Deep discharge protection safeguards your battery by preventing it from being drained beyond a safe voltage level, preserving battery life and performance. Overcurrent protection, on the other hand, limits excessive current flow to avoid damage to electrical components and wiring; explore the rest of the article to understand how these protections work together for optimum device safety.
Table of Comparison
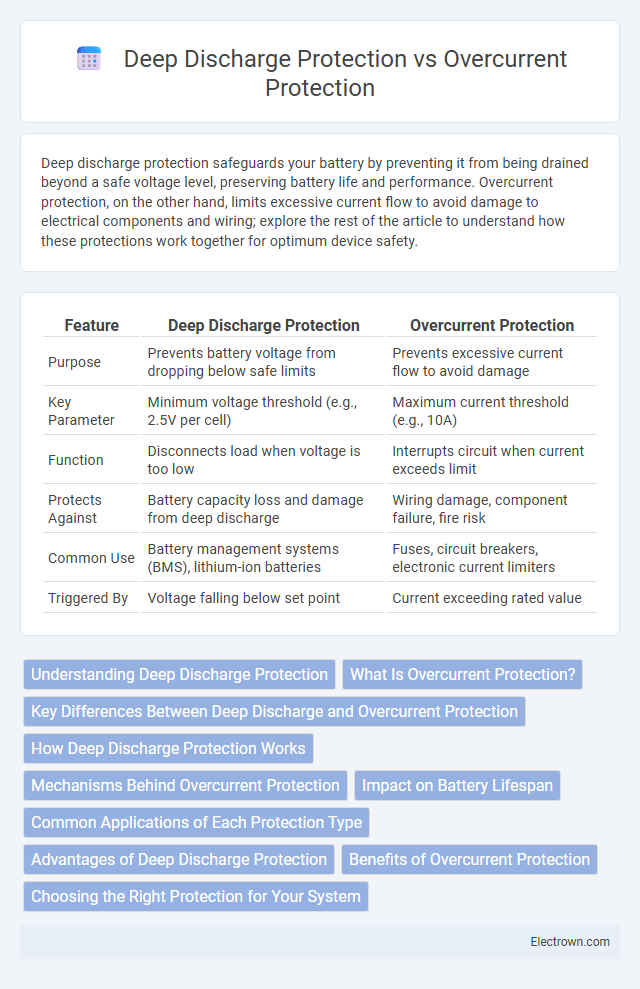
| Feature | Deep Discharge Protection | Overcurrent Protection |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Prevents battery voltage from dropping below safe limits | Prevents excessive current flow to avoid damage |
| Key Parameter | Minimum voltage threshold (e.g., 2.5V per cell) | Maximum current threshold (e.g., 10A) |
| Function | Disconnects load when voltage is too low | Interrupts circuit when current exceeds limit |
| Protects Against | Battery capacity loss and damage from deep discharge | Wiring damage, component failure, fire risk |
| Common Use | Battery management systems (BMS), lithium-ion batteries | Fuses, circuit breakers, electronic current limiters |
| Triggered By | Voltage falling below set point | Current exceeding rated value |
Understanding Deep Discharge Protection
Deep discharge protection prevents battery damage by stopping discharge before voltage drops below a critical threshold, preserving battery lifespan and efficiency. Overcurrent protection focuses on limiting excessive current flow that can cause overheating or component failure. Deep discharge protection is essential for maintaining battery health during extended use, whereas overcurrent protection safeguards electrical circuits from sudden current surges.
What Is Overcurrent Protection?
Overcurrent protection safeguards electrical circuits by interrupting excessive current flow that can cause damage or fire hazards. It operates through devices like fuses, circuit breakers, and relays designed to detect current exceeding safe thresholds. Your electrical system's reliability and safety depend on effective overcurrent protection to prevent overheating and equipment failure.
Key Differences Between Deep Discharge and Overcurrent Protection
Deep discharge protection prevents a battery from being discharged below a critical voltage level, safeguarding battery life and capacity, while overcurrent protection stops excessive current flow to avoid damage to electrical components or wiring. Deep discharge protection primarily targets battery health and longevity, whereas overcurrent protection ensures circuit safety by interrupting current surges that can cause overheating or fires. Your devices benefit from both protections working together to maintain both power efficiency and operational safety.
How Deep Discharge Protection Works
Deep discharge protection works by monitoring the battery voltage and disconnecting the load when the voltage drops below a predefined threshold, preventing the battery from being drained excessively. This safeguard preserves the battery's health and extends its lifespan by avoiding irreversible damage caused by excessive depletion. Your device's battery management system ensures reliable operation by balancing deep discharge protection with overcurrent protection to maintain optimal performance.
Mechanisms Behind Overcurrent Protection
Overcurrent protection mechanisms rely on detecting excessive current flow through devices such as fuses, circuit breakers, or electronic sensors that interrupt the circuit when current surpasses safe thresholds. Thermal sensors detect temperature rises caused by overload currents, triggering disconnection to prevent damage. Magnetic trip units respond instantly to short-circuit faults by generating a magnetic field proportional to current magnitude, ensuring rapid circuit interruption to protect electrical components.
Impact on Battery Lifespan
Deep discharge protection prevents your battery from discharging below a critical voltage threshold, significantly extending its lifespan by avoiding irreversible damage and capacity loss. Overcurrent protection safeguards against excessive current flow that can overheat and degrade battery cells, preserving overall battery health. Both protections play crucial roles in maintaining optimal battery performance and longevity by mitigating different electrical stress factors.
Common Applications of Each Protection Type
Deep discharge protection is commonly utilized in battery-operated devices such as electric vehicles, renewable energy storage systems, and portable electronics to prevent battery damage from excessive voltage depletion. Overcurrent protection is widely applied in electrical circuits, industrial machinery, and power distribution systems to safeguard against excessive current flow that can cause overheating or equipment failure. Both protection types are essential in maintaining the longevity and safety of electronic and electrical systems by addressing distinct operational risks.
Advantages of Deep Discharge Protection
Deep discharge protection prevents battery damage by stopping excessive depletion, thereby extending battery lifespan and maintaining optimal capacity over time. This protection helps avoid irreversible chemical changes and structural degradation within lithium-ion or lead-acid cells, ensuring reliable energy storage performance. Compared to overcurrent protection, it specifically targets the depth of discharge, delivering enhanced battery health and safety benefits in energy management systems.
Benefits of Overcurrent Protection
Overcurrent protection safeguards your electrical system by preventing excessive current flow that can cause overheating, equipment damage, or fire hazards, ensuring a longer lifespan for your devices. It enables the detection and interruption of short circuits and overloads quickly, minimizing downtime and costly repairs. Unlike deep discharge protection, which primarily protects batteries from capacity loss, overcurrent protection provides comprehensive security for the entire circuit and connected components.
Choosing the Right Protection for Your System
Selecting the appropriate protection for your system requires understanding the distinct roles of deep discharge protection and overcurrent protection. Deep discharge protection safeguards batteries from damage caused by excessive depletion, thereby extending battery lifespan and maintaining system reliability. Overcurrent protection prevents harm from excessive current flow, protecting wiring and components from overheating and potential failure.
Deep discharge protection vs overcurrent protection Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com