Isolated power supplies provide electrical separation between input and output, enhancing safety and reducing noise interference, while non-isolated power supplies directly connect input and output grounds, offering simpler design and cost savings. Understanding the differences can help you choose the right power solution for your application--explore the rest of the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
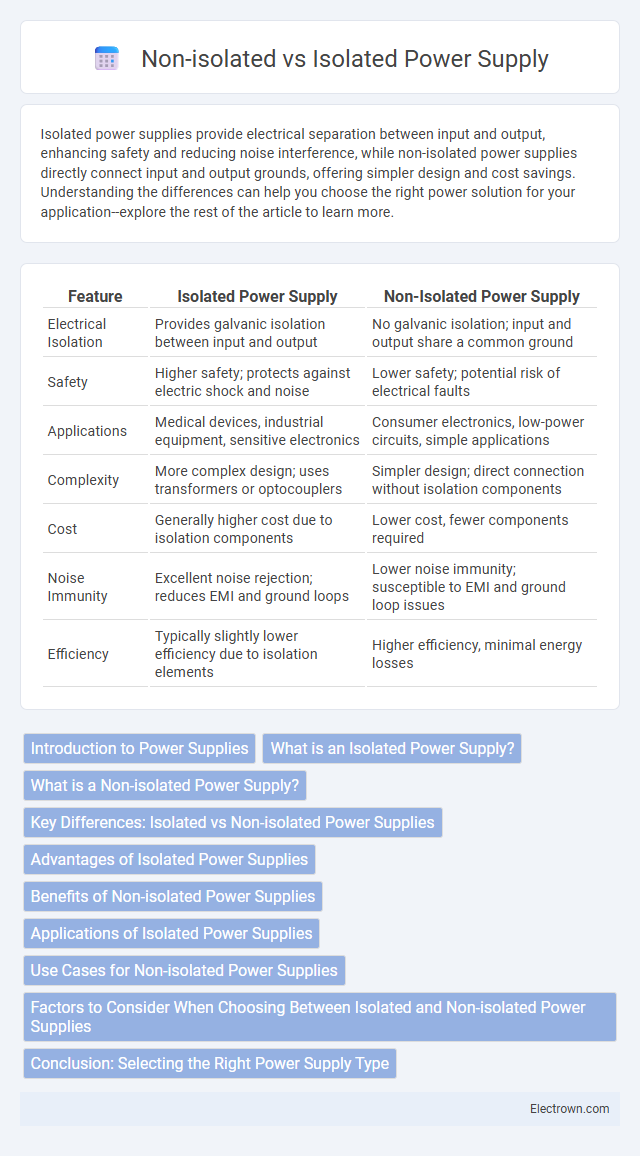
| Feature | Isolated Power Supply | Non-Isolated Power Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Isolation | Provides galvanic isolation between input and output | No galvanic isolation; input and output share a common ground |
| Safety | Higher safety; protects against electric shock and noise | Lower safety; potential risk of electrical faults |
| Applications | Medical devices, industrial equipment, sensitive electronics | Consumer electronics, low-power circuits, simple applications |
| Complexity | More complex design; uses transformers or optocouplers | Simpler design; direct connection without isolation components |
| Cost | Generally higher cost due to isolation components | Lower cost, fewer components required |
| Noise Immunity | Excellent noise rejection; reduces EMI and ground loops | Lower noise immunity; susceptible to EMI and ground loop issues |
| Efficiency | Typically slightly lower efficiency due to isolation elements | Higher efficiency, minimal energy losses |
Introduction to Power Supplies
Power supplies convert electrical energy to a suitable form for electronic devices, either isolated or non-isolated based on design. Isolated power supplies use transformers or optocouplers to separate input and output grounds, enhancing safety and noise reduction in sensitive applications. Non-isolated power supplies share a common ground between input and output, providing simpler and more efficient designs for low-voltage, non-sensitive devices.
What is an Isolated Power Supply?
An isolated power supply separates the input from the output through a transformer or optocoupler, ensuring no direct electrical connection and enhancing safety and noise reduction. It provides galvanic isolation, protecting sensitive equipment from voltage spikes and ground loops while maintaining signal integrity. Your choice of an isolated power supply is crucial for applications requiring reliable isolation to prevent electrical interference and improve system performance.
What is a Non-isolated Power Supply?
A non-isolated power supply directly connects the input and output grounds, resulting in a common reference point without electrical separation. This design offers simpler circuitry, higher efficiency, and reduced cost but lacks safety features found in isolated systems. Understanding your application's requirements for safety and noise sensitivity helps determine if a non-isolated power supply suits your needs.
Key Differences: Isolated vs Non-isolated Power Supplies
Isolated power supplies use transformers or optocouplers to ensure complete galvanic separation between input and output, enhancing safety and reducing noise interference, ideal for sensitive electronics. Non-isolated power supplies share a common ground between input and output, offering higher efficiency and smaller size but with less protection against electrical noise and faults. Your choice depends on the application's requirements for safety, noise immunity, and physical space constraints.
Advantages of Isolated Power Supplies
Isolated power supplies provide superior safety by preventing direct electrical connections between input and output, reducing the risk of electric shock and equipment damage. They enhance noise reduction and signal integrity in sensitive electronic devices by minimizing ground loops and electromagnetic interference. These supplies are essential in medical, industrial, and communication equipment where reliability and protection against electrical faults are critical.
Benefits of Non-isolated Power Supplies
Non-isolated power supplies offer higher efficiency and reduced size because they eliminate the need for bulky transformers. Their design enables faster transient response and simpler circuitry, making them ideal for applications with low voltage differences and where galvanic isolation is unnecessary. Cost-effectiveness and improved energy conversion rates are key advantages driving their use in embedded systems and low-power electronic devices.
Applications of Isolated Power Supplies
Isolated power supplies are crucial in medical equipment, industrial automation, and communication systems where preventing electrical noise and ensuring safety are paramount. Their ability to provide galvanic isolation protects sensitive components and users from voltage spikes and ground loops. You benefit from improved system reliability and compliance with strict safety standards when using isolated power supplies in critical applications.
Use Cases for Non-isolated Power Supplies
Non-isolated power supplies are ideal for applications requiring direct electrical connections between input and output, such as in low-voltage DC-DC converters, point-of-load regulation, and battery charging systems. They offer higher efficiency and smaller size compared to isolated supplies, making them suitable for embedded systems, LED drivers, and telecom equipment where galvanic isolation is not mandatory. Non-isolated designs are commonly used in scenarios prioritizing cost-effectiveness and simplicity over electrical isolation safety requirements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Isolated and Non-isolated Power Supplies
When choosing between isolated and non-isolated power supplies, consider factors such as safety requirements, noise sensitivity, and application environment. Isolated power supplies provide galvanic isolation, essential for protecting sensitive equipment and maintaining signal integrity in noisy industrial settings. Non-isolated power supplies offer higher efficiency and simpler design but are suitable only when isolation is not a critical concern.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Power Supply Type
Selecting the right power supply type depends on your application's electrical isolation needs and safety requirements. Isolated power supplies provide galvanic isolation to protect sensitive components and prevent ground loops, ideal for medical or industrial environments. Non-isolated power supplies offer higher efficiency and simpler design for low-risk applications where isolation is not critical.
Isolated vs Non-isolated Power Supply Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com