Full mesh topology offers robust reliability and fault tolerance by connecting every device directly to all others, ensuring uninterrupted communication even if multiple links fail. Star topology simplifies network management and reduces cable use by connecting all devices to a central hub, but it risks network downtime if the hub fails; explore the rest of the article to understand which topology best suits your network needs.
Table of Comparison
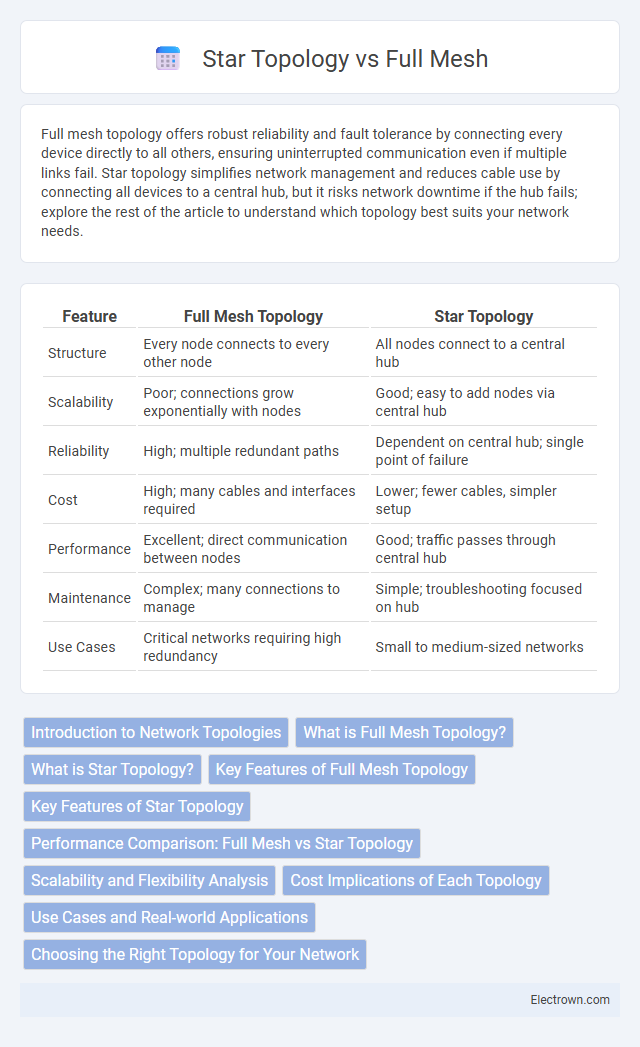
| Feature | Full Mesh Topology | Star Topology |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Every node connects to every other node | All nodes connect to a central hub |
| Scalability | Poor; connections grow exponentially with nodes | Good; easy to add nodes via central hub |
| Reliability | High; multiple redundant paths | Dependent on central hub; single point of failure |
| Cost | High; many cables and interfaces required | Lower; fewer cables, simpler setup |
| Performance | Excellent; direct communication between nodes | Good; traffic passes through central hub |
| Maintenance | Complex; many connections to manage | Simple; troubleshooting focused on hub |
| Use Cases | Critical networks requiring high redundancy | Small to medium-sized networks |
Introduction to Network Topologies
Full Mesh topology connects every device directly to all others, ensuring maximum redundancy and fault tolerance, ideal for mission-critical networks requiring constant uptime. Star topology links all devices to a central hub, simplifying management and troubleshooting but creating a single point of failure. Your choice between Full Mesh and Star Topology impacts network scalability, reliability, and maintenance complexity.
What is Full Mesh Topology?
Full Mesh Topology is a network structure where each node connects directly to every other node, creating multiple redundant paths for data transmission. This design enhances fault tolerance and network reliability by ensuring communication persists even if one connection fails. Due to its complexity and high number of connections, Full Mesh is typically used in critical systems requiring robust performance, such as financial trading networks and large data centers.
What is Star Topology?
Star topology is a network configuration where all devices are individually connected to a central hub or switch, enabling efficient communication and easy fault isolation. This setup minimizes the impact of a single device failure, as the rest of the network remains operational without interruption. Your network benefits from simplified management and scalability by adding or removing devices without affecting the overall performance.
Key Features of Full Mesh Topology
Full Mesh Topology features direct, point-to-point connections between all nodes, ensuring high redundancy and fault tolerance. Each device communicates independently, which enhances network reliability and reduces the risk of total network failure. Your network benefits from robust data transmission paths, making Full Mesh ideal for critical systems requiring consistent uptime and minimal latency.
Key Features of Star Topology
Star topology features a central hub or switch connecting all nodes individually, ensuring easy fault isolation and straightforward network management. Each device communicates through the central hub, which simplifies adding or removing devices without disrupting the entire network. This topology offers improved performance and reliability compared to other layouts by minimizing data collision and facilitating efficient traffic handling.
Performance Comparison: Full Mesh vs Star Topology
Full Mesh topology offers superior performance with direct point-to-point connections between all nodes, minimizing latency and maximizing redundancy, which ensures continuous network availability even if multiple links fail. In contrast, Star topology centralizes communication through a single hub, which can become a bottleneck under high traffic loads, impacting overall network speed and reliability. Your choice should consider the trade-off between Full Mesh's higher complexity and cost versus Star's simpler design but potential performance constraints.
Scalability and Flexibility Analysis
Full mesh topology offers high scalability by providing direct connections between all nodes, facilitating seamless communication and fault tolerance, but it becomes less practical as the number of nodes increases due to exponential growth in connections (n(n-1)/2). Star topology scales more efficiently for large networks, connecting each node to a central hub, simplifying management and network expansion without extensive cabling, though it creates a single point of failure at the hub. Flexibility is greater in full mesh networks because any node can communicate directly without routing through a central point, whereas star topology offers straightforward flexibility by allowing easy addition or removal of nodes at the hub with minimal network disruption.
Cost Implications of Each Topology
Full mesh topology incurs higher costs due to extensive cabling and numerous network interfaces required for direct connections between all nodes, making it optimal for small networks with critical uptime needs. Star topology offers a cost-effective solution by connecting all nodes to a central hub, reducing cabling expenses and simplifying network management but increasing dependency on the central device. Budget considerations must balance the robust redundancy of full mesh against the economical scalability and maintenance ease of star topology.
Use Cases and Real-world Applications
Full mesh topology is ideal for mission-critical networks requiring high redundancy and fault tolerance, such as financial trading platforms and military communication systems, where uninterrupted connectivity is essential. Star topology is commonly used in home networks, office LANs, and IoT deployments due to its straightforward setup, centralized management, and scalability, making it suitable for environments with moderate traffic and easier fault isolation. In real-world applications, full mesh excels in environments demanding low latency and maximum uptime, while star topology supports cost-effective, easily expandable networks with simplified troubleshooting.
Choosing the Right Topology for Your Network
Choosing the right network topology depends on your specific needs for scalability, reliability, and cost. Full mesh topology offers high redundancy and fault tolerance by connecting every device to all others, ideal for mission-critical environments requiring maximum uptime. Star topology simplifies management and reduces cable costs by connecting all devices to a central hub, making it suitable for small to medium-sized networks prioritizing ease of maintenance.
Full Mesh vs Star Topology Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com