Video laryngoscopes provide enhanced visualization of the airway, improving intubation success rates especially in difficult cases compared to standard laryngoscopes. Discover how choosing the right device can impact your airway management skills by reading the rest of the article.
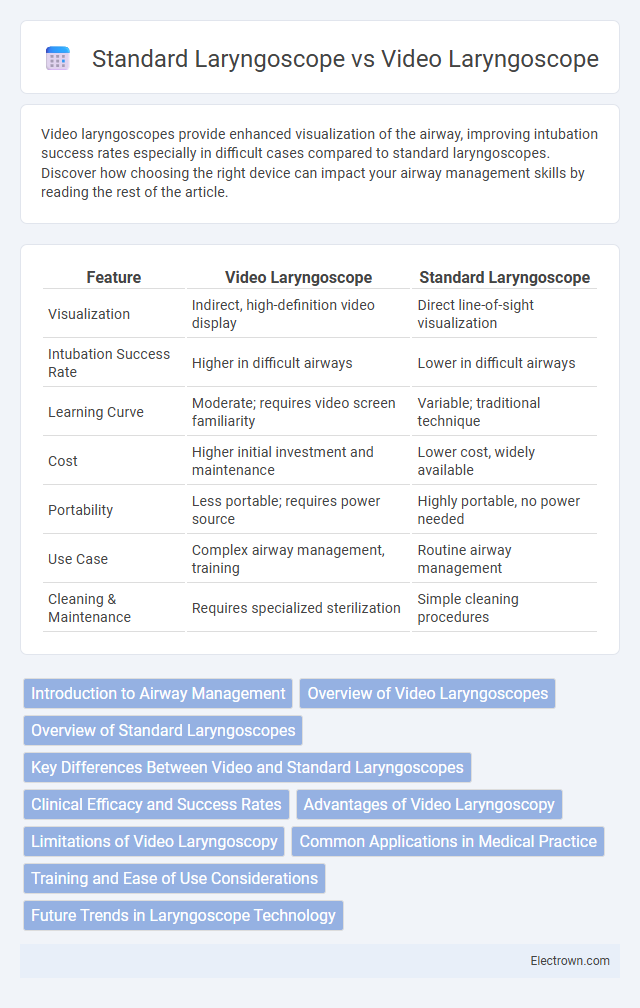
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Video Laryngoscope | Standard Laryngoscope |
|---|---|---|
| Visualization | Indirect, high-definition video display | Direct line-of-sight visualization |
| Intubation Success Rate | Higher in difficult airways | Lower in difficult airways |
| Learning Curve | Moderate; requires video screen familiarity | Variable; traditional technique |
| Cost | Higher initial investment and maintenance | Lower cost, widely available |
| Portability | Less portable; requires power source | Highly portable, no power needed |
| Use Case | Complex airway management, training | Routine airway management |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Requires specialized sterilization | Simple cleaning procedures |
Introduction to Airway Management
Video laryngoscopes provide enhanced visualization of the glottis during intubation, significantly improving success rates in difficult airway management compared to standard laryngoscopes. Standard laryngoscopes rely on direct line-of-sight visualization, which can be challenging in patients with anatomical variations or trauma. Incorporating video laryngoscopy into airway management protocols reduces complications and increases first-attempt intubation success, critical for patient safety in emergency and surgical settings.
Overview of Video Laryngoscopes
Video laryngoscopes offer enhanced visualization of the vocal cords through a high-resolution camera and a video screen, improving intubation success rates especially in difficult airway cases. These devices provide an indirect view of the glottis, reducing the need for alignment of oral, pharyngeal, and tracheal axes compared to standard laryngoscopes. Increased adoption of video laryngoscopes in emergency and operative settings reflects their superiority in facilitating safer and more efficient airway management.
Overview of Standard Laryngoscopes
Standard laryngoscopes, commonly used in airway management, feature a rigid blade and a handle with a light source to facilitate direct visualization of the vocal cords during intubation. These devices rely on a direct line of sight, requiring proper alignment of the oral, pharyngeal, and laryngeal axes for successful intubation. Your familiarity with the basic mechanics and limitations of standard laryngoscopes can help optimize airway management decisions, especially in emergency or routine clinical settings.
Key Differences Between Video and Standard Laryngoscopes
Video laryngoscopes feature a camera and display system that provides an enhanced, real-time view of the airway, facilitating easier intubation especially in difficult cases. Standard laryngoscopes rely on direct line-of-sight visualization, which can be limited by anatomical variations or patient conditions. The improved glottic visualization and increased success rates in difficult airway management with video laryngoscopes highlight their growing preference in clinical practice.
Clinical Efficacy and Success Rates
Video laryngoscopes demonstrate higher first-attempt success rates compared to standard laryngoscopes, particularly in patients with difficult airways. Studies reveal improved glottic visualization and reduced intubation time using video laryngoscopy, enhancing clinical efficacy in emergency and elective settings. Meta-analyses confirm decreased airway trauma and fewer complications, supporting video laryngoscopes as superior tools for airway management.
Advantages of Video Laryngoscopy
Video laryngoscopy offers enhanced visualization of the vocal cords through a high-definition camera, improving intubation success rates, especially in difficult airway scenarios. It reduces the need for excessive neck manipulation, minimizing patient trauma and increasing procedure safety. Your airway management becomes more efficient with real-time video feedback, aiding both training and clinical decision-making.
Limitations of Video Laryngoscopy
Video laryngoscopy offers improved glottic visualization but has limitations such as dependence on a functioning video screen, susceptibility to fogging and secretions obstructing the camera view, and higher costs compared to standard laryngoscopes. In emergency situations, device malfunction or battery failure may delay intubation. Training requirements and reduced tactile feedback can also pose challenges during difficult airway management.
Common Applications in Medical Practice
Video laryngoscopes are commonly used in difficult airway management, emergency intubations, and in training scenarios due to their enhanced visualization of the vocal cords. Standard laryngoscopes remain prevalent in routine elective surgeries and settings where quick, direct laryngoscopy is sufficient. Your choice between the two should consider patient condition, airway complexity, and clinical setting to optimize intubation success rates.
Training and Ease of Use Considerations
Video laryngoscopes provide enhanced visualization of the airway, making them particularly advantageous for training and increasing first-attempt intubation success rates among novices. Standard laryngoscopes require more experience and skill to achieve optimal glottic exposure, often presenting steeper learning curves for trainees. Your choice may impact procedural confidence and patient safety, especially in emergency or difficult airway scenarios.
Future Trends in Laryngoscope Technology
Video laryngoscopes are advancing with enhanced high-definition imaging, integrated artificial intelligence for real-time airway assessment, and improved ergonomics for faster intubation. Standard laryngoscopes continue to evolve with lightweight materials and improved blade designs but lack the visual feedback capabilities of video devices. Emerging technologies predict augmented reality overlays and wireless connectivity, positioning video laryngoscopy as the future standard in airway management.
Video Laryngoscope vs Standard Laryngoscope Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com