Digital audio captures sound using discrete numerical values, offering precise editing capabilities and consistent quality free from degradation over time. Analog audio records continuous waveforms, delivering a warmer, more natural sound that some listeners prefer; explore the rest of this article to understand which format best suits your listening needs and preferences.
Table of Comparison
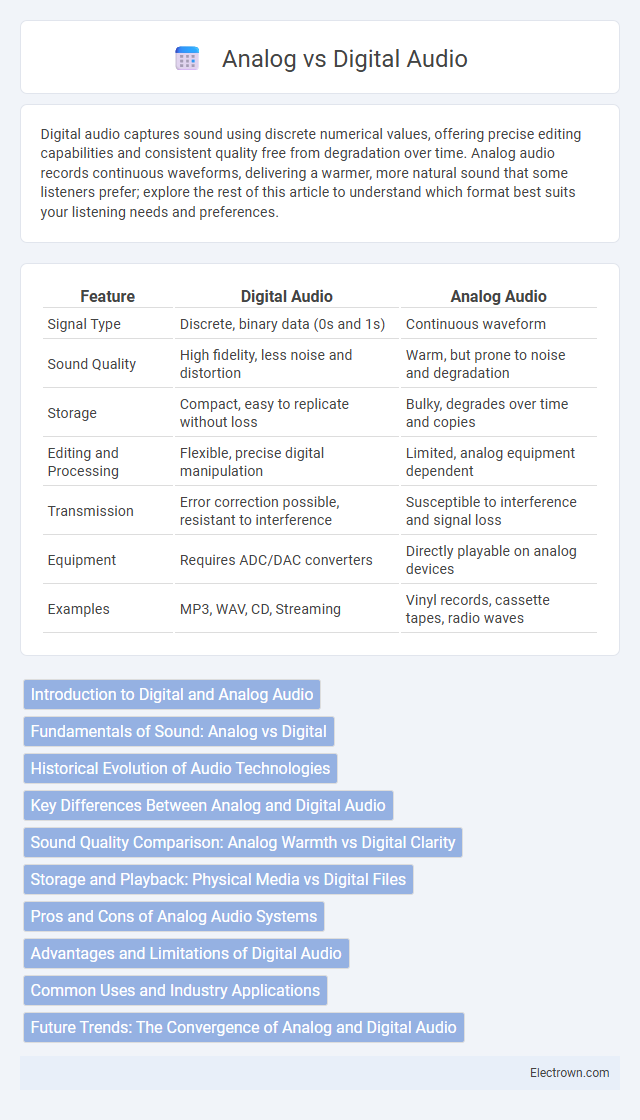
| Feature | Digital Audio | Analog Audio |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Type | Discrete, binary data (0s and 1s) | Continuous waveform |
| Sound Quality | High fidelity, less noise and distortion | Warm, but prone to noise and degradation |
| Storage | Compact, easy to replicate without loss | Bulky, degrades over time and copies |
| Editing and Processing | Flexible, precise digital manipulation | Limited, analog equipment dependent |
| Transmission | Error correction possible, resistant to interference | Susceptible to interference and signal loss |
| Equipment | Requires ADC/DAC converters | Directly playable on analog devices |
| Examples | MP3, WAV, CD, Streaming | Vinyl records, cassette tapes, radio waves |
Introduction to Digital and Analog Audio
Digital audio captures sound by converting analog signals into binary data through sampling and quantization processes that preserve sound quality with minimal noise and distortion. Analog audio records continuous waveforms directly, maintaining natural sound characteristics but is more susceptible to degradation over time and interference. Understanding these differences helps you choose the best format for your audio needs based on fidelity, durability, and usage.
Fundamentals of Sound: Analog vs Digital
Analog audio captures sound as continuous waveforms, representing natural fluctuations in air pressure, while digital audio samples these waveforms at discrete intervals, converting them into binary data. The fundamental difference lies in analog's seamless representation of sound waves versus digital's reliance on sampling rate and bit depth to approximate those waves. Your choice between analog and digital affects audio fidelity, noise levels, and editing flexibility due to these fundamental sound representations.
Historical Evolution of Audio Technologies
The historical evolution of audio technologies traces its roots back to the early 20th century with the advent of analog recording methods, such as phonograph cylinders and magnetic tape, which revolutionized sound capture and reproduction. The transition to digital audio emerged in the late 1970s and early 1980s, highlighted by the development of the Compact Disc (CD) and digital signal processing, enabling higher fidelity, lower noise, and easier manipulation of sound data. This shift from analog waveforms to binary digital encoding marked a transformative milestone, profoundly impacting music production, broadcasting, and audio archiving practices worldwide.
Key Differences Between Analog and Digital Audio
Analog audio captures sound as continuous waveforms, preserving natural sound variations and warmth, while digital audio converts sound into discrete binary data, enabling precise editing and noise reduction. Analog signals are prone to degradation and distortion over time, whereas digital audio maintains quality through error correction and lossless storage. Understanding these key differences allows you to choose the best audio format for fidelity, flexibility, and application needs.
Sound Quality Comparison: Analog Warmth vs Digital Clarity
Analog audio delivers a warm, rich sound characterized by natural warmth and subtle harmonic distortion that many audiophiles appreciate for its authentic listening experience. Digital audio offers superior clarity and precision by accurately capturing sound waves with minimal noise, providing a clean and detailed sound profile ideal for modern playback systems. Your choice between analog warmth and digital clarity depends on whether you prioritize emotional depth or technical accuracy in sound quality.
Storage and Playback: Physical Media vs Digital Files
Digital audio files offer compact storage with high fidelity and easy access across multiple devices, while analog audio relies on physical media like vinyl records or tapes, which require more space and are prone to degradation over time. Your digital collection can be instantly copied, edited, or streamed without loss of quality, whereas analog playback depends on mechanical components that affect sound consistency. Choosing between digital and analog audio impacts how you store, manage, and experience your music collection in terms of convenience and longevity.
Pros and Cons of Analog Audio Systems
Analog audio systems offer warm, natural sound reproduction prized by audiophiles for its rich harmonic content and smooth frequency response. These systems tend to be more susceptible to noise, distortion, and signal degradation over time or during transmission compared to digital alternatives. Maintenance can also be more demanding, as analog components like tapes and vinyl records require careful handling and regular upkeep to preserve audio quality.
Advantages and Limitations of Digital Audio
Digital audio offers precise sound replication through binary encoding, enabling easy manipulation, storage, and transmission with minimal noise interference. It provides consistent quality across multiple copies and supports advanced features like error correction and compression formats such as MP3 and FLAC. However, digital audio faces limitations including potential loss of audio nuances due to sampling rates and bit depth constraints, as well as increased latency in real-time processing scenarios.
Common Uses and Industry Applications
Digital audio dominates in music production, streaming services, and broadcasting due to its high fidelity, ease of editing, and compression capabilities, making it ideal for studios, online platforms, and radio. Analog audio remains crucial in live sound reinforcement, vinyl records, and vintage equipment enthusiasts, prized for its warm, natural sound quality and reliability in certain recording environments. Industries such as film, gaming, and telecommunications rely heavily on digital audio for precise sound manipulation, while analog techniques persist in analog synthesizers and audio mastering to preserve sonic character.
Future Trends: The Convergence of Analog and Digital Audio
Emerging trends indicate a growing convergence between analog warmth and digital precision, with hybrid audio systems combining analog signal paths and digital processing for enhanced sound quality. New technologies such as high-resolution digital audio formats and advanced analog modeling plugins allow you to experience the best of both worlds, preserving the character of analog sound alongside the flexibility of digital editing. Industry innovations focus on seamless integration, promising future audio equipment that leverages the strengths of both domains to deliver immersive, high-fidelity listening experiences.
Digital vs Analog Audio Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com