Soft handoff maintains simultaneous connections to multiple base stations during a call transition, ensuring seamless connectivity and reduced call drops. Understanding the differences between soft and hard handoff can help you optimize your wireless communication experience--read on to explore the detailed advantages of each method.
Table of Comparison
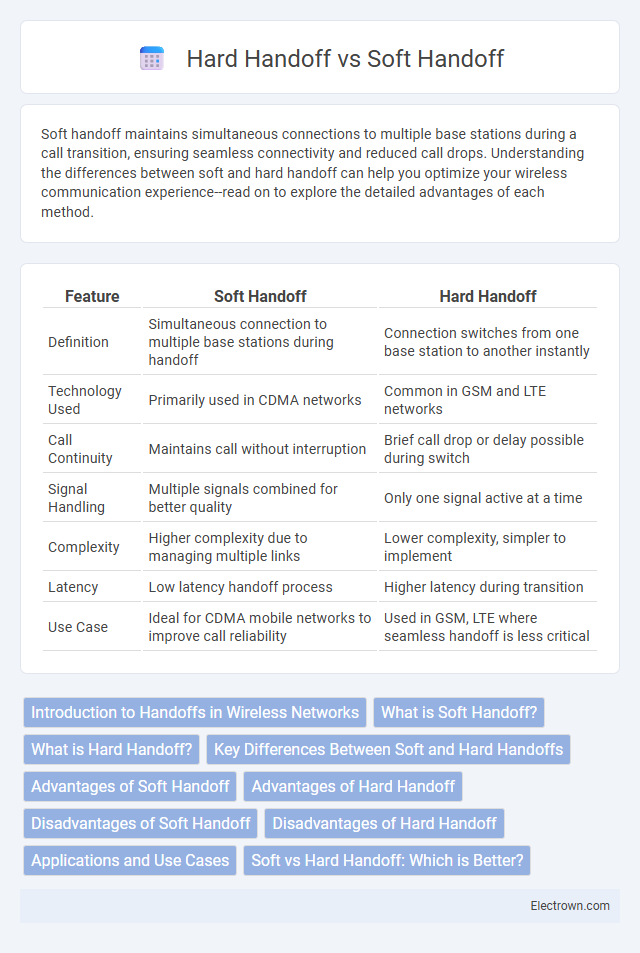
| Feature | Soft Handoff | Hard Handoff |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Simultaneous connection to multiple base stations during handoff | Connection switches from one base station to another instantly |
| Technology Used | Primarily used in CDMA networks | Common in GSM and LTE networks |
| Call Continuity | Maintains call without interruption | Brief call drop or delay possible during switch |
| Signal Handling | Multiple signals combined for better quality | Only one signal active at a time |
| Complexity | Higher complexity due to managing multiple links | Lower complexity, simpler to implement |
| Latency | Low latency handoff process | Higher latency during transition |
| Use Case | Ideal for CDMA mobile networks to improve call reliability | Used in GSM, LTE where seamless handoff is less critical |
Introduction to Handoffs in Wireless Networks
Handoffs in wireless networks ensure continuous connectivity when a mobile device moves between cells or base stations, with soft handoff maintaining simultaneous connections to multiple cells and hard handoff switching connections abruptly from one cell to another. Soft handoff reduces call drops and improves signal quality by overlapping signals during the transition, commonly used in CDMA networks. Your mobile experience benefits from soft handoff's seamless transition, whereas hard handoff, typical in GSM networks, offers a faster but riskier switch with brief connection interruptions.
What is Soft Handoff?
Soft Handoff is a cellular communication technique where a mobile device simultaneously connects to multiple cell towers during a call or data session, ensuring seamless transition and minimizing connection drops. This method enhances call quality and network reliability by maintaining overlapping signal coverage before switching fully to a new tower. Your mobile experience benefits from reduced interference and improved stability during movement within the network.
What is Hard Handoff?
Hard handoff is a mobile communication process where a call or data session is transferred from one cell tower to another by breaking the connection before establishing a new one, resulting in a brief interruption. This type of handoff is commonly used in 2G GSM networks and can cause a momentary loss of signal if the transition is not seamless. Hard handoff contrasts with soft handoff, which maintains simultaneous connections to multiple towers during the handover, reducing call drops and improving network reliability.
Key Differences Between Soft and Hard Handoffs
Soft handoff involves simultaneous connections to multiple base stations, ensuring seamless signal transition and reducing the risk of call drops. Hard handoff requires your device to disconnect from the current base station before establishing a connection with a new one, potentially causing brief interruptions. Key differences include connection overlap in soft handoff for smoother transitions versus the break-before-make approach in hard handoff, affecting call continuity and network reliability.
Advantages of Soft Handoff
Soft handoff improves call quality by enabling simultaneous connections to multiple cell towers, reducing the risk of dropped calls. It enhances network reliability through seamless transitions without interrupting the communication session. This handoff method optimizes signal strength and minimizes interference, leading to better overall user experience in CDMA and UMTS networks.
Advantages of Hard Handoff
Hard handoff offers advantages such as seamless frequency switching and reduced interference by completely breaking the connection with the current cell before connecting to the next. This method ensures clear channel allocation, minimizing signal overlap and improving overall network performance. Your mobile device benefits from a stable and efficient transition in scenarios where simultaneous connections are not feasible.
Disadvantages of Soft Handoff
Soft handoff can lead to increased power consumption due to simultaneous connections with multiple base stations. It may also cause network resource inefficiency as more bandwidth and processing are required to maintain overlapping signals. Moreover, complex signal management during soft handoff increases the risk of interference and dropped calls under certain conditions.
Disadvantages of Hard Handoff
Hard handoff causes a brief disconnection during the transition between cells, leading to potential call drops and degraded voice quality. This method lacks seamless data transfer, resulting in increased latency and higher packet loss in mobile communications. Additionally, hard handoff consumes more network resources due to frequent connection establishments and terminations.
Applications and Use Cases
Soft handoff is extensively used in CDMA networks to enable seamless transition between cells, minimizing dropped calls and enhancing voice quality during mobile communication. Hard handoff is commonly applied in GSM and LTE networks where quick switching between cells is necessary, particularly in high-speed mobile scenarios like driving. Both handoff types are crucial in cellular networks for maintaining continuous connectivity, with soft handoff suited for environments requiring greater call stability and hard handoff optimized for faster network resource reallocation.
Soft vs Hard Handoff: Which is Better?
Soft handoff offers better call quality and reduced dropped connections by allowing Your device to communicate with multiple base stations simultaneously during the transition. Hard handoff is simpler and faster, switching Your signal abruptly between cells, which can lead to brief interruptions or dropped calls. In environments where seamless connectivity is crucial, soft handoff is generally the preferred method.
Soft Handoff vs Hard Handoff Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com