G-Sync and FreeSync are two leading adaptive sync technologies that prevent screen tearing and stuttering by synchronizing your monitor's refresh rate with your graphics card's frame rate. Explore the key differences and performance benefits of each to determine which one suits your gaming setup best.
Table of Comparison
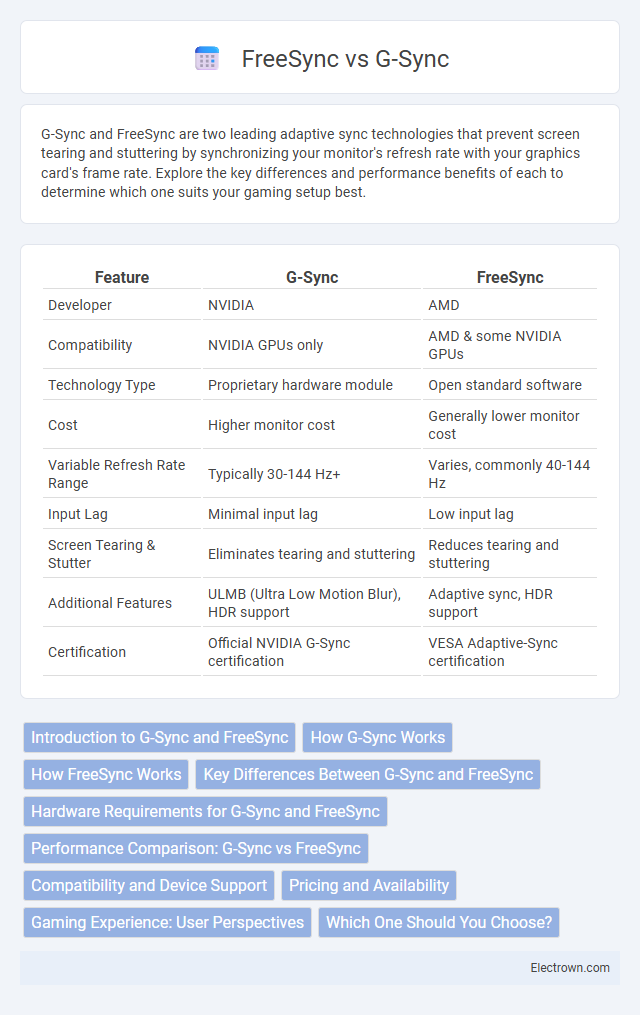
| Feature | G-Sync | FreeSync |
|---|---|---|
| Developer | NVIDIA | AMD |
| Compatibility | NVIDIA GPUs only | AMD & some NVIDIA GPUs |
| Technology Type | Proprietary hardware module | Open standard software |
| Cost | Higher monitor cost | Generally lower monitor cost |
| Variable Refresh Rate Range | Typically 30-144 Hz+ | Varies, commonly 40-144 Hz |
| Input Lag | Minimal input lag | Low input lag |
| Screen Tearing & Stutter | Eliminates tearing and stuttering | Reduces tearing and stuttering |
| Additional Features | ULMB (Ultra Low Motion Blur), HDR support | Adaptive sync, HDR support |
| Certification | Official NVIDIA G-Sync certification | VESA Adaptive-Sync certification |
Introduction to G-Sync and FreeSync
G-Sync and FreeSync are advanced adaptive sync technologies designed to eliminate screen tearing and reduce stuttering in gaming monitors. G-Sync, developed by NVIDIA, utilizes proprietary hardware modules and synchronization protocols to provide smooth, consistent frame rates with NVIDIA GPUs. FreeSync, created by AMD, uses the VESA Adaptive-Sync standard integrated into DisplayPort and HDMI connections, offering variable refresh rates compatible with AMD and some NVIDIA graphics cards.
How G-Sync Works
G-Sync operates by synchronizing the monitor's refresh rate with the GPU's frame output, eliminating screen tearing and minimizing input lag for smoother gameplay. It utilizes a dedicated module inside the monitor to dynamically adjust refresh rates, ensuring frames are delivered as soon as they are rendered. This hardware-driven approach provides consistent performance across varying frame rates compared to software-based alternatives.
How FreeSync Works
FreeSync works by synchronizing the refresh rate of a compatible monitor with the frame rate of an AMD graphics card, reducing screen tearing and stuttering during gameplay. It uses Adaptive-Sync technology built into the DisplayPort and HDMI standards to dynamically adjust refresh rates within a variable range. This results in smoother visuals and improved overall gaming performance without the need for proprietary hardware modules like Nvidia's G-Sync.
Key Differences Between G-Sync and FreeSync
G-Sync uses proprietary NVIDIA hardware modules to deliver smoother gameplay with reduced screen tearing and input lag, while FreeSync relies on open standards supported by AMD graphics cards, offering a cost-effective alternative without extra hardware costs. G-Sync tends to provide more consistent performance with better compatibility and lower latency, whereas FreeSync offers wider monitor compatibility and flexibility across various devices. Your choice between G-Sync and FreeSync should consider your GPU brand and desired balance between price and performance when optimizing your gaming experience.
Hardware Requirements for G-Sync and FreeSync
G-Sync requires a dedicated NVIDIA module built into the monitor, which increases both hardware costs and overall system compatibility limits. FreeSync leverages the Adaptive-Sync standard integrated into DisplayPort and HDMI, making it compatible with a wider range of monitors without additional hardware requirements. You should consider your GPU brand and monitor options carefully since G-Sync demands specific NVIDIA hardware, while FreeSync works primarily with AMD GPUs and some NVIDIA cards supporting Adaptive-Sync.
Performance Comparison: G-Sync vs FreeSync
G-Sync offers superior performance with its dedicated hardware module, providing consistently smoother gameplay and lower input lag compared to FreeSync, which relies on open standards and variable refresh rates. FreeSync supports a wider range of monitors at a lower cost, but G-Sync excels in eliminating screen tearing and stuttering, especially in high-demand gaming scenarios. The choice between G-Sync and FreeSync ultimately hinges on budget and compatibility, with G-Sync favored for premium performance and FreeSync for broader accessibility.
Compatibility and Device Support
G-Sync technology, developed by NVIDIA, offers wide compatibility primarily with NVIDIA graphics cards and a range of G-Sync-certified monitors, ensuring smooth gameplay with minimal screen tearing. FreeSync, created by AMD, supports a broader variety of devices, including many AMD and some NVIDIA GPUs, and is integrated into numerous monitors at various price points. Your choice between G-Sync and FreeSync will largely depend on your existing device ecosystem and desired monitor compatibility for optimal performance.
Pricing and Availability
G-Sync monitors generally carry a higher price tag due to proprietary NVIDIA hardware modules and stricter certification processes, which limit availability to premium models. FreeSync utilizes the more broadly adopted Adaptive-Sync standard, enabling wider compatibility with AMD GPUs and a larger selection of budget to mid-range monitors. Consumers seeking cost-effective options with broad availability tend to find more FreeSync displays, while G-Sync remains a premium choice targeted at enthusiasts.
Gaming Experience: User Perspectives
G-Sync and FreeSync both enhance gaming experience by reducing screen tearing and input lag, but users often highlight G-Sync's superior performance in delivering smoother frame rates and consistent visuals, especially on NVIDIA GPUs. FreeSync offers a cost-effective solution with broad compatibility on AMD graphics cards, appealing to budget-conscious gamers seeking variable refresh rate technology. Your choice depends on your GPU brand and priority for premium smoothness or affordable quality.
Which One Should You Choose?
Choosing between G-Sync and FreeSync depends largely on your GPU brand and budget. G-Sync, developed by NVIDIA, offers superior performance, lower input lag, and enhanced tear-free gaming but requires a compatible NVIDIA graphics card and typically costs more due to proprietary hardware modules. FreeSync, supported by AMD and now increasingly compatible with some NVIDIA cards, provides a more affordable variable refresh rate solution with broad monitor support, making it ideal if you want smoother gameplay without breaking your budget.
G-Sync vs FreeSync Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com