Wired biopotential recording offers stable signal quality with minimal interference, while wireless systems provide greater mobility and user comfort by eliminating physical constraints. Discover which option best suits your needs and enhances your biopotential monitoring experience in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
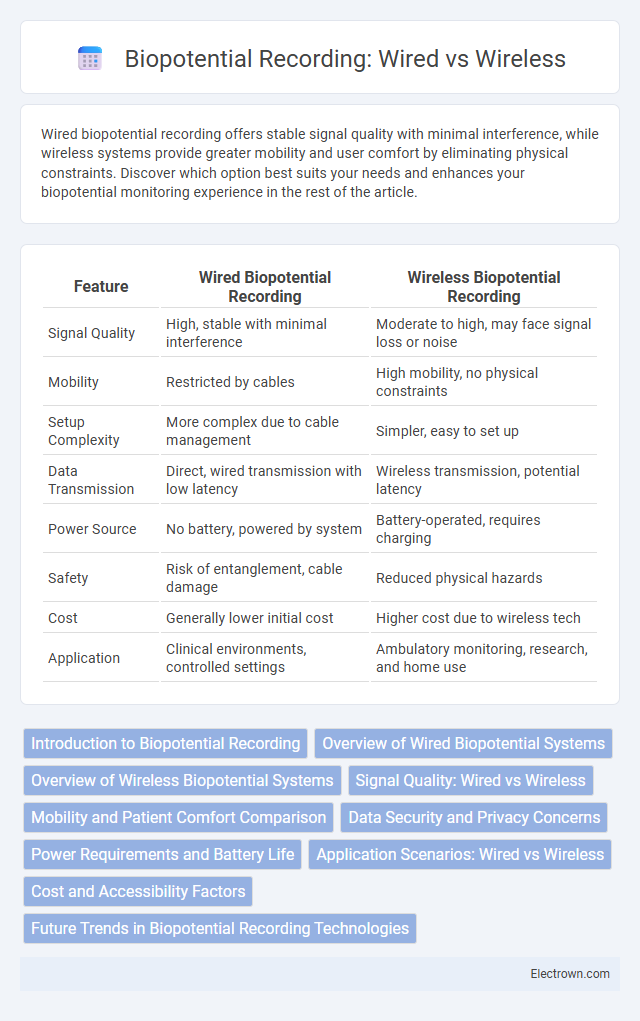
| Feature | Wired Biopotential Recording | Wireless Biopotential Recording |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Quality | High, stable with minimal interference | Moderate to high, may face signal loss or noise |
| Mobility | Restricted by cables | High mobility, no physical constraints |
| Setup Complexity | More complex due to cable management | Simpler, easy to set up |
| Data Transmission | Direct, wired transmission with low latency | Wireless transmission, potential latency |
| Power Source | No battery, powered by system | Battery-operated, requires charging |
| Safety | Risk of entanglement, cable damage | Reduced physical hazards |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher cost due to wireless tech |
| Application | Clinical environments, controlled settings | Ambulatory monitoring, research, and home use |
Introduction to Biopotential Recording
Biopotential recording measures electrical signals generated by physiological activities such as cardiac, muscular, and neural functions using electrodes placed on the body. Wired biopotential systems offer high fidelity and stable signal acquisition by maintaining a consistent physical connection, which minimizes interference and noise. Wireless biopotential recording enhances mobility and patient comfort by transmitting data remotely, but it may face challenges like signal latency and power limitations.
Overview of Wired Biopotential Systems
Wired biopotential recording systems utilize physical cables to connect electrodes to amplifiers, ensuring stable signal transmission with minimal interference and high fidelity. These systems typically feature low noise levels and reliable data acquisition, making them ideal for clinical and research settings requiring precise electroencephalogram (EEG), electrocardiogram (ECG), or electromyography (EMG) measurements. Although wired setups offer superior signal quality, they limit patient mobility and may cause discomfort during extended monitoring sessions.
Overview of Wireless Biopotential Systems
Wireless biopotential systems utilize advanced telemetry technology to capture electrical signals from the body, such as ECG, EEG, and EMG, without the constraints of physical cables. These systems prioritize patient mobility and comfort, enabling real-time monitoring with reduced noise interference and enhanced data transmission reliability over Bluetooth or Wi-Fi protocols. Integration of miniaturized sensors and low-power electronics ensures prolonged usage, making wireless biopotential recording ideal for ambulatory diagnostics and remote health monitoring applications.
Signal Quality: Wired vs Wireless
Wired biopotential recording systems generally offer superior signal quality due to stable connections and minimal interference, ensuring high fidelity and low noise in data acquisition. Wireless systems, while providing greater mobility and convenience, may experience signal degradation or data loss from electromagnetic interference and transmission delays. Your choice depends on whether the priority is maximum signal accuracy or flexibility during biopotential monitoring.
Mobility and Patient Comfort Comparison
Wireless biopotential recording systems significantly enhance patient mobility by eliminating the restrictions imposed by cables, allowing for more natural movement during monitoring sessions. This increased mobility not only improves patient comfort but also facilitates long-term wearable applications and ambulatory monitoring outside clinical settings. Conversely, wired systems, while often providing stable signal quality, can cause discomfort and limit patient activity due to tethering, potentially impacting the accuracy of recorded biopotentials in dynamic environments.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
Wired biopotential recording systems offer enhanced data security by minimizing exposure to wireless interception, ensuring your sensitive physiological signals remain protected through physical connections. Wireless systems, while offering greater mobility and convenience, may present increased risks of unauthorized access or data breaches due to potential signal interception if encryption protocols are not robust. Implementing advanced security measures such as end-to-end encryption and secure authentication is essential for maintaining privacy in wireless biopotential recordings.
Power Requirements and Battery Life
Wired biopotential recording devices generally consume less power as they rely on external power sources, ensuring continuous operation without battery limitations. Wireless systems depend on internal batteries, requiring efficient power management to maximize battery life while maintaining signal quality and transmission range. You should consider your application's duration and mobility needs when choosing between wired and wireless options to optimize power usage and device longevity.
Application Scenarios: Wired vs Wireless
Wired biopotential recording systems are primarily used in controlled laboratory environments and clinical settings where high data fidelity and minimal signal interference are critical, such as electroencephalography (EEG) and electromyography (EMG) during diagnostic tests. Wireless biopotential recording systems enable real-time monitoring in ambulatory and remote healthcare scenarios, including telemedicine and long-term patient monitoring, where mobility and comfort are prioritized. The choice between wired and wireless depends on factors like required signal quality, patient mobility, and the specific application context, with wired setups offering superior accuracy and wireless systems providing greater convenience.
Cost and Accessibility Factors
Wired biopotential recording systems typically involve higher upfront costs due to complex hardware and installation requirements, limiting accessibility for smaller clinics or research facilities. Wireless biopotential devices offer increased affordability and ease of use, promoting widespread adoption in remote or resource-limited settings. Cost-efficiency and enhanced mobility make wireless systems preferable for scalable biopotential monitoring applications.
Future Trends in Biopotential Recording Technologies
Future trends in biopotential recording technologies emphasize wireless systems due to their enhanced patient mobility, reduced noise interference, and improved data integration with wearable devices. Advancements in low-power Bluetooth, flexible electrodes, and AI-driven signal processing enable more accurate, continuous monitoring in real-time for clinical and remote health applications. The shift toward miniaturization and cloud-connected platforms supports scalable, personalized diagnostics and telemedicine.
Wired vs Wireless Biopotential Recording Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com