Hydrophilic catheter coatings attract and retain water, creating a slippery surface that reduces friction and enhances patient comfort during insertion, while hydrophobic coatings repel water, providing durability and resistance to microbial adhesion. Understanding the differences between these coatings can help you choose the most suitable catheter for your specific medical needs; read on to explore the benefits and applications of each type.
Table of Comparison
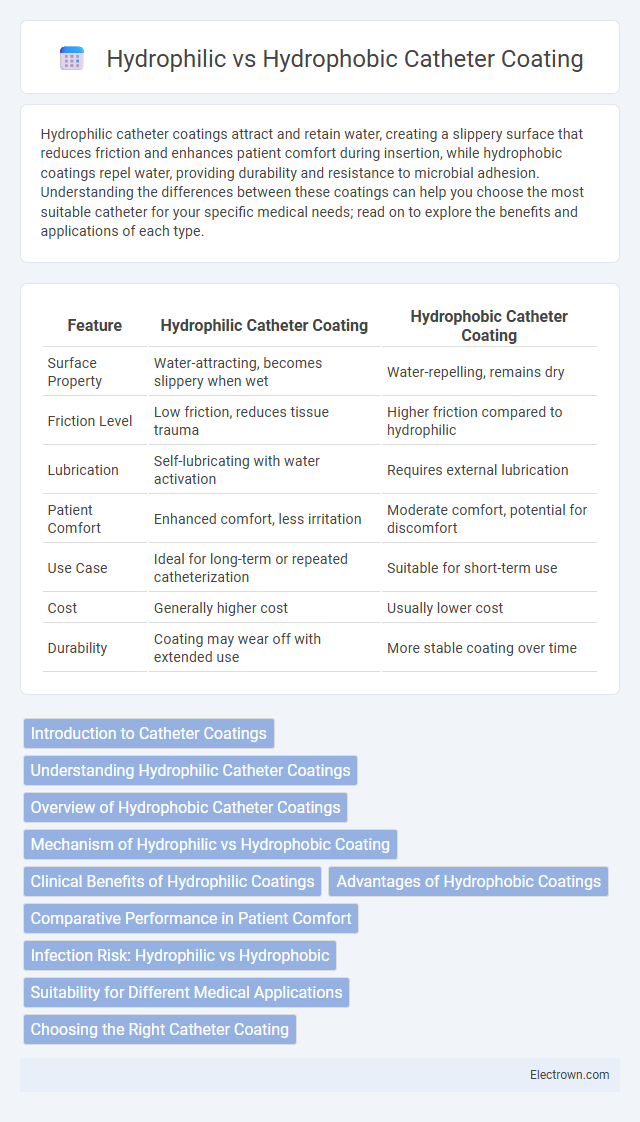
| Feature | Hydrophilic Catheter Coating | Hydrophobic Catheter Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Property | Water-attracting, becomes slippery when wet | Water-repelling, remains dry |
| Friction Level | Low friction, reduces tissue trauma | Higher friction compared to hydrophilic |
| Lubrication | Self-lubricating with water activation | Requires external lubrication |
| Patient Comfort | Enhanced comfort, less irritation | Moderate comfort, potential for discomfort |
| Use Case | Ideal for long-term or repeated catheterization | Suitable for short-term use |
| Cost | Generally higher cost | Usually lower cost |
| Durability | Coating may wear off with extended use | More stable coating over time |
Introduction to Catheter Coatings
Catheter coatings significantly influence device biocompatibility and patient comfort, with hydrophilic coatings enhancing lubrication by absorbing water to create a slippery surface that reduces friction during insertion. Hydrophobic coatings repel water, providing a dry surface that minimizes protein adhesion and bacterial colonization. Selecting between hydrophilic and hydrophobic coatings depends on clinical needs, catheter type, and desired performance characteristics.
Understanding Hydrophilic Catheter Coatings
Hydrophilic catheter coatings create a lubricious surface when activated by water or bodily fluids, significantly reducing friction during insertion and enhancing patient comfort. These coatings improve catheter maneuverability and decrease tissue trauma, lowering the risk of infections and complications. Your choice of a hydrophilic catheter can optimize procedural efficiency and promote safer catheterization practices.
Overview of Hydrophobic Catheter Coatings
Hydrophobic catheter coatings repel water, reducing friction by creating a non-wettable surface that minimizes contact with bodily fluids. These coatings typically consist of materials such as silicone or fluorinated polymers, enhancing catheter maneuverability and patient comfort during insertion. Their low surface energy also helps prevent bacterial adhesion, contributing to reduced infection risks in clinical settings.
Mechanism of Hydrophilic vs Hydrophobic Coating
Hydrophilic catheter coatings absorb water, forming a lubricious, slippery surface that reduces friction during insertion and enhances patient comfort. Hydrophobic coatings repel water, maintaining a dry surface that can resist bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation. Understanding the distinct mechanisms of these coatings helps you choose the appropriate catheter type for improved clinical outcomes and infection control.
Clinical Benefits of Hydrophilic Coatings
Hydrophilic catheter coatings enhance patient comfort by reducing friction during insertion and removal, minimizing urethral trauma and irritation. These coatings decrease the risk of urinary tract infections by promoting a smoother, more lubricated surface that discourages bacterial adhesion. Choosing a hydrophilic catheter can improve your overall catheterization experience through increased safety and reduced complications.
Advantages of Hydrophobic Coatings
Hydrophobic catheter coatings offer significant advantages such as reduced friction and enhanced biocompatibility, which help minimize tissue irritation during insertion. Their water-repellent properties prevent bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation, lowering the risk of infections. You can benefit from improved catheter longevity and greater patient comfort due to these characteristics.
Comparative Performance in Patient Comfort
Hydrophilic catheter coatings significantly reduce friction during insertion, enhancing patient comfort by minimizing urethral irritation and trauma compared to hydrophobic coatings. Studies indicate that hydrophilic catheters provide smoother lubrication retention, leading to less pain and fewer complications such as urethral bleeding. In contrast, hydrophobic coatings often show increased resistance and dryness, which can cause discomfort and higher incidence of urinary tract infections.
Infection Risk: Hydrophilic vs Hydrophobic
Hydrophilic catheter coatings create a smooth, water-attracting surface that reduces friction and minimizes bacterial adhesion, significantly lowering infection risk compared to hydrophobic coatings. Hydrophobic coatings repel water, potentially allowing more bacterial accumulation and increasing the likelihood of catheter-associated urinary tract infections (CAUTIs). Clinical studies indicate that hydrophilic-coated catheters demonstrate a measurable decrease in infection rates due to their enhanced surface wettability and reduced biofilm formation.
Suitability for Different Medical Applications
Hydrophilic catheter coatings provide enhanced lubrication and reduced friction, making them ideal for delicate procedures such as urinary catheterization or vascular interventions where minimizing tissue trauma is crucial. Hydrophobic coatings resist moisture and reduce protein adhesion, which suits long-term indwelling catheters by lowering the risk of bacterial colonization and biofilm formation. Your choice between hydrophilic and hydrophobic catheters should depend on specific clinical needs, patient comfort, and infection control priorities.
Choosing the Right Catheter Coating
Choosing the right catheter coating involves understanding the distinct benefits of hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Hydrophilic coatings attract water, creating a lubricious layer that reduces friction and enhances patient comfort during insertion and use, making them ideal for sensitive or long-term catheterization. Hydrophobic coatings repel water, minimizing bacterial adhesion and reducing the risk of infection, which is crucial for maintaining catheter hygiene and preventing complications in clinical settings.
Hydrophilic vs Hydrophobic Catheter Coating Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com