A load switch is designed to control and manage the power delivery to a specific load, offering features like controlled turn-on and inrush current limiting, while a power switch primarily serves as a simple on/off control for power flow. Understanding these differences can help you optimize your circuit design and ensure efficient power management; explore the rest of the article to deepen your knowledge on selecting the right switch for your needs.
Table of Comparison
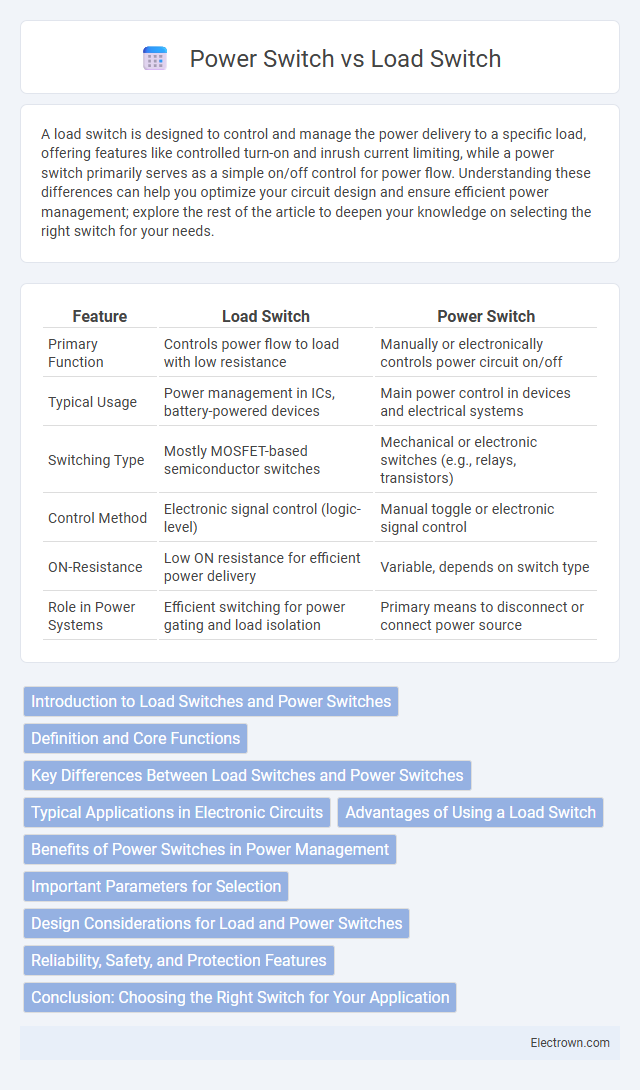
| Feature | Load Switch | Power Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Controls power flow to load with low resistance | Manually or electronically controls power circuit on/off |
| Typical Usage | Power management in ICs, battery-powered devices | Main power control in devices and electrical systems |
| Switching Type | Mostly MOSFET-based semiconductor switches | Mechanical or electronic switches (e.g., relays, transistors) |
| Control Method | Electronic signal control (logic-level) | Manual toggle or electronic signal control |
| ON-Resistance | Low ON resistance for efficient power delivery | Variable, depends on switch type |
| Role in Power Systems | Efficient switching for power gating and load isolation | Primary means to disconnect or connect power source |
Introduction to Load Switches and Power Switches
Load switches and power switches both control electrical power flow but serve distinct functions in electronic circuits, optimizing energy management and device protection. Load switches regulate voltage and current to connected loads, ensuring efficient power delivery without interruption, while power switches mainly control high-current paths to enable or disable entire power sources. Understanding your application's voltage, current requirements, and switching speed helps choose between load switches and power switches for optimal performance and reliability.
Definition and Core Functions
A Load Switch controls the flow of electrical power to a device or circuit by enabling or disabling power delivery, often used for power management and protection in electronic systems. A Power Switch, in contrast, refers broadly to any switch designed to turn a power supply on or off, including manual and automated types across various voltage and current ratings. The core function of a Load Switch emphasizes safe and efficient load control with features like current limiting and soft-start, while a Power Switch primarily serves as the main control point for powering devices on or off.
Key Differences Between Load Switches and Power Switches
Load switches primarily manage the controlled connection and disconnection of power to a load, offering features like inrush current limiting and soft start to protect circuit components. Power switches, typically used for general on/off control of electrical power, often handle higher currents without the specialized control functions found in load switches. Key differences include load switches' emphasis on precise power sequencing and protection versus power switches' straightforward switching capability for power routing.
Typical Applications in Electronic Circuits
Load switches are commonly used in battery-powered devices to control power distribution efficiently, ensuring minimal voltage drop and protecting sensitive components. Power switches handle higher current loads and are often found in power management circuits for appliances, motor controllers, and power supplies where robust switching is essential. Your choice between a load switch and a power switch depends on the specific current rating and switching speed required by your electronic circuit's application.
Advantages of Using a Load Switch
Load switches offer precise control over power distribution in electronic circuits, enabling efficient management of current flow while minimizing power loss and heat generation. They provide robust protection features such as overcurrent, undervoltage lockout, and thermal shutdown, enhancing the reliability and safety of devices. Utilizing load switches contributes to longer battery life in portable electronics by reducing quiescent current and enabling selective powering of subsystems.
Benefits of Power Switches in Power Management
Power switches offer precise control over voltage and current within power management systems, enhancing efficiency and reducing energy loss. Their ability to handle higher current loads and provide robust protection against short circuits and overheating ensures system reliability and longevity. By integrating power switches, you optimize power distribution and safety, crucial for effective power management.
Important Parameters for Selection
When selecting between a load switch and a power switch, key parameters include maximum current rating, on-resistance (R_DS(on)), and voltage rating to ensure efficient power delivery and minimal energy loss. Switching speed and thermal performance also influence reliability under dynamic load conditions and thermal stress. Additionally, control logic compatibility and protection features such as overcurrent protection and reverse current blocking are critical for safe and seamless integration in power management systems.
Design Considerations for Load and Power Switches
Design considerations for load switches emphasize low on-resistance (R_DS(on)) to minimize power loss and heat generation, fast switching times to improve efficiency, and integrated protection features such as overcurrent and thermal shutdown. Power switches require robust voltage and current handling capabilities with a focus on maximizing reliability under high power conditions, thermal management solutions, and ensuring minimal leakage current in off states. Both switch types demand careful selection of semiconductor materials and packaging to optimize performance for specific application requirements like battery management and power distribution.
Reliability, Safety, and Protection Features
Load switches offer enhanced reliability with solid-state components that minimize wear and mechanical failure, while power switches typically rely on mechanical contacts, which can degrade over time. Safety is improved in load switches through integrated features such as current limiting, thermal shutdown, and fault detection, providing better protection against overloads and short circuits. Power switches, although simpler, lack these advanced protection mechanisms, making load switches a more robust choice for sensitive electronic applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Switch for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate switch depends on the specific requirements of the application, such as current load, voltage rating, and switching speed. Load switches excel in managing power distribution with integrated protection features, making them ideal for battery-powered devices and power sequencing. Power switches, often used for controlling high-current circuits, provide robust on/off control but may lack the advanced functionality found in load switches.
Load Switch vs Power Switch Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com