Y capacitors are designed for safety in filtering electromagnetic interference on the line-to-ground side, preventing electric shock hazards, while X capacitors handle noise between line-to-line connections to protect against voltage spikes and surges. Understanding the differences between Y and X capacitors ensures your circuits maintain both safety and performance; continue reading to explore their specific applications and characteristics.
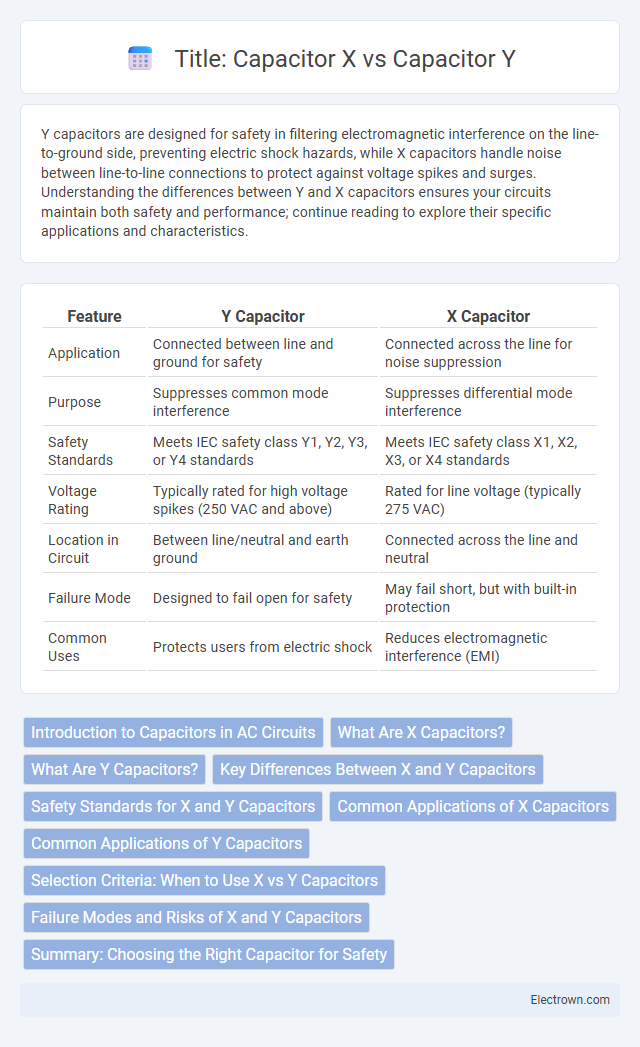
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Y Capacitor | X Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Connected between line and ground for safety | Connected across the line for noise suppression |
| Purpose | Suppresses common mode interference | Suppresses differential mode interference |
| Safety Standards | Meets IEC safety class Y1, Y2, Y3, or Y4 standards | Meets IEC safety class X1, X2, X3, or X4 standards |
| Voltage Rating | Typically rated for high voltage spikes (250 VAC and above) | Rated for line voltage (typically 275 VAC) |
| Location in Circuit | Between line/neutral and earth ground | Connected across the line and neutral |
| Failure Mode | Designed to fail open for safety | May fail short, but with built-in protection |
| Common Uses | Protects users from electric shock | Reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) |
Introduction to Capacitors in AC Circuits
In AC circuits, Y capacitors and X capacitors serve distinct safety and noise suppression roles. X capacitors are connected across the line and primarily handle differential mode interference, while Y capacitors connect line to ground, addressing common mode interference and preventing electric shock hazards. Understanding the differences ensures your circuit's reliability and compliance with safety standards.
What Are X Capacitors?
X capacitors are safety components designed for electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression in AC power lines, connected across the live and neutral wires to filter noise and protect electronic circuits. They must comply with strict international safety standards to prevent electrical shock and fire hazards during transient voltage spikes. Your devices rely on these capacitors to maintain stable operation by reducing high-frequency disturbances from power sources.
What Are Y Capacitors?
Y capacitors, also known as line-to-ground capacitors, are specialized components designed to filter EMI (electromagnetic interference) in power supply circuits by connecting between the line and ground terminals. They are crucial for safety compliance and reducing noise that can interfere with electronic device performance. Y capacitors typically have higher safety ratings and are constructed to withstand voltage surges and prevent electric shock hazards.
Key Differences Between X and Y Capacitors
X capacitors are designed for across-the-line applications, connected between live and neutral wires to suppress differential mode noise, while Y capacitors connect between line and earth to reduce common mode interference. X capacitors typically have higher capacitance values and are built to withstand voltage surges directly across the supply lines, whereas Y capacitors are constructed with stronger isolation and safety standards to prevent electric shock. The primary distinction lies in their placement within electrical circuits and their specific roles in filtering noise and ensuring user safety in electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression.
Safety Standards for X and Y Capacitors
X and Y capacitors adhere to strict safety standards defined by international bodies such as IEC and UL to prevent electrical hazards. X capacitors are designed for across-the-line applications, handling differential-mode interference, and must meet criteria for voltage surge and current ratings to avoid fire risks. Your choice between X and Y capacitors depends on the specific safety ratings required for either line-to-line (X) or line-to-ground (Y) suppression, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Common Applications of X Capacitors
X capacitors are primarily used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression on the input side of power supplies, protecting devices from voltage spikes and surges. Typical applications include AC line filtering in appliances, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics to improve safety and reduce noise. Your devices benefit from enhanced reliability and compliance with regulatory standards through the use of properly selected X capacitors.
Common Applications of Y Capacitors
Y capacitors are commonly used in line-to-ground applications within power supplies and electrical appliances to suppress electromagnetic interference (EMI) and enhance safety. These capacitors are integral in devices such as televisions, computers, and industrial equipment where leakage current control is critical to meet safety standards. Your electronic devices benefit from Y capacitors by effectively reducing noise and preventing electrical shock hazards.
Selection Criteria: When to Use X vs Y Capacitors
X capacitors are designed for in-line filtering between live and neutral wires, effectively suppressing differential mode noise in power supplies and electronic devices. Y capacitors are used for line-to-ground applications, providing safety by limiting leakage currents and preventing electric shock in case of insulation failure. Your selection should prioritize X capacitors for EMI filtering within the circuit path and Y capacitors when ensuring user safety and regulatory compliance in equipment exposed to grounding.
Failure Modes and Risks of X and Y Capacitors
X capacitors primarily fail due to voltage spikes causing insulation breakdown, leading to short circuits or open circuits that compromise EMI suppression and potentially damage connected equipment. Y capacitors, designed for safety across isolation barriers, can degrade over time from continuous exposure to high-frequency noise and voltage surges, resulting in leakage currents that pose shock hazards and regulatory compliance risks. Both capacitor types require rigorous testing and adherence to safety standards like UL and IEC to minimize failure-related risks in power supply systems.
Summary: Choosing the Right Capacitor for Safety
Y capacitors are designed for line-to-ground filtering and provide safety by preventing electric shock in case of insulation failure, while X capacitors are used across the line for suppressing differential mode noise. Selecting the appropriate capacitor involves considering the application's safety standards, voltage ratings, and failure modes to ensure reliable protection and compliance with regulations. Prioritizing the correct capacitor type enhances circuit safety, minimizes risk of electrical hazards, and maintains electromagnetic compatibility.
Y Capacitor vs X Capacitor Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com