Zener diodes regulate voltage by allowing current to flow in reverse once a specific breakdown voltage is reached, effectively protecting circuits from overvoltage. Schottky diodes offer fast switching and low forward voltage drop, enhancing efficiency in circuit protection applications; explore the detailed comparison to understand which diode suits Your needs best.
Table of Comparison
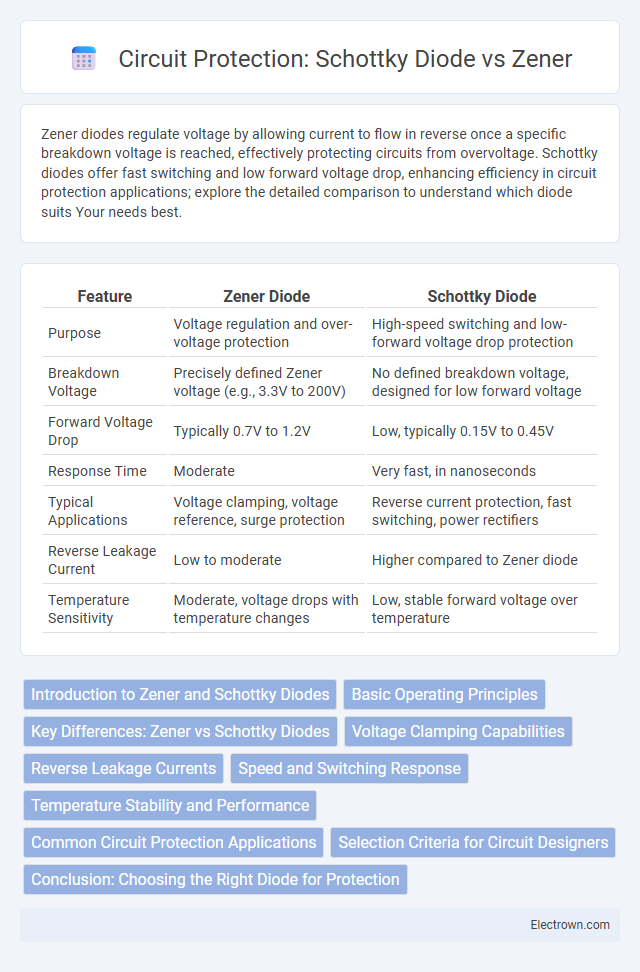
| Feature | Zener Diode | Schottky Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Voltage regulation and over-voltage protection | High-speed switching and low-forward voltage drop protection |
| Breakdown Voltage | Precisely defined Zener voltage (e.g., 3.3V to 200V) | No defined breakdown voltage, designed for low forward voltage |
| Forward Voltage Drop | Typically 0.7V to 1.2V | Low, typically 0.15V to 0.45V |
| Response Time | Moderate | Very fast, in nanoseconds |
| Typical Applications | Voltage clamping, voltage reference, surge protection | Reverse current protection, fast switching, power rectifiers |
| Reverse Leakage Current | Low to moderate | Higher compared to Zener diode |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Moderate, voltage drops with temperature changes | Low, stable forward voltage over temperature |
Introduction to Zener and Schottky Diodes
Zener diodes are designed for voltage regulation by allowing current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific breakdown voltage is reached, making them ideal for overvoltage protection in circuits. Schottky diodes feature low forward voltage drop and fast switching characteristics, resulting from their metal-semiconductor junction, which enhances efficiency in preventing reverse current and voltage spikes. Both diodes play critical roles in circuit protection, with Zener diodes providing voltage clamping and Schottky diodes offering rapid response and minimal power loss.
Basic Operating Principles
Zener diodes regulate voltage by allowing current to flow in reverse once a specific breakdown voltage is reached, protecting circuits from overvoltage. Schottky diodes operate with a low forward voltage drop and fast switching speeds, preventing voltage spikes and reducing power loss. Your choice depends on whether precise voltage regulation (Zener) or efficient rectification and fast response (Schottky) is more critical in your circuit protection design.
Key Differences: Zener vs Schottky Diodes
Zener diodes regulate voltage by maintaining a stable reference voltage during reverse breakdown, making them ideal for precise voltage clamping in circuit protection. Schottky diodes feature low forward voltage drop and fast switching speed, minimizing power loss and protecting circuits from reverse current or voltage spikes efficiently. Your choice depends on whether voltage regulation or fast, low-loss rectification is critical for your circuit's protection needs.
Voltage Clamping Capabilities
Zener diodes provide precise voltage clamping thanks to their well-defined breakdown voltage, making them ideal for protecting circuits from voltage spikes by regulating voltage within a specified range. Schottky diodes offer faster switching speeds and lower forward voltage drops but lack the sharp voltage clamping characteristic of Zener diodes, limiting their effectiveness in voltage regulation applications. For circuit protection requiring strict voltage clamping, Zener diodes are preferred over Schottky diodes due to their stable and predictable avalanche breakdown behavior.
Reverse Leakage Currents
Zener diodes exhibit higher reverse leakage currents compared to Schottky diodes, which can impact circuit stability in sensitive applications. Schottky diodes, known for their low forward voltage drop and minimal reverse leakage, are preferred for protecting low-voltage circuits where leakage current must be minimized. In circuit protection, the reduced reverse leakage of Schottky diodes enhances efficiency and reduces power loss, making them ideal for high-speed switching and clamping roles.
Speed and Switching Response
Zener diodes have a slower switching response due to their avalanche breakdown mechanism, making them less ideal for high-speed circuit protection. Schottky diodes exhibit faster switching speeds and lower forward voltage drops, enabling rapid response to voltage transients and minimizing power loss. Your choice between the two depends on the required response time and efficiency in protecting sensitive electronic components.
Temperature Stability and Performance
Zener diodes provide reliable voltage regulation with moderate temperature stability, typically exhibiting a positive temperature coefficient that can cause voltage shifts under varying heat conditions. Schottky diodes excel in temperature stability due to their low forward voltage drop and minimal leakage current at higher temperatures, enhancing overall circuit performance in demanding environments. Your choice depends on the specific thermal characteristics of your application, with Schottky diodes often preferred for high-speed and high-temperature protection scenarios.
Common Circuit Protection Applications
Zener diodes are commonly used in voltage regulation and overvoltage protection circuits due to their ability to maintain a stable reference voltage by operating in the breakdown region. Schottky diodes, favored for their low forward voltage drop and fast switching speed, are often implemented in reverse polarity protection and high-frequency clamping applications. Both diodes serve critical roles in safeguarding electronic components by preventing voltage spikes, with Zener diodes excelling in voltage clamp roles and Schottky diodes in minimizing power loss during transient events.
Selection Criteria for Circuit Designers
Circuit designers select Zener diodes for voltage regulation and precise voltage clamping due to their stable breakdown voltage characteristics, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronics from voltage spikes. Schottky diodes are preferred for low forward voltage drop and fast switching speeds, essential in high-frequency circuit protection and power rectification to minimize power loss and heat generation. The choice depends on operating voltage, response time, power dissipation, and the specific application requirements such as voltage regulation versus fast transient suppression.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Diode for Protection
Selecting the right diode for circuit protection depends on the specific application requirements such as voltage regulation precision and switching speed. Zener diodes offer reliable voltage clamping and reference voltage stability, ideal for overvoltage protection and voltage regulation in low-speed circuits. Schottky diodes provide faster switching and lower forward voltage drop, making them suitable for high-frequency and low-voltage dropout protection scenarios.
Zener vs Schottky Diode in Circuit Protection Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com