Open-loop insulin pumps require manual input for insulin dosage adjustments, making them dependent on your vigilance and blood sugar monitoring. Closed-loop systems automatically regulate insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings, enhancing precision and convenience; discover how each type can impact your diabetes management in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
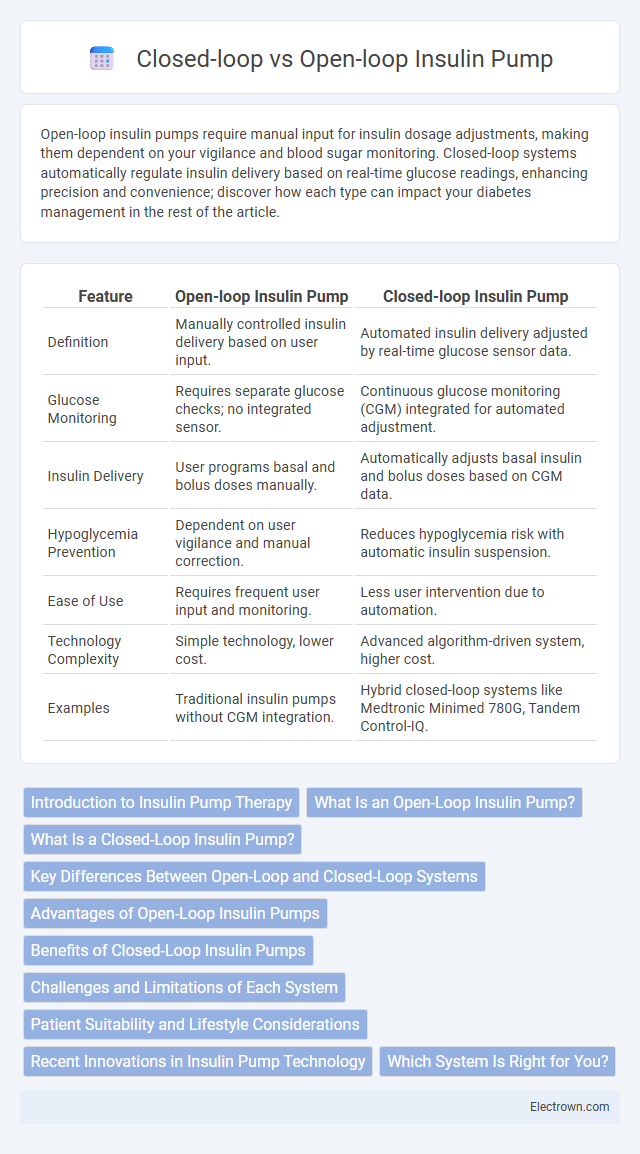
| Feature | Open-loop Insulin Pump | Closed-loop Insulin Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Manually controlled insulin delivery based on user input. | Automated insulin delivery adjusted by real-time glucose sensor data. |
| Glucose Monitoring | Requires separate glucose checks; no integrated sensor. | Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) integrated for automated adjustment. |
| Insulin Delivery | User programs basal and bolus doses manually. | Automatically adjusts basal insulin and bolus doses based on CGM data. |
| Hypoglycemia Prevention | Dependent on user vigilance and manual correction. | Reduces hypoglycemia risk with automatic insulin suspension. |
| Ease of Use | Requires frequent user input and monitoring. | Less user intervention due to automation. |
| Technology Complexity | Simple technology, lower cost. | Advanced algorithm-driven system, higher cost. |
| Examples | Traditional insulin pumps without CGM integration. | Hybrid closed-loop systems like Medtronic Minimed 780G, Tandem Control-IQ. |
Introduction to Insulin Pump Therapy
Insulin pump therapy offers precise, continuous insulin delivery, improving blood glucose control for individuals with diabetes. Open-loop systems require manual adjustment of insulin doses based on glucose readings, while closed-loop pumps automatically adjust insulin delivery using real-time glucose sensor data. This technology enhances glucose management by reducing hypoglycemia risk and improving overall metabolic stability.
What Is an Open-Loop Insulin Pump?
An open-loop insulin pump is a device that delivers insulin continuously based on preset rates programmed by the user or healthcare provider, without real-time glucose sensor feedback. It requires manual adjustments for insulin doses, relying on blood glucose measurements taken separately. This type of pump offers flexible insulin management but lacks automatic glucose-responsive insulin delivery.
What Is a Closed-Loop Insulin Pump?
A closed-loop insulin pump, often referred to as an artificial pancreas, continuously monitors blood glucose levels through a connected continuous glucose monitor (CGM) and automatically adjusts insulin delivery accordingly. This system uses sophisticated algorithms to predict glucose trends and maintain optimal blood sugar control in real time, reducing the risk of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Closed-loop pumps enhance diabetes management by integrating real-time data and automation, offering more precise and responsive insulin dosing compared to open-loop systems.
Key Differences Between Open-Loop and Closed-Loop Systems
Open-loop insulin pumps require manual input from you to adjust insulin delivery based on blood glucose readings, lacking automatic feedback correction. Closed-loop systems, often referred to as artificial pancreas systems, automatically monitor glucose levels using continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and adjust insulin delivery in real-time to maintain target glucose ranges. The key difference lies in automation: closed-loop systems reduce the burden of constant decision-making by using algorithms for insulin dosing, while open-loop systems depend entirely on user intervention for dose adjustments.
Advantages of Open-Loop Insulin Pumps
Open-loop insulin pumps provide users with straightforward control over basal and bolus insulin delivery, allowing for manual adjustment tailored to their daily routines and meal intake. These pumps simplify diabetes management by eliminating the need for continuous glucose sensor integration, making them more affordable and easier to use for many patients. Your ability to actively manage insulin dosing can lead to improved glycemic control while maintaining flexibility in your treatment plan.
Benefits of Closed-Loop Insulin Pumps
Closed-loop insulin pumps automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time glucose sensor data, significantly improving glycemic control and reducing episodes of hypoglycemia. These systems enhance user convenience by minimizing manual insulin dose calculations and adjustments, promoting better adherence to diabetes management. Clinical studies demonstrate that closed-loop pumps lead to increased time in target glucose range and improved overall metabolic outcomes for people with type 1 diabetes.
Challenges and Limitations of Each System
Open-loop insulin pumps require manual input for insulin delivery, presenting challenges such as user errors and inconsistent glucose control. Closed-loop systems, while more automated, face limitations including sensor inaccuracies and algorithm delays that can affect real-time insulin adjustments. Understanding these challenges helps you choose the system that best fits your lifestyle and diabetes management needs.
Patient Suitability and Lifestyle Considerations
Open-loop insulin pumps require manual insulin dose adjustments, making them suitable for patients who are comfortable with frequent monitoring and active management of their blood glucose. Closed-loop systems automate insulin delivery based on continuous glucose monitoring, benefiting patients seeking greater convenience and tighter glucose control with less manual intervention. Lifestyle factors such as daily routine flexibility, willingness to engage with technology, and sensitivity to glucose fluctuations play crucial roles in determining the ideal insulin pump system for each patient.
Recent Innovations in Insulin Pump Technology
Recent innovations in insulin pump technology have advanced both open-loop and closed-loop systems, enhancing glucose management and user convenience. Closed-loop pumps, also known as artificial pancreas systems, integrate continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data to automatically adjust insulin delivery, improving glycemic control and reducing hypoglycemia risk. Your diabetes management can greatly benefit from these smart pumps, which combine real-time data analytics and adaptive algorithms for personalized insulin dosing.
Which System Is Right for You?
Choosing between an open-loop and closed-loop insulin pump depends on your diabetes management goals and lifestyle. Open-loop systems require manual adjustments for insulin delivery, offering flexibility but demanding constant user input, while closed-loop systems automate insulin delivery by continuously monitoring glucose levels for more precise control. Evaluate your comfort with technology, desire for automation, and willingness to monitor glucose closely to determine which system aligns best with your needs.
Open-loop vs Closed-loop Insulin Pump Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com