A repeater captures and retransmits signals to extend their range without altering the original content, while a booster amplifies existing signals to enhance strength and clarity directly. Explore the rest of this article to understand which option best suits your needs.
Table of Comparison
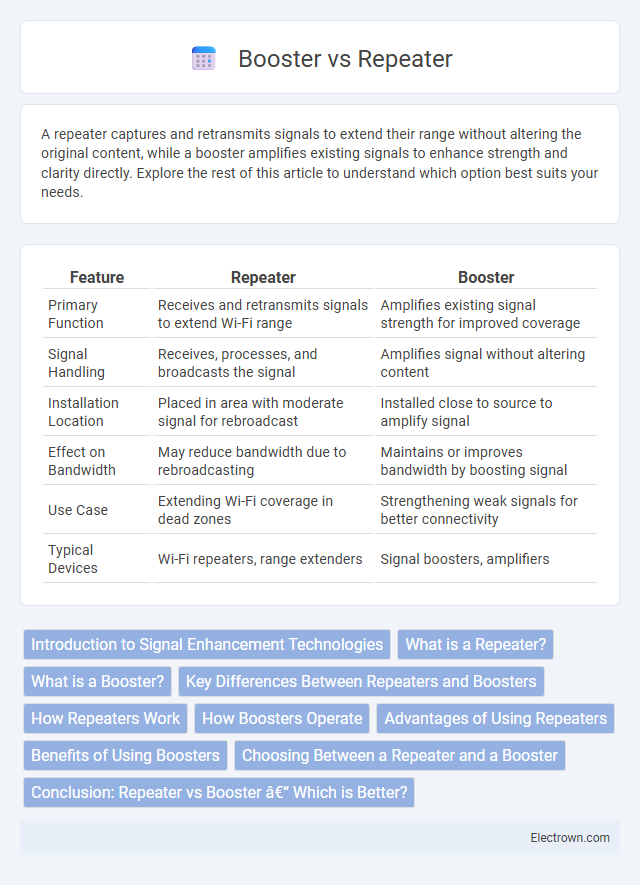
| Feature | Repeater | Booster |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Receives and retransmits signals to extend Wi-Fi range | Amplifies existing signal strength for improved coverage |
| Signal Handling | Receives, processes, and broadcasts the signal | Amplifies signal without altering content |
| Installation Location | Placed in area with moderate signal for rebroadcast | Installed close to source to amplify signal |
| Effect on Bandwidth | May reduce bandwidth due to rebroadcasting | Maintains or improves bandwidth by boosting signal |
| Use Case | Extending Wi-Fi coverage in dead zones | Strengthening weak signals for better connectivity |
| Typical Devices | Wi-Fi repeaters, range extenders | Signal boosters, amplifiers |
Introduction to Signal Enhancement Technologies
Repeater and booster technologies enhance wireless signal strength by amplifying and retransmitting signals to improve coverage in weak reception areas. A repeater captures the original signal, amplifies it, and transmits it again, effectively extending the network's reach without introducing additional noise. Your choice between a repeater and booster depends on the specific environment and signal requirements for optimal connectivity.
What is a Repeater?
A repeater is a device designed to receive, amplify, and retransmit signals to extend the coverage area of a wireless network or communication system. It captures weak or distant signals, strengthens them without altering the original content, and broadcasts them to eliminate dead zones. Your network's range and signal quality significantly improve with the strategic placement of a repeater.
What is a Booster?
A booster is a device designed to amplify and strengthen your existing cell signal to improve coverage and call quality in areas with weak reception. It works by capturing the weak signal, boosting its power, and retransmitting it inside your home or office, ensuring reliable connectivity. Unlike repeaters that simply rebroadcast signals, boosters enhance signal strength to deliver faster data speeds and clearer voice calls.
Key Differences Between Repeaters and Boosters
Repeaters and boosters both enhance wireless signals, but repeaters receive and retransmit the signal to extend coverage, while boosters amplify the existing signal strength without changing its source. Your choice depends on whether you need to extend coverage over a wider area (repeater) or strengthen the signal within the same area (booster). Repeaters typically handle entire signals with possible latency, whereas boosters increase signal power instantly but require a strong original signal to be effective.
How Repeaters Work
Repeaters work by receiving a weak or low-level signal and retransmitting it at a higher power, effectively extending the coverage area of your network. They amplify the signal without changing its format, making them ideal for overcoming obstacles like walls or long distances between devices. By regenerating the signal, repeaters help maintain data integrity and reduce signal loss in wireless communication.
How Boosters Operate
Boosters amplify existing signals by increasing their strength and quality, ensuring better coverage in areas with weak reception. They capture the signal from a nearby tower, boost it, and retransmit it within your home or vehicle, improving connectivity without altering the original content. Your improved signal strength leads to fewer dropped calls and faster data speeds in previously low-signal zones.
Advantages of Using Repeaters
Repeaters amplify and regenerate original signals, ensuring stronger and clearer transmission over long distances without quality degradation. They effectively extend network coverage in wired and wireless communication systems, supporting high-speed data transfer and reducing latency. Their ability to eliminate noise and interference enhances overall network performance and reliability.
Benefits of Using Boosters
Boosters enhance signal strength by amplifying existing signals, providing extended coverage in areas with weak reception. They reduce dropped calls and improve data speeds, contributing to a more reliable and consistent wireless experience. Boosters are particularly effective in large buildings and remote locations where signal penetration is challenging.
Choosing Between a Repeater and a Booster
Choosing between a repeater and a booster depends primarily on the coverage area and signal strength needs; repeaters are ideal for extending Wi-Fi signals over longer distances by capturing and rebroadcasting the signal, while boosters amplify the existing signal to improve strength within a limited range. Repeaters create a new network extension that can reduce overall speed due to retransmission, whereas boosters enhance the current network performance without creating a separate network. Evaluating the size of the space, signal obstacles, and the need for consistent bandwidth helps determine the best solution for effective wireless coverage.
Conclusion: Repeater vs Booster – Which is Better?
Repeaters regenerate and retransmit the exact signal, making them ideal for extending coverage without altering the original data, while boosters amplify the existing signal strength to improve reception quality. In environments with weak signals and minimal interference, boosters provide a simple and cost-effective solution, whereas repeaters excel in complex setups requiring signal clarity over longer distances. Choosing between a repeater and booster depends on specific needs such as signal quality, distance, and network complexity, with repeaters generally favored for maintaining data integrity and boosters preferred for enhancing signal power.
Repeater vs Booster Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com