Decentralized storage offers enhanced security and control by distributing data across multiple nodes, reducing reliance on a single provider and mitigating risks of data breaches and censorship. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these differences impact your data management choices.
Table of Comparison
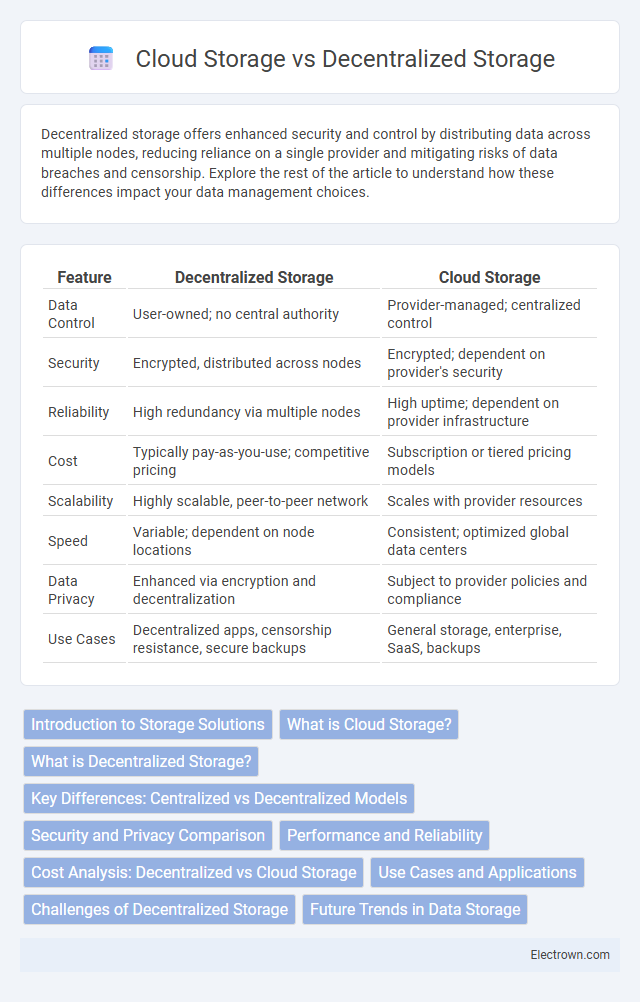
| Feature | Decentralized Storage | Cloud Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Data Control | User-owned; no central authority | Provider-managed; centralized control |
| Security | Encrypted, distributed across nodes | Encrypted; dependent on provider's security |
| Reliability | High redundancy via multiple nodes | High uptime; dependent on provider infrastructure |
| Cost | Typically pay-as-you-use; competitive pricing | Subscription or tiered pricing models |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, peer-to-peer network | Scales with provider resources |
| Speed | Variable; dependent on node locations | Consistent; optimized global data centers |
| Data Privacy | Enhanced via encryption and decentralization | Subject to provider policies and compliance |
| Use Cases | Decentralized apps, censorship resistance, secure backups | General storage, enterprise, SaaS, backups |
Introduction to Storage Solutions
Decentralized storage leverages blockchain technology to distribute data across multiple nodes, enhancing security, privacy, and resistance to censorship. Cloud storage relies on centralized servers managed by providers like Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud, offering ease of access, scalability, and reliable infrastructure. Your choice between these solutions depends on the need for control over data, cost considerations, and desired transparency.
What is Cloud Storage?
Cloud storage is a service that allows you to save data on remote servers accessed via the internet, offering scalability and easy accessibility. Major providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure ensure data redundancy and security through centralized data centers. Your files are managed and maintained by these providers, enabling real-time synchronization and seamless backup without the need for physical hardware.
What is Decentralized Storage?
Decentralized storage stores data across multiple nodes in a distributed network, enhancing security and reducing reliance on a single provider unlike traditional cloud storage. Your data is encrypted and fragmented, ensuring privacy and resistance to censorship or data loss. This approach offers increased control and transparency, making it a robust alternative to centralized cloud services.
Key Differences: Centralized vs Decentralized Models
Decentralized storage distributes data across multiple nodes in a peer-to-peer network, enhancing security, privacy, and resistance to censorship compared to centralized cloud storage, which relies on singular data centers controlled by service providers. Cloud storage offers streamlined management, scalable resources, and faster access due to centralized infrastructure, whereas decentralized models reduce single points of failure and increase data redundancy by leveraging blockchain or distributed ledger technologies. These fundamental differences impact cost, control, data sovereignty, and vulnerability to attacks, making decentralized storage ideal for users prioritizing privacy and resilience.
Security and Privacy Comparison
Decentralized storage offers enhanced security by distributing data across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of centralized breaches and single points of failure, while cloud storage typically relies on centralized servers vulnerable to targeted attacks. Privacy in decentralized systems is strengthened through encryption and user-controlled access, giving you full ownership of your data without dependence on third-party providers. Cloud storage can expose your information to unauthorized access or governmental surveillance due to centralized data management and weaker encryption protocols.
Performance and Reliability
Decentralized storage leverages a distributed network of nodes, enhancing data redundancy and fault tolerance, resulting in improved reliability compared to traditional cloud storage that depends on centralized servers. Performance in decentralized systems can vary based on network conditions and node availability, whereas cloud storage typically offers consistent speeds due to optimized infrastructure and data centers. Your choice between these solutions should consider the specific performance needs and reliability expectations of your applications or data management strategy.
Cost Analysis: Decentralized vs Cloud Storage
Decentralized storage often offers lower long-term costs by utilizing distributed peer-to-peer networks, reducing dependence on centralized data centers and associated overhead expenses. Cloud storage providers typically charge recurring fees based on storage capacity, data transfer, and access frequency, which can escalate with scale and usage spikes. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires considering factors such as data redundancy, latency, security, and vendor lock-in risks inherent to each storage model.
Use Cases and Applications
Decentralized storage excels in secure data sharing, content distribution, and censorship-resistant applications by leveraging blockchain technology and peer-to-peer networks, making it ideal for privacy-focused projects and distributed web platforms. Cloud storage is widely adopted for enterprise backup, real-time collaboration, and scalable infrastructure needs, supporting applications such as SaaS, disaster recovery, and big data analytics with centralized control and high availability. Use cases for decentralized storage emphasize user sovereignty and data integrity, while cloud storage focuses on seamless integration, ease of management, and global accessibility.
Challenges of Decentralized Storage
Decentralized storage faces significant challenges including data retrieval speed, network reliability, and security concerns due to the distributed nature of nodes. Unlike centralized cloud storage, ensuring consistent availability and managing data redundancy can be complex and resource-intensive. Your experience may be impacted by latency issues and the difficulty of maintaining data integrity across a decentralized network.
Future Trends in Data Storage
Decentralized storage platforms leverage blockchain technology to enhance security, transparency, and user control, signaling a shift from traditional centralized cloud storage models. Innovations in distributed ledger technology and edge computing are driving increased adoption of decentralized storage solutions, reducing reliance on single data centers and minimizing downtime risks. Future trends emphasize integration of hybrid models, combining the scalability of cloud storage with the resilience and privacy features of decentralized networks.
Decentralized Storage vs Cloud Storage Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com