ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) and EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) both disrupt electronic devices but differ in origin and effect; ESD is a sudden, high-voltage static shock, while EMI is continuous electromagnetic noise affecting signal integrity. Understanding these differences can help you protect your devices effectively - explore the article to learn more.
Table of Comparison
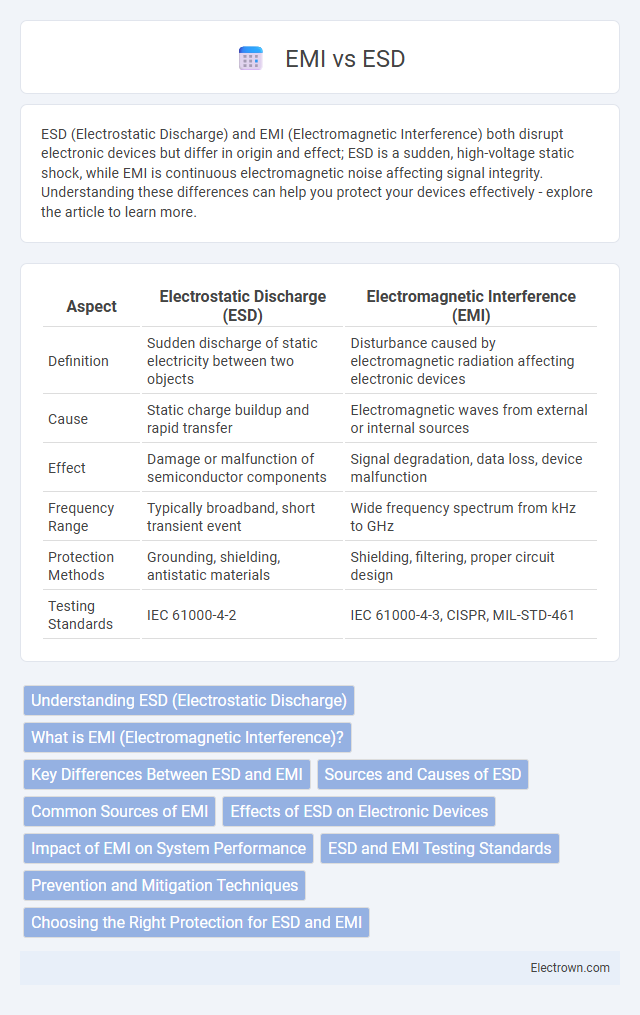
| Aspect | Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) | Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sudden discharge of static electricity between two objects | Disturbance caused by electromagnetic radiation affecting electronic devices |
| Cause | Static charge buildup and rapid transfer | Electromagnetic waves from external or internal sources |
| Effect | Damage or malfunction of semiconductor components | Signal degradation, data loss, device malfunction |
| Frequency Range | Typically broadband, short transient event | Wide frequency spectrum from kHz to GHz |
| Protection Methods | Grounding, shielding, antistatic materials | Shielding, filtering, proper circuit design |
| Testing Standards | IEC 61000-4-2 | IEC 61000-4-3, CISPR, MIL-STD-461 |
Understanding ESD (Electrostatic Discharge)
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) refers to the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects caused by contact or proximity, often resulting in damage to electronic components. ESD protection is critical in sensitive electronics to prevent data loss, malfunction, or permanent hardware failure. Understanding how ESD occurs enables you to implement effective grounding, shielding, and handling practices to safeguard your devices.
What is EMI (Electromagnetic Interference)?
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) refers to the disruption or degradation of electronic device performance caused by unwanted electromagnetic waves emitted from external sources or other electronic devices. EMI can affect communication systems, medical equipment, and sensitive electronics by introducing noise or signal distortion. Understanding EMI helps you implement effective shielding, grounding, and filtering techniques to protect your devices and ensure reliable operation.
Key Differences Between ESD and EMI
ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) involves the sudden flow of static electricity between two objects, causing potential damage to electronic components, while EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) refers to unwanted electromagnetic signals that disrupt the normal functioning of electronic devices. ESD typically results from contact or proximity between charged objects, whereas EMI arises from electromagnetic radiation emitted by various electrical sources. Understanding these key differences helps you implement targeted protection strategies to safeguard sensitive electronics from both transient discharges and ongoing electromagnetic disturbances.
Sources and Causes of ESD
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) originates from the sudden flow of electricity between two electrically charged objects caused by contact, an electrical short, or dielectric breakdown, commonly triggered by human touch, frictional contact between materials, or separation of surfaces. Sources of ESD include synthetic clothing, plastic packaging, and carpeted floors, where static charge accumulates due to triboelectric effects. Understanding these causes helps you implement effective grounding and anti-static measures to protect sensitive electronic components from potential damage.
Common Sources of EMI
Common sources of electromagnetic interference (EMI) include power lines, radio transmitters, electrical motors, and fluorescent lighting. Devices such as computers, mobile phones, and microwave ovens also generate EMI that can disrupt signal integrity and cause data loss. Your electronic systems require proper shielding and grounding to minimize the impact of these frequent EMI sources.
Effects of ESD on Electronic Devices
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can cause significant damage to electronic devices by generating high voltage spikes that exceed component voltage ratings, leading to immediate or latent failures. Sensitive semiconductor components such as MOSFETs and integrated circuits are particularly vulnerable to ESD events, which can degrade device reliability or cause permanent operational failures. Effective ESD protection mechanisms, including transient voltage suppression diodes and grounding techniques, are essential to prevent device malfunction and extend electronic system lifespan.
Impact of EMI on System Performance
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) can significantly degrade system performance by causing data corruption, signal distortion, and unexpected device behavior. Unlike Electrostatic Discharge (ESD), which typically results in sudden, high-voltage damage, EMI presents ongoing noise that interferes with circuit operation and communication integrity. Minimizing EMI ensures your system maintains reliability, reduces error rates, and enhances overall performance in sensitive electronic environments.
ESD and EMI Testing Standards
ESD and EMI testing standards are critical for ensuring electronic device reliability and compliance with industry regulations. The IEC 61000-4-2 standard governs ESD testing, simulating electrostatic discharge events, while EMI testing follows standards like CISPR 22 and FCC Part 15, measuring electromagnetic emissions and immunity. Understanding these standards helps you design and validate devices that withstand electrostatic discharge and electromagnetic interference effectively.
Prevention and Mitigation Techniques
Prevention and mitigation techniques for ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) include grounding, using anti-static wrist straps, and implementing conductive materials to safely dissipate static charges. EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) mitigation involves shielding cables and components with metal enclosures, filtering power supplies, and maintaining proper circuit layout to minimize noise coupling. Your electronic designs benefit significantly by integrating both ESD protection devices and EMI filters to ensure reliable performance and compliance with industry standards.
Choosing the Right Protection for ESD and EMI
Selecting the appropriate protection for ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) and EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) involves understanding their distinct sources and effects on electronic devices. ESD protection typically includes transient voltage suppressors and grounded conductive materials to prevent sudden high-voltage discharges. EMI protection requires shielding, filters, and proper grounding techniques to reduce electromagnetic noise and interference in sensitive circuits.
ESD vs EMI Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com