Lateral flow immunoassays offer rapid, user-friendly testing with visual results ideal for point-of-care uses, while microfluidic immunoassays provide higher sensitivity and multiplexing capabilities suited for detailed laboratory analysis. Explore the rest of the article to understand which immunoassay best meets your diagnostic needs.
Table of Comparison
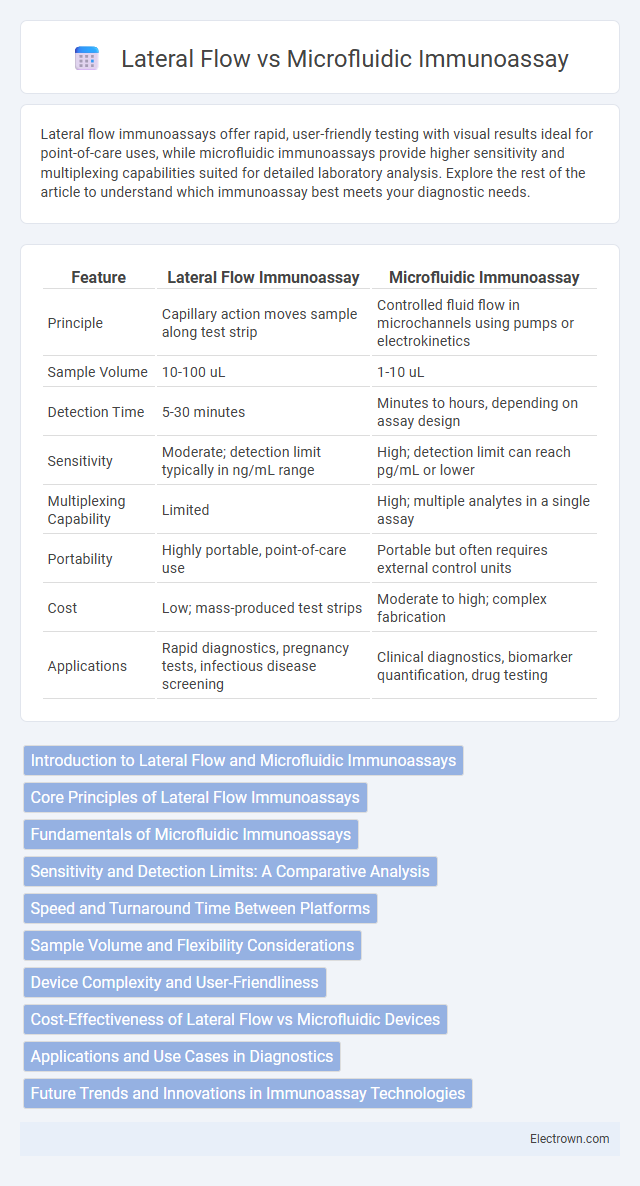
| Feature | Lateral Flow Immunoassay | Microfluidic Immunoassay |
|---|---|---|
| Principle | Capillary action moves sample along test strip | Controlled fluid flow in microchannels using pumps or electrokinetics |
| Sample Volume | 10-100 uL | 1-10 uL |
| Detection Time | 5-30 minutes | Minutes to hours, depending on assay design |
| Sensitivity | Moderate; detection limit typically in ng/mL range | High; detection limit can reach pg/mL or lower |
| Multiplexing Capability | Limited | High; multiple analytes in a single assay |
| Portability | Highly portable, point-of-care use | Portable but often requires external control units |
| Cost | Low; mass-produced test strips | Moderate to high; complex fabrication |
| Applications | Rapid diagnostics, pregnancy tests, infectious disease screening | Clinical diagnostics, biomarker quantification, drug testing |
Introduction to Lateral Flow and Microfluidic Immunoassays
Lateral flow immunoassays utilize capillary action to rapidly detect analytes on a test strip, making them ideal for point-of-care diagnostics due to their simplicity and speed. Microfluidic immunoassays, on the other hand, employ precisely controlled fluid channels on a microscale to enable highly sensitive and multiplexed detection, often used in advanced laboratory settings. Understanding the differences in sensitivity, throughput, and application helps you select the appropriate immunoassay platform for your diagnostic needs.
Core Principles of Lateral Flow Immunoassays
Lateral Flow Immunoassays (LFIA) operate on the principle of capillary action to transport a liquid sample along a porous membrane where target analytes bind to labeled antibodies, creating a visible signal at the test line. The core components include a sample pad, conjugate pad with detection antibodies, nitrocellulose membrane with immobilized capture antibodies, and an absorbent pad to maintain flow. This design enables rapid, point-of-care diagnostics by combining simplicity, speed, and qualitative or semi-quantitative detection without requiring complex instrumentation.
Fundamentals of Microfluidic Immunoassays
Microfluidic immunoassays utilize precisely engineered microchannels to manipulate fluids at the microscale, enabling highly sensitive and multiplexed detection of biomarkers with minimal sample volumes. These devices integrate multiple steps such as sample preparation, reaction, and detection into a compact platform, improving assay speed and accuracy compared to traditional lateral flow immunoassays. The controlled fluid dynamics in microfluidic systems facilitate enhanced antibody-antigen interactions, resulting in superior analytical performance and reduced reagent consumption.
Sensitivity and Detection Limits: A Comparative Analysis
Microfluidic immunoassays exhibit superior sensitivity and lower detection limits compared to lateral flow assays due to their precise fluid control and enhanced surface-to-volume ratio, enabling detection of analytes at picomolar or even femtomolar concentrations. Lateral flow assays typically achieve nanomolar to micromolar detection limits, making them suitable for rapid, qualitative diagnostics but less effective in applications requiring ultra-sensitive quantification. Advances in microfluidic platforms leverage miniaturized channels and integrated detection modules, significantly improving assay reproducibility and dynamic range over traditional lateral flow devices.
Speed and Turnaround Time Between Platforms
Lateral flow immunoassays provide rapid results within minutes, making them ideal for point-of-care diagnostics with minimal turnaround time. Microfluidic immunoassays, while slightly slower, offer enhanced sensitivity and quantification, typically delivering results within 30 minutes to an hour. Your choice depends on whether you prioritize immediate results or greater analytical accuracy.
Sample Volume and Flexibility Considerations
Lateral flow immunoassays typically require larger sample volumes, ranging from 50 to 200 microliters, while microfluidic immunoassays operate efficiently with much smaller volumes, often under 10 microliters. Microfluidic platforms offer greater flexibility in multiplexing and precise fluid control, enabling complex assay designs and enhanced sensitivity. Sample handling in microfluidics allows rapid analysis and integration with automated systems, contrasting with the simpler but less adaptable lateral flow format.
Device Complexity and User-Friendliness
Lateral flow immunoassays offer simple device complexity with easy-to-use test strips ideal for rapid, point-of-care diagnostics that require minimal user training. Microfluidic immunoassays involve advanced device complexity featuring integrated channels and precise fluid control, enabling multiplexed and highly sensitive analyses but often necessitating specialized equipment and user expertise. Your choice depends on balancing ease of use with the need for detailed, quantitative data in diagnostic applications.
Cost-Effectiveness of Lateral Flow vs Microfluidic Devices
Lateral flow immunoassays offer a highly cost-effective solution due to their simple design, low material costs, and ease of mass production, making them ideal for large-scale, rapid diagnostics. Microfluidic immunoassay devices, while providing higher sensitivity and multiplexing capabilities, often entail greater initial investment and operational expenses due to sophisticated fabrication and associated equipment. Balancing your budget with required performance is essential when choosing between these diagnostic technologies.
Applications and Use Cases in Diagnostics
Lateral flow immunoassays are widely used for rapid point-of-care testing, such as pregnancy tests and infectious disease screening, due to their ease of use and quick results. Microfluidic immunoassays offer higher sensitivity and multiplexing capabilities, making them suitable for complex diagnostics in clinical laboratories and personalized medicine. Your choice depends on whether speed and simplicity or detailed analysis and accuracy are prioritized.
Future Trends and Innovations in Immunoassay Technologies
Future trends in immunoassay technologies emphasize enhanced sensitivity and multiplexing capabilities, with microfluidic immunoassays leading innovation through miniaturization and automation. Lateral flow assays continue to evolve by integrating smartphone-based detection and advanced nanomaterials for improved quantitative analysis. Emerging innovations drive point-of-care diagnostics toward rapid, cost-effective solutions with high analytical performance in decentralized healthcare settings.
Lateral Flow vs Microfluidic Immunoassay Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com