DLNA enables seamless streaming of media files between compatible devices on the same network, focusing on content sharing rather than screen mirroring. To understand which technology best suits Your wireless streaming needs, explore the detailed comparison in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
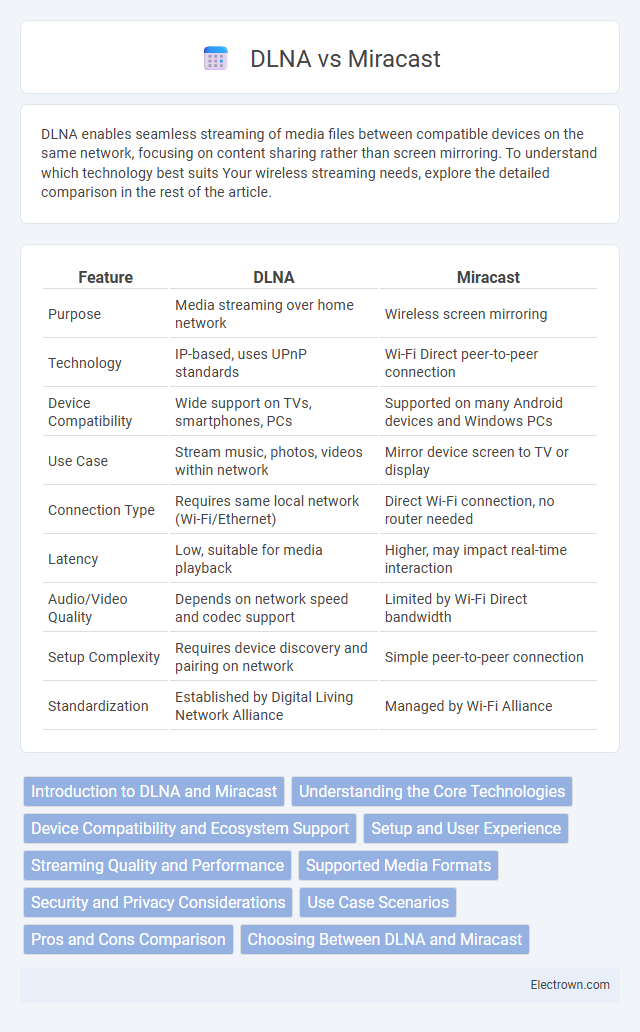
| Feature | DLNA | Miracast |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Media streaming over home network | Wireless screen mirroring |
| Technology | IP-based, uses UPnP standards | Wi-Fi Direct peer-to-peer connection |
| Device Compatibility | Wide support on TVs, smartphones, PCs | Supported on many Android devices and Windows PCs |
| Use Case | Stream music, photos, videos within network | Mirror device screen to TV or display |
| Connection Type | Requires same local network (Wi-Fi/Ethernet) | Direct Wi-Fi connection, no router needed |
| Latency | Low, suitable for media playback | Higher, may impact real-time interaction |
| Audio/Video Quality | Depends on network speed and codec support | Limited by Wi-Fi Direct bandwidth |
| Setup Complexity | Requires device discovery and pairing on network | Simple peer-to-peer connection |
| Standardization | Established by Digital Living Network Alliance | Managed by Wi-Fi Alliance |
Introduction to DLNA and Miracast
DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance) is a standard that enables seamless sharing of multimedia content like videos, photos, and music across compatible devices on a home network. Miracast is a wireless display technology that mirrors the screen of smartphones, tablets, or PCs directly to TVs or monitors without needing an internet connection. Both technologies serve distinct purposes: DLNA focuses on media streaming within connected devices, while Miracast emphasizes real-time screen mirroring over Wi-Fi Direct.
Understanding the Core Technologies
DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance) enables seamless streaming and sharing of multimedia content across compatible devices within a home network using UPnP protocols, ensuring interoperability. Miracast utilizes Wi-Fi Direct technology to mirror your device's screen wirelessly to a compatible display without relying on a traditional network. Understanding these core technologies helps you choose between media sharing versatility (DLNA) and real-time screen mirroring (Miracast) based on your specific needs.
Device Compatibility and Ecosystem Support
DLNA supports a wide range of devices, including smart TVs, gaming consoles, and media players, making it highly compatible within established home entertainment ecosystems. Miracast offers seamless peer-to-peer screen mirroring primarily between smartphones, tablets, and TVs, emphasizing direct device-to-device connectivity without relying on a Wi-Fi network. Understanding your device compatibility and preferred ecosystem ensures you choose the streaming technology that best fits your media sharing needs.
Setup and User Experience
DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance) requires connecting devices through a shared Wi-Fi network, offering seamless media streaming but often demanding initial configuration of compatible devices and media servers. Miracast enables direct device-to-device screen mirroring via Wi-Fi Direct, providing a quicker setup without a router, ideal for real-time display sharing but sometimes prone to latency or connection instability. User experience with DLNA emphasizes high-quality playback across multiple devices, while Miracast prioritizes ease of use for mirroring displays with minimal delay.
Streaming Quality and Performance
DLNA supports high-quality streaming by leveraging local network connections, ensuring minimal latency and stable video playback suitable for full HD and 4K content. Miracast mirrors screens wirelessly with moderate latency, which can cause slight lag or reduced video quality depending on Wi-Fi interference and bandwidth limitations. Streaming performance in DLNA generally surpasses Miracast in stability and resolution due to its reliance on direct device-to-device file sharing over Wi-Fi or Ethernet.
Supported Media Formats
DLNA supports a wide range of media formats including JPEG, BMP, PNG for images, MP3, WAV, AAC for audio, and MPEG-2, MPEG-4, WMV for video, ensuring compatibility with most consumer electronics. Miracast primarily focuses on screen mirroring regardless of the original file format, streaming content as video frames encoded with H.264, making it format-agnostic but limited by device display capabilities. Media format support in DLNA is more extensive for direct file sharing, while Miracast excels in real-time wireless display transmission.
Security and Privacy Considerations
DLNA relies on home network security protocols, making it susceptible to vulnerabilities if the Wi-Fi network is not secured with strong encryption such as WPA3. Miracast employs Wi-Fi Direct with WPA2 encryption, offering a direct peer-to-peer connection that reduces exposure to network-based attacks but may still be vulnerable to unauthorized access without strict device authentication. Both technologies require users to implement robust password protections and regularly update firmware to mitigate risks related to data interception and unauthorized streaming.
Use Case Scenarios
DLNA excels in multi-room media streaming, enabling users to share music, videos, and photos across compatible devices within a home network, ideal for synchronized entertainment experiences. Miracast is suited for screen mirroring from smartphones, tablets, or laptops to TVs and projectors without requiring a Wi-Fi network, making it perfect for presentations, gaming, and real-time content sharing. Both technologies support wireless media transmission but differ in network dependency and device compatibility, influencing their optimal use cases.
Pros and Cons Comparison
DLNA offers broad device compatibility and seamless streaming across home networks but requires a shared Wi-Fi connection, which may cause lag or buffering issues. Miracast provides direct screen mirroring without needing a router, ensuring low latency and real-time display, but it has limited device support and may face connection instability. When choosing, consider your environment and whether you prioritize network-wide streaming (DLNA) or quick, device-to-device mirroring (Miracast) for your needs.
Choosing Between DLNA and Miracast
Choosing between DLNA and Miracast depends on your streaming needs and device compatibility. DLNA excels in streaming stored media files over a home network to compatible devices with better support for a wide range of file formats. Miracast offers real-time screen mirroring with low latency, ideal for sharing live content and presentations without requiring a Wi-Fi network.
DLNA vs Miracast Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com