Monophasic pulses deliver electrical stimulation in a single, unidirectional phase, often used in targeted neuromodulation for precise neural activation, while biphasic pulses alternate polarity, reducing tissue damage and improving safety during longer stimulation sessions. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Your choice between monophasic and biphasic pulses can impact therapeutic outcomes.
Table of Comparison
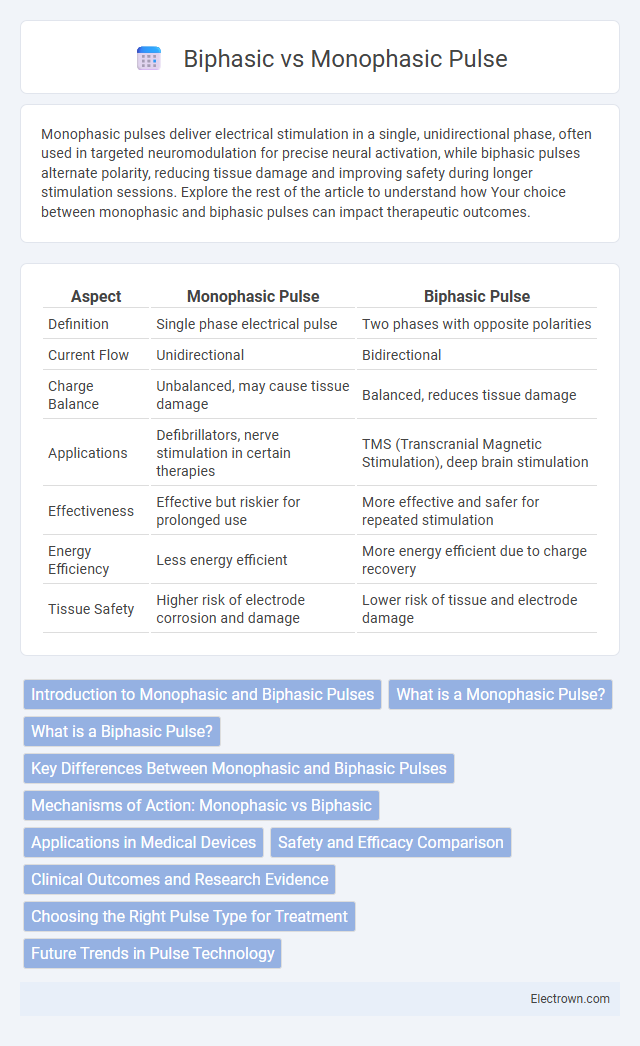
| Aspect | Monophasic Pulse | Biphasic Pulse |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single phase electrical pulse | Two phases with opposite polarities |
| Current Flow | Unidirectional | Bidirectional |
| Charge Balance | Unbalanced, may cause tissue damage | Balanced, reduces tissue damage |
| Applications | Defibrillators, nerve stimulation in certain therapies | TMS (Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation), deep brain stimulation |
| Effectiveness | Effective but riskier for prolonged use | More effective and safer for repeated stimulation |
| Energy Efficiency | Less energy efficient | More energy efficient due to charge recovery |
| Tissue Safety | Higher risk of electrode corrosion and damage | Lower risk of tissue and electrode damage |
Introduction to Monophasic and Biphasic Pulses
Monophasic pulses deliver electrical stimulation in a single direction, making them effective for targeted nerve activation and muscle contraction with minimal charge balance concerns. Biphasic pulses alternate the current direction between positive and negative phases, enhancing safety by reducing tissue damage and electrode polarization during neurostimulation. Understanding the fundamental differences between monophasic and biphasic pulse shapes is essential for optimizing therapeutic applications in neuromodulation and electrophysiology.
What is a Monophasic Pulse?
A monophasic pulse is an electrical signal characterized by a single-phase waveform that moves in only one direction from baseline to a peak before returning to baseline. This type of pulse delivers current exclusively during the positive or negative phase, making it commonly used in applications like nerve stimulation and defibrillation where unidirectional charge delivery is critical. Monophasic pulses provide precise control over stimulus intensity and duration, minimizing charge accumulation and tissue damage.
What is a Biphasic Pulse?
A biphasic pulse is an electrical waveform consisting of two phases: a positive phase followed by a negative phase, or vice versa, which helps balance charge delivery during stimulation. This type of pulse is commonly used in neural and muscle stimulation to reduce tissue damage and electrode corrosion compared to monophasic pulses. Understanding biphasic pulses can improve your application of electrical stimulation by enhancing safety and efficiency.
Key Differences Between Monophasic and Biphasic Pulses
Monophasic pulses deliver a single unidirectional current flow, often used for nerve stimulation and muscle activation, providing focused and consistent stimulation. Biphasic pulses alternate current direction within each pulse cycle, reducing electrode polarization and tissue damage risk while improving overall comfort during electrical stimulation therapy. Understanding these key differences helps optimize Your device choice for effective neuromodulation and rehabilitation outcomes.
Mechanisms of Action: Monophasic vs Biphasic
Monophasic pulses deliver a unidirectional current that causes a net charge transfer, primarily affecting neuronal membranes through depolarization at the cathode, leading to localized and directional neural activation. Biphasic pulses alternate current direction, balancing charge delivery which minimizes tissue damage and reduces electrode polarization while enabling more effective stimulation of neural circuits by recruiting different populations of neurons. The alternating polarity in biphasic pulses facilitates reversible electrochemical reactions, optimizing safety and efficacy in neuromodulation therapies compared to the strictly unidirectional mechanism of monophasic pulses.
Applications in Medical Devices
Monophasic pulses, delivering current in a single direction, are commonly used in defibrillators to restore normal heart rhythm and in nerve stimulation for precise muscle activation. Biphasic pulses, which alternate current direction, enhance energy efficiency and reduce tissue damage, making them preferred in implantable cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) and deep brain stimulators. These pulse modes optimize therapeutic outcomes by balancing efficacy and safety in various medical device applications.
Safety and Efficacy Comparison
Monophasic pulses deliver current in a single direction, often resulting in more tissue damage and lower safety profiles compared to biphasic pulses, which alternate current flow to reduce net charge buildup and minimize electrode corrosion. Biphasic pulses demonstrate higher efficacy by promoting more consistent neural activation and reducing the risk of adverse effects such as nerve fatigue and tissue injury. Clinical studies reveal biphasic stimulation significantly improves patient outcomes in neuromodulation therapies due to enhanced charge balancing and improved biocompatibility.
Clinical Outcomes and Research Evidence
Monophasic pulses deliver unidirectional current, often resulting in more targeted stimulation, while biphasic pulses provide bidirectional flow that reduces tissue damage and enhances patient comfort. Clinical outcomes indicate biphasic pulse waveforms demonstrate superior efficacy in neuromodulation therapies, with numerous studies showing improved symptom relief and fewer adverse effects compared to monophasic pulses. Research evidence highlights biphasic pulses' role in optimizing electrical stimulation protocols for conditions like chronic pain, muscle rehabilitation, and neural disorders, emphasizing enhanced long-term safety and functional recovery.
Choosing the Right Pulse Type for Treatment
Selecting the appropriate pulse type between monophasic and biphasic pulses depends on the specific therapeutic goals and patient needs. Monophasic pulses are often preferred for nerve stimulation due to their unidirectional current, which enhances neural activation and reduces tissue damage. Biphasic pulses offer balanced charge delivery, minimizing electrode corrosion and increasing comfort during repetitive treatments, making them ideal for muscle rehabilitation and pain management.
Future Trends in Pulse Technology
Future trends in pulse technology emphasize the development of adaptive biphasic pulses that optimize energy efficiency and reduce tissue damage during neurostimulation. Advances in biomaterials and real-time feedback systems enable more precise control of pulse parameters, enhancing therapeutic outcomes for neurological disorders. Integration of AI-driven algorithms promises personalized pulse modulation, improving effectiveness and patient-specific treatment customization.
Monophasic vs Biphasic Pulse Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com