Polyfuses offer resettable protection by increasing resistance when overheating, while glass fuses provide a one-time, reliable break in the circuit upon failure. Explore the rest of this article to understand which fuse type best suits your electrical safety needs.
Table of Comparison
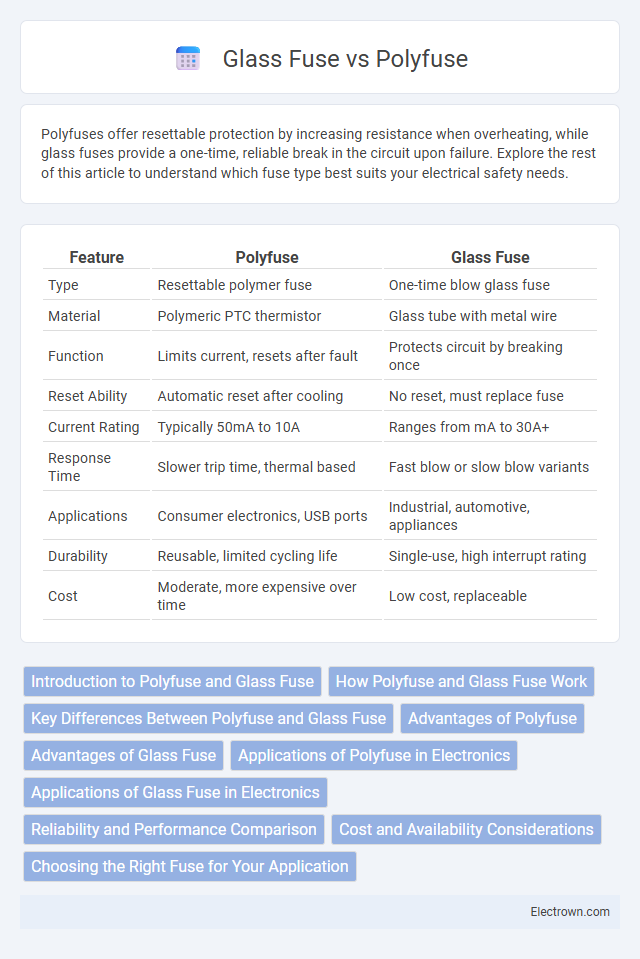
| Feature | Polyfuse | Glass Fuse |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Resettable polymer fuse | One-time blow glass fuse |
| Material | Polymeric PTC thermistor | Glass tube with metal wire |
| Function | Limits current, resets after fault | Protects circuit by breaking once |
| Reset Ability | Automatic reset after cooling | No reset, must replace fuse |
| Current Rating | Typically 50mA to 10A | Ranges from mA to 30A+ |
| Response Time | Slower trip time, thermal based | Fast blow or slow blow variants |
| Applications | Consumer electronics, USB ports | Industrial, automotive, appliances |
| Durability | Reusable, limited cycling life | Single-use, high interrupt rating |
| Cost | Moderate, more expensive over time | Low cost, replaceable |
Introduction to Polyfuse and Glass Fuse
Polyfuses, also known as resettable fuses or PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) fuses, protect circuits by increasing resistance when excessive current flows, automatically resetting once conditions normalize. Glass fuses are traditional one-time-use devices made of a thin metal wire enclosed in a glass tube, designed to break the circuit permanently when current exceeds a specific threshold. Understanding the differences between Polyfuse and Glass Fuse helps you choose the right component for reliable circuit protection in your electronic projects.
How Polyfuse and Glass Fuse Work
Polyfuses, also known as polymeric positive temperature coefficient (PTC) devices, protect circuits by increasing their resistance when exposed to excessive current, effectively limiting the flow and resetting automatically once cooled. Glass fuses contain a metal wire that melts when current exceeds a specified limit, breaking the circuit permanently to prevent damage. Understanding how these devices function helps you choose the right protection method for your electronic projects.
Key Differences Between Polyfuse and Glass Fuse
Polyfuses are resettable polymer-based fuses that protect circuits by increasing resistance when heated, allowing automatic recovery after overloads, while glass fuses are single-use devices with a metal filament that melts to interrupt current flow permanently. Polyfuses offer durability and convenience by eliminating replacement needs, whereas glass fuses provide precise current ratings and fast response times suited for sensitive electronics. Your choice between these fuses depends on whether you prioritize reusability and self-resetting features or accurate and one-time protection.
Advantages of Polyfuse
Polyfuses offer self-resetting protection, allowing your circuit to recover automatically after an overcurrent event without the need for replacement, unlike glass fuses which must be replaced once blown. They provide greater durability and reliability in frequent fault conditions, reducing maintenance time and costs. Polyfuses also improve safety by limiting current flow quickly and minimizing downtime in electronic devices.
Advantages of Glass Fuse
Glass fuses provide clear visibility of the fuse element, allowing for easy inspection and quick identification of blown fuses, which enhances maintenance efficiency. They offer precise and reliable overcurrent protection for delicate electronic circuits, ensuring circuit safety without unnecessary interruptions. Your choice of glass fuse ensures better transparency and quick fault diagnosis compared to the more opaque, resettable polyfuses.
Applications of Polyfuse in Electronics
Polyfuses are widely used in electronic devices for overcurrent protection, safeguarding circuits from damage due to excessive current flow. Common applications include power supply lines, USB ports, and battery packs in consumer electronics, ensuring reliable and resettable protection without the need for replacement. Their self-resetting capabilities make them ideal for use in portable gadgets, telecommunications equipment, and computer motherboards.
Applications of Glass Fuse in Electronics
Glass fuses are widely used in electronics to protect circuits from overcurrent by breaking the connection when current exceeds a certain threshold, ensuring device safety. They are commonly found in consumer electronics, power supplies, and automotive applications due to their transparent casing, which allows easy visual inspection of fuse status. You can rely on glass fuses for precise, reliable protection in low to moderate current applications where quick identification of blown fuses is crucial.
Reliability and Performance Comparison
Polyfuse offers superior reliability due to its resettable nature, allowing it to protect circuits by automatically restoring functionality after overcurrent events without requiring replacement. Glass fuses provide consistent performance with precise current interruption but fail permanently after a single fault, necessitating replacement and potentially causing downtime. Your choice depends on the need for reusable protection with Polyfuse or the simplicity and rapid response of glass fuses for critical, single-fault scenarios.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Polyfuses generally offer lower upfront costs and widespread availability, making them a budget-friendly choice for overcurrent protection in many electronic applications. Glass fuses, while sometimes pricier, provide precise current ratings and are readily available in standardized sizes from most electronic component suppliers. Your choice between polyfuse and glass fuse should balance budget constraints with the need for specific fuse characteristics and supply reliability.
Choosing the Right Fuse for Your Application
Selecting the right fuse between Polyfuse and Glass Fuse depends on your application's specific requirements for reset capability and current protection. Polyfuses automatically reset after tripping, making them ideal for circuit protection in devices prone to frequent overloads, while glass fuses provide a one-time, precise current interruption suited for high-precision, single-use protection scenarios. Understanding your circuit's tolerance for downtime and reset needs ensures the optimal fuse choice for safeguarding your electronics.
Polyfuse vs Glass Fuse Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com