BLE offers low power consumption and fast data transfer ideal for personal devices, while Zigbee excels in creating robust mesh networks for smart home automation with extended range. Discover how these wireless technologies compare and which suits Your needs best by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
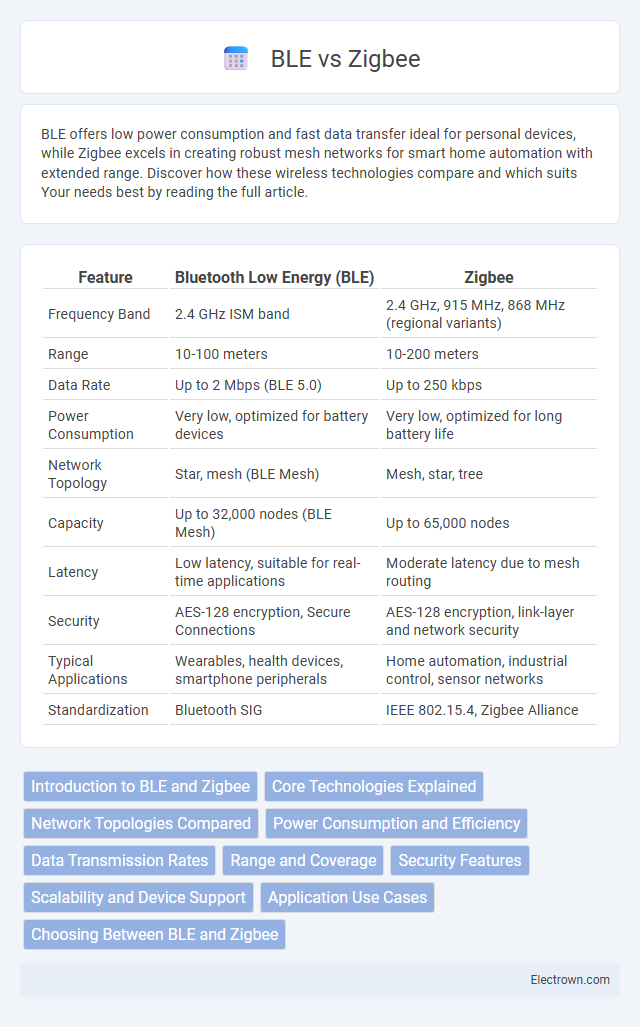
| Feature | Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) | Zigbee |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Band | 2.4 GHz ISM band | 2.4 GHz, 915 MHz, 868 MHz (regional variants) |
| Range | 10-100 meters | 10-200 meters |
| Data Rate | Up to 2 Mbps (BLE 5.0) | Up to 250 kbps |
| Power Consumption | Very low, optimized for battery devices | Very low, optimized for long battery life |
| Network Topology | Star, mesh (BLE Mesh) | Mesh, star, tree |
| Capacity | Up to 32,000 nodes (BLE Mesh) | Up to 65,000 nodes |
| Latency | Low latency, suitable for real-time applications | Moderate latency due to mesh routing |
| Security | AES-128 encryption, Secure Connections | AES-128 encryption, link-layer and network security |
| Typical Applications | Wearables, health devices, smartphone peripherals | Home automation, industrial control, sensor networks |
| Standardization | Bluetooth SIG | IEEE 802.15.4, Zigbee Alliance |
Introduction to BLE and Zigbee
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) enables energy-efficient wireless communication ideal for short-range applications like fitness trackers and smart home devices. Zigbee excels in creating reliable, low-power mesh networks suitable for large-scale automation and sensor systems. Your choice depends on specific requirements such as range, network size, and power consumption.
Core Technologies Explained
BLE operates on Bluetooth Low Energy protocol, using frequency hopping spread spectrum at 2.4 GHz for efficient short-range communication with low power consumption. Zigbee relies on IEEE 802.15.4 standard, also on 2.4 GHz, featuring mesh networking for extended range and robust device interoperability. BLE excels in simple device connections, while Zigbee supports complex, scalable networks ideal for smart home and industrial IoT applications.
Network Topologies Compared
BLE primarily supports star and mesh topologies, offering flexibility for point-to-point and device-to-device communication, while Zigbee relies on mesh topology for robust, scalable networks suited for extensive device interconnectivity. Zigbee's mesh topology enhances self-healing capabilities and network reliability by automatically rerouting data through multiple paths, whereas BLE mesh is optimized for low power consumption and simple device-to-device communication within smaller areas. Both protocols excel in IoT applications, but Zigbee's advanced mesh network infrastructure is preferred for large-scale smart home and industrial networks.
Power Consumption and Efficiency
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) consumes significantly less power compared to Zigbee, making it ideal for battery-powered devices requiring long operational life. BLE operates with low duty cycles and efficient sleep modes, optimizing energy use during intermittent data transmissions. Zigbee, while slightly higher in power consumption, supports mesh networking that enhances overall network efficiency and robustness in larger, complex IoT deployments.
Data Transmission Rates
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) typically supports data transmission rates up to 2 Mbps, optimized for low power consumption and short bursts of data transfer. Zigbee operates at lower speeds, generally around 250 kbps, prioritizing reliable mesh networking for sensor and control devices over longer ranges. Your choice depends on whether faster data rates or robust network scalability is more critical for your application.
Range and Coverage
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) typically offers a range of up to 100 meters in open spaces, making it suitable for personal area networks and close-proximity communications. Zigbee supports a more extensive range, often reaching up to 300 meters outdoors and leveraging mesh networking to extend coverage across large areas such as smart homes and industrial environments. Zigbee's ability to create multi-hop mesh networks significantly enhances coverage reliability compared to BLE's star topology.
Security Features
BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) employs AES-128 encryption with Secure Connections pairing to provide robust security and prevent eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. Zigbee utilizes AES-128 encryption with network keys and link keys, enabling secure device authentication and message integrity through its distributed trust model. Both protocols support secure key management, but Zigbee's mesh network architecture offers enhanced resilience against single points of failure in security.
Scalability and Device Support
BLE supports a high density of devices in personal area networks, making it ideal for small-scale, short-range applications with efficient power consumption. Zigbee excels in large-scale mesh networks, enabling thousands of devices to communicate reliably across extended ranges with robust scalability for smart home or industrial use. Your choice depends on whether your application requires extensive device interoperability and range (Zigbee) or streamlined, low-energy connectivity for fewer devices (BLE).
Application Use Cases
BLE excels in personal fitness trackers, smartwatches, and proximity-based marketing due to its low power consumption and seamless smartphone integration. Zigbee dominates in smart home automation, industrial monitoring, and building controls with its robust mesh networking and scalability. Both protocols serve distinct IoT environments where BLE targets short-range, user-centric applications while Zigbee supports extensive, energy-efficient device networks.
Choosing Between BLE and Zigbee
Choosing between BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) and Zigbee depends on the specific requirements of your IoT project, including range, power consumption, and device density. BLE excels in short-range applications with low energy use and seamless smartphone integration, making it ideal for fitness trackers and home automation. Zigbee offers superior mesh networking capabilities and scalability, supporting hundreds of devices over extended ranges, preferred in smart lighting and industrial sensor networks.
BLE vs Zigbee Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com