Digital hearing aids offer customizable sound processing and noise reduction for clearer audio, while analog models amplify all sounds uniformly, often lacking advanced features. Explore the rest of the article to understand which type best suits your hearing needs.
Table of Comparison
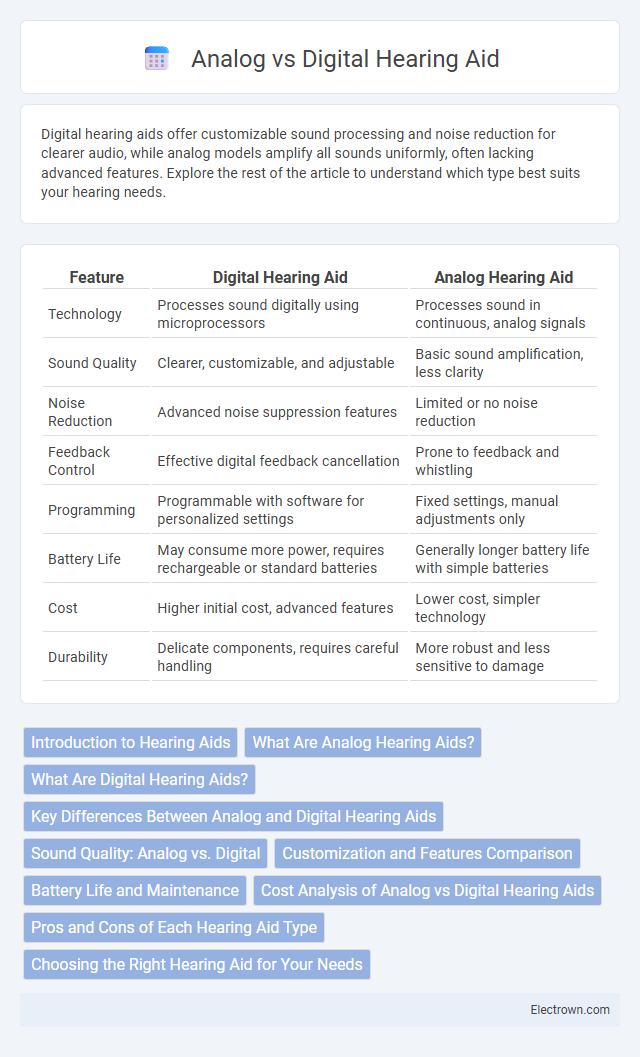
| Feature | Digital Hearing Aid | Analog Hearing Aid |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Processes sound digitally using microprocessors | Processes sound in continuous, analog signals |
| Sound Quality | Clearer, customizable, and adjustable | Basic sound amplification, less clarity |
| Noise Reduction | Advanced noise suppression features | Limited or no noise reduction |
| Feedback Control | Effective digital feedback cancellation | Prone to feedback and whistling |
| Programming | Programmable with software for personalized settings | Fixed settings, manual adjustments only |
| Battery Life | May consume more power, requires rechargeable or standard batteries | Generally longer battery life with simple batteries |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, advanced features | Lower cost, simpler technology |
| Durability | Delicate components, requires careful handling | More robust and less sensitive to damage |
Introduction to Hearing Aids
Hearing aids amplify sound to improve hearing clarity, available in two main types: digital and analog. Digital hearing aids convert sound into digital signals, allowing for customizable adjustments and noise reduction, while analog devices amplify all sounds uniformly. Your choice depends on lifestyle needs, with digital aids offering more advanced technology for personalized hearing experiences.
What Are Analog Hearing Aids?
Analog hearing aids convert sound waves into electrical signals that are amplified to a fixed level, providing a consistent but less customizable hearing experience compared to digital models. These devices often have simpler technology, which may appeal to users seeking a more straightforward option or lower cost. Understanding the specific benefits of analog hearing aids can help you decide if their basic amplification features align with your hearing needs.
What Are Digital Hearing Aids?
Digital hearing aids convert sound into digital signals, allowing for precise sound processing and customization to individual hearing loss patterns. These devices use advanced algorithms to reduce background noise, enhance speech clarity, and adjust settings automatically based on the listening environment. Their ability to store user preferences and connect with smartphones makes digital hearing aids highly versatile and effective compared to analog models.
Key Differences Between Analog and Digital Hearing Aids
Digital hearing aids convert sound into numerical signals, allowing precise tuning and noise reduction, while analog devices amplify all sounds uniformly. Digital models offer customizable features such as feedback cancellation and multiple listening programs, enhancing your listening experience in various environments. Analog hearing aids tend to be simpler and less expensive but lack the advanced processing capabilities of digital technology.
Sound Quality: Analog vs. Digital
Digital hearing aids deliver superior sound quality by processing sound signals with advanced algorithms, resulting in clearer and more natural audio compared to analog models. Analog hearing aids amplify all sounds uniformly, which can cause background noise to be less distinguishable from speech. Your hearing experience improves significantly with digital technology that filters noise and adapts to different environments for optimal clarity.
Customization and Features Comparison
Digital hearing aids offer enhanced customization options through advanced signal processing, allowing features such as noise reduction, directional microphones, and feedback cancellation tailored to your specific hearing loss profile. Analog hearing aids provide a simpler, fixed amplification of sound but lack the nuanced adjustments and programmability found in digital devices. Your choice impacts the precision of sound quality and adaptability to different listening environments, with digital aids typically delivering superior performance and personalized comfort.
Battery Life and Maintenance
Digital hearing aids typically offer longer battery life due to energy-efficient microprocessors and automatic power management features, often lasting 5 to 7 days on a single zinc-air battery. Analog hearing aids require more frequent battery replacements, usually every 3 to 5 days, because they consume continuous power without adaptive regulation. Maintenance for digital devices is often more complex, involving software updates and moisture protection, whereas analog aids demand simpler upkeep such as regular cleaning and battery checks.
Cost Analysis of Analog vs Digital Hearing Aids
Analog hearing aids generally cost less upfront, ranging from $200 to $1,000, but they offer limited features and adjustability compared to digital models. Digital hearing aids, priced between $1,000 and $4,000, provide advanced sound processing, noise reduction, and customizable programming, justifying the higher investment for better hearing quality. Over time, digital devices may reduce maintenance and replacement costs through software updates and enhanced durability, making them a cost-effective option despite the initial expense.
Pros and Cons of Each Hearing Aid Type
Digital hearing aids offer customizable sound processing, improved noise reduction, and better adaptability to various listening environments, enhancing speech clarity and user comfort; however, they are typically more expensive and require regular software updates. Analog hearing aids provide a simpler, continuous sound amplification with fewer electronic components, often resulting in lower costs and easier repairs, but they lack advanced features, leading to less precise sound quality and higher background noise interference. Choosing between digital and analog depends on individual hearing loss severity, lifestyle needs, and budget considerations.
Choosing the Right Hearing Aid for Your Needs
Digital hearing aids offer advanced sound processing, noise reduction, and customizable settings, making them ideal for individuals seeking precise audio clarity and adaptability. Analog hearing aids amplify all sounds uniformly, often preferred for simplicity and lower cost by users with mild to moderate hearing loss. Selecting the right hearing aid depends on factors like lifestyle, degree of hearing loss, budget, and preference for sound quality and technology features.
Digital vs Analog Hearing Aid Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com