gel-based electrodes involves careful application and removal of the gel to avoid skin irritation and electrode degradation, increasing ongoing costs and preparation time.
Cost Analysis: Dry vs Gel-Based EMG
Dry EMG electrodes generally offer a lower long-term cost due to their reusable nature and minimal maintenance requirements, compared to gel-based EMG electrodes that require continuous purchasing of conductive gels and disposable sensors. Initial investment for dry EMG systems can be higher, but reduced consumable expenses and ease of use make them more cost-effective in extended clinical and research applications. Gel-based EMG remains cost-efficient for short-term or single-use diagnostics but incurs higher operational costs over repeated use cycles.
Clinical and Research Use Cases
Dry EMG electrodes offer rapid setup and enhanced patient comfort, making them ideal for clinical environments requiring frequent or long-term monitoring such as rehabilitation and neuromuscular disorder diagnostics. Gel-based EMG provides superior signal quality and reduced impedance, preferred in research settings that demand precise muscle activity analysis and high-fidelity data collection for biomechanics or motor control studies. Both modalities are pivotal, with dry sensors optimizing usability in ambulatory care and gel-based electrodes facilitating rigorous experimental protocols.
Future Trends in EMG Electrode Technology
Future trends in EMG electrode technology emphasize enhanced signal quality and user comfort, with hybrid designs combining dry and gel-based electrodes to optimize performance in diverse conditions. Innovations in flexible, biocompatible materials and wireless integration are set to improve real-time muscle activity monitoring for medical and wearable applications. Your ability to capture accurate, stable EMG signals will benefit from these advancements, facilitating improved diagnostics and rehabilitation outcomes.
Dry vs Gel-based EMG Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com