DMR offers a cost-effective digital radio solution with excellent audio clarity and extended battery life, making it ideal for commercial and amateur use. P25 provides robust interoperability and enhanced security features tailored for public safety agencies; explore the article to understand which system best fits Your communication needs.
Table of Comparison
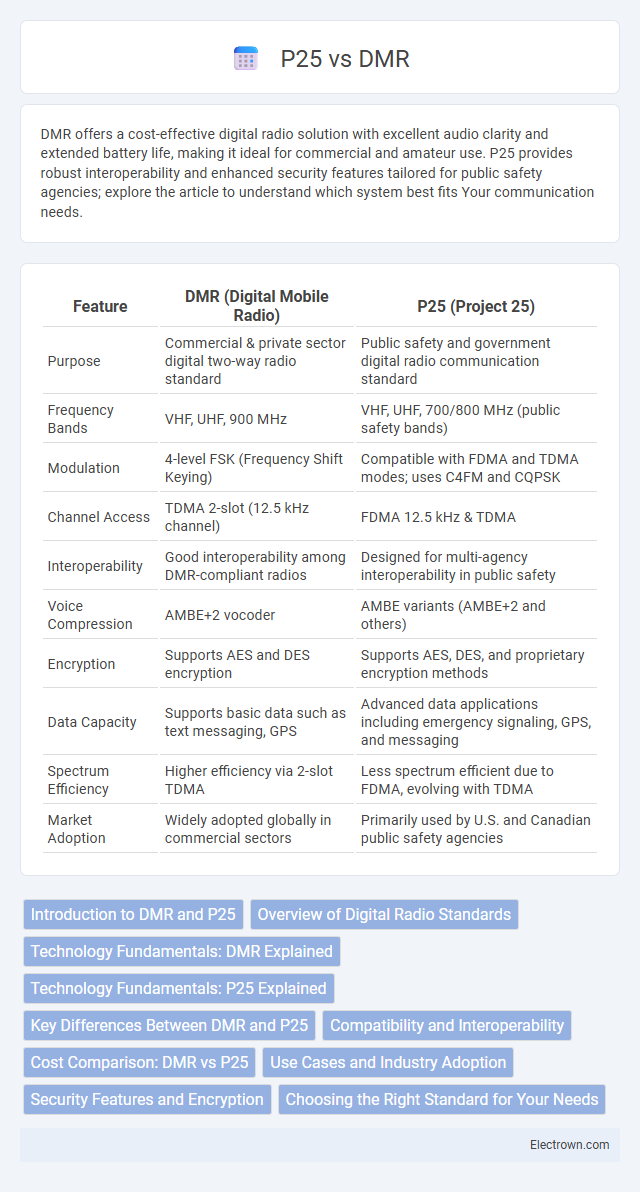
| Feature | DMR (Digital Mobile Radio) | P25 (Project 25) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Commercial & private sector digital two-way radio standard | Public safety and government digital radio communication standard |
| Frequency Bands | VHF, UHF, 900 MHz | VHF, UHF, 700/800 MHz (public safety bands) |
| Modulation | 4-level FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) | Compatible with FDMA and TDMA modes; uses C4FM and CQPSK |
| Channel Access | TDMA 2-slot (12.5 kHz channel) | FDMA 12.5 kHz & TDMA |
| Interoperability | Good interoperability among DMR-compliant radios | Designed for multi-agency interoperability in public safety |
| Voice Compression | AMBE+2 vocoder | AMBE variants (AMBE+2 and others) |
| Encryption | Supports AES and DES encryption | Supports AES, DES, and proprietary encryption methods |
| Data Capacity | Supports basic data such as text messaging, GPS | Advanced data applications including emergency signaling, GPS, and messaging |
| Spectrum Efficiency | Higher efficiency via 2-slot TDMA | Less spectrum efficient due to FDMA, evolving with TDMA |
| Market Adoption | Widely adopted globally in commercial sectors | Primarily used by U.S. and Canadian public safety agencies |
Introduction to DMR and P25
Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) is an open digital radio standard designed for professional mobile radio users, offering efficient spectrum use and interoperability across manufacturers. Project 25 (P25) is a suite of standards developed primarily for public safety organizations, focusing on secure, reliable communication with backward compatibility to analog systems. Both standards support voice and data transmission, but DMR emphasizes cost-effective scalability while P25 prioritizes mission-critical functionality and encrypted communication.
Overview of Digital Radio Standards
Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) and Project 25 (P25) are two key digital radio standards designed primarily for professional and emergency services communication. DMR operates on a TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) protocol offering two voice channels per 12.5 kHz, optimizing spectrum efficiency, while P25 utilizes FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) with a focus on interoperability across various agencies and manufacturers, especially in North America. Your choice between DMR and P25 depends on specific operational needs, regional compatibility, and the importance of open standard features for mission-critical communications.
Technology Fundamentals: DMR Explained
Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) uses Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) technology to provide two voice channels on a single 12.5 kHz frequency slot, enhancing spectrum efficiency. It operates through three tiers: Tier I for unlicensed use, Tier II for licensed conventional systems, and Tier III for trunked systems with advanced features. This open standard ensures interoperability across manufacturers, making DMR a scalable and cost-effective solution for professional mobile radio communications compared to P25's primarily public safety focus.
Technology Fundamentals: P25 Explained
P25, or Project 25, is a suite of standards for digital radio communications used primarily by public safety and government organizations, designed to ensure interoperability between agencies. It operates on both conventional and trunked radio systems using Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA) within 12.5 kHz channels, enhancing spectrum efficiency and providing secure, encrypted voice and data transmission. Unlike DMR's global commercial focus, P25 emphasizes ruggedness, reliability, and compliance with specific FCC and APCO standards critical for mission-critical communication.
Key Differences Between DMR and P25
DMR (Digital Mobile Radio) and P25 (Project 25) differ primarily in their intended use and technology standards; DMR is an open digital radio standard widely adopted globally for commercial and industrial applications, while P25 is a suite of standards designed specifically for public safety and emergency services in North America. P25 supports seamless interoperability among different agencies and prioritizes secure, encrypted communications, whereas DMR emphasizes cost-effective deployment and enhanced spectrum efficiency using TDMA technology. Your choice between DMR and P25 should consider factors such as interoperability requirements, encryption needs, and the specific communication environment.
Compatibility and Interoperability
DMR and P25 differ significantly in compatibility and interoperability, with P25 designed primarily for public safety agencies ensuring seamless communication across various manufacturers' equipment. DMR systems offer broader commercial use and easier integration but may face limitations when connecting disparate brands or legacy systems. Your choice depends on whether mission-critical interoperability or cost-effective, versatile communication solutions are paramount.
Cost Comparison: DMR vs P25
Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) systems generally offer a lower initial cost compared to Project 25 (P25) networks, making them more cost-effective for small to medium-sized organizations. P25 solutions, designed primarily for public safety and government use, involve higher expenses due to stringent interoperability standards and specialized encryption features. When evaluating your communication infrastructure, consider that DMR provides affordable scalability, whereas P25 investments deliver robust security and compliance at a premium price.
Use Cases and Industry Adoption
DMR (Digital Mobile Radio) is widely adopted in commercial sectors such as transportation, manufacturing, and utilities due to its cost-effectiveness and interoperability. P25 (Project 25) is primarily used by public safety agencies and first responders because of its enhanced encryption and standardized communication protocols. Both technologies support mission-critical communication, but DMR's global use in private businesses contrasts with P25's predominance in government and emergency response networks.
Security Features and Encryption
DMR (Digital Mobile Radio) offers AES 256-bit encryption for securing voice and data transmissions, ensuring robust protection against eavesdropping and unauthorized access. P25 (Project 25) employs AES encryption as well, with a widely adopted standard for public safety communications, featuring over-the-air rekeying (OTAR) to maintain encryption keys securely. Your choice between DMR and P25 depends on the security level required, with P25 often preferred for critical mission communications due to its comprehensive encryption management and interoperability standards.
Choosing the Right Standard for Your Needs
DMR (Digital Mobile Radio) offers cost-effective, scalable solutions ideal for small to medium organizations requiring efficient voice communication and interoperability. P25 (Project 25) provides enhanced encryption, interoperability across agencies, and higher audio clarity, making it suitable for public safety and critical communication needs. Assess Your communication requirements, budget, and security priorities to select the best standard for Your operational environment.
DMR vs P25 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com