Wi-Fi 6 offers faster speeds, improved capacity, and better performance in crowded environments compared to Wi-Fi 5, making it ideal for modern homes and businesses with multiple connected devices. Explore this article to understand how upgrading your Wi-Fi can enhance your internet experience and determine which standard suits your needs best.
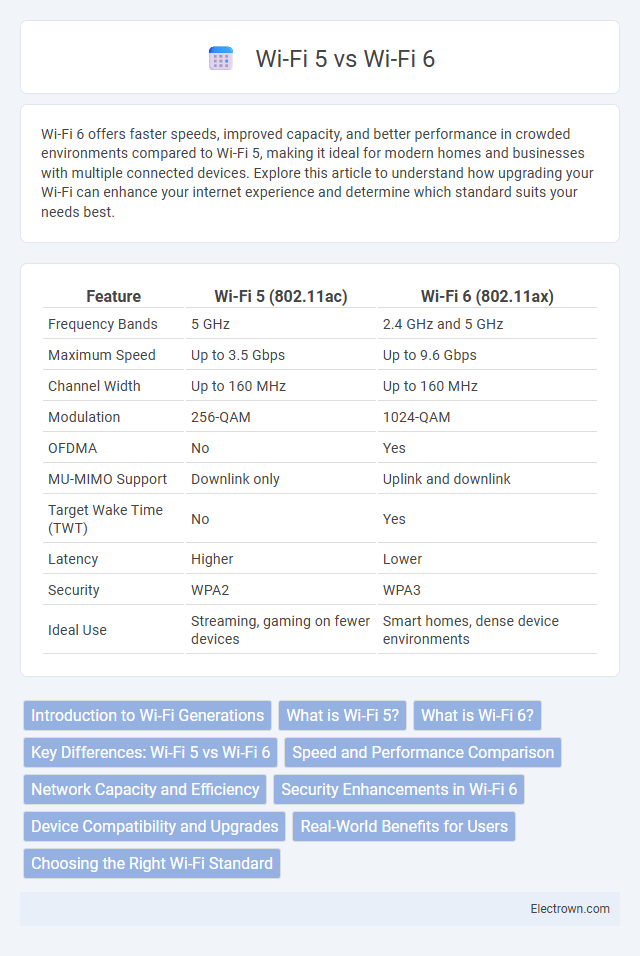
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) | Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Bands | 5 GHz | 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz |
| Maximum Speed | Up to 3.5 Gbps | Up to 9.6 Gbps |
| Channel Width | Up to 160 MHz | Up to 160 MHz |
| Modulation | 256-QAM | 1024-QAM |
| OFDMA | No | Yes |
| MU-MIMO Support | Downlink only | Uplink and downlink |
| Target Wake Time (TWT) | No | Yes |
| Latency | Higher | Lower |
| Security | WPA2 | WPA3 |
| Ideal Use | Streaming, gaming on fewer devices | Smart homes, dense device environments |
Introduction to Wi-Fi Generations
Wi-Fi 5, also known as 802.11ac, introduced significant improvements in speed and capacity compared to previous generations, supporting up to 3.5 Gbps and operating on the 5 GHz band. Wi-Fi 6, or 802.11ax, advances this further by enhancing throughput, reducing latency, and improving performance in crowded environments with speeds reaching up to 9.6 Gbps while utilizing both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands. Your network experience benefits from Wi-Fi 6's more efficient data management and increased device capacity, making it ideal for modern, connected households and offices.
What is Wi-Fi 5?
Wi-Fi 5, also known as 802.11ac, is a wireless networking standard that offers faster speeds and improved performance over its predecessor, Wi-Fi 4. It operates primarily in the 5 GHz band, providing higher data rates up to 3.5 Gbps, which enhances streaming, gaming, and large file transfers. Your devices connected to Wi-Fi 5 benefit from reduced interference and better handling of multiple simultaneous connections compared to earlier standards.
What is Wi-Fi 6?
Wi-Fi 6, also known as 802.11ax, is the latest generation of Wi-Fi technology designed to deliver faster speeds, increased capacity, and improved performance in crowded environments compared to Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac). It utilizes advanced technologies like OFDMA and MU-MIMO to enhance network efficiency and reduce latency, making it ideal for smart homes, offices, and IoT devices. Upgrading to Wi-Fi 6 can significantly improve your wireless experience by supporting more devices simultaneously without compromising speed or reliability.
Key Differences: Wi-Fi 5 vs Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 offers significant improvements over Wi-Fi 5, including faster speeds up to 9.6 Gbps compared to Wi-Fi 5's maximum of 3.5 Gbps, enhanced capacity to support more devices simultaneously through OFDMA technology, and improved energy efficiency with Target Wake Time (TWT). Wi-Fi 6 also provides better performance in congested environments, reducing latency and increasing reliability for your connected devices. These advancements make Wi-Fi 6 the preferred choice for high-density areas and smart home networks.
Speed and Performance Comparison
Wi-Fi 6 offers significantly faster speeds and better performance compared to Wi-Fi 5, with maximum theoretical speeds up to 9.6 Gbps versus Wi-Fi 5's 3.5 Gbps. Enhanced technologies like OFDMA and MU-MIMO in Wi-Fi 6 improve network efficiency and reduce latency, especially in environments with many connected devices. Your network experience will benefit from increased capacity, reduced congestion, and more consistent high-speed connections with Wi-Fi 6.
Network Capacity and Efficiency
Wi-Fi 6 significantly improves network capacity and efficiency by utilizing Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA), allowing multiple devices to share channels simultaneously, unlike Wi-Fi 5, which uses a less efficient method called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). Wi-Fi 6 supports up to 8 streams per user with MU-MIMO both uplink and downlink, enhancing performance in dense environments compared to Wi-Fi 5's limited multi-user capabilities. These advancements reduce latency and increase throughput, making Wi-Fi 6 ideal for congested networks and bandwidth-intensive applications.
Security Enhancements in Wi-Fi 6
Wi-Fi 6 introduces enhanced security protocols such as WPA3, which provides stronger encryption and improved protection against brute-force attacks compared to Wi-Fi 5's WPA2. This upgrade ensures Your network remains more secure against emerging cyber threats while supporting safer authentication methods. Enhanced security features in Wi-Fi 6 also improve data privacy and safeguard IoT devices connected to Your network.
Device Compatibility and Upgrades
Wi-Fi 5 devices are widely compatible with most modern routers, but they do not support the enhanced features of Wi-Fi 6, such as OFDMA and Improved MU-MIMO, which significantly boost network efficiency and performance. Upgrading to Wi-Fi 6 requires compatible devices and routers, but it provides backward compatibility, allowing Wi-Fi 5 devices to connect while benefiting from improved network management and reduced latency for Wi-Fi 6-capable devices. This upgrade enhances the overall wireless experience in dense environments with multiple connected devices.
Real-World Benefits for Users
Wi-Fi 6 delivers faster speeds and lower latency compared to Wi-Fi 5, enabling smoother streaming, gaming, and video conferencing in congested environments. Enhanced MU-MIMO and OFDMA technologies in Wi-Fi 6 improve capacity and efficiency, allowing multiple devices to connect simultaneously without performance degradation. These advancements result in more reliable connections and longer battery life for smartphones, laptops, and IoT devices in everyday use.
Choosing the Right Wi-Fi Standard
Choosing the right Wi-Fi standard depends on your device compatibility and network demands. Wi-Fi 6 offers faster speeds, increased capacity, and improved performance in congested environments compared to Wi-Fi 5, making it ideal for smart homes and multiple connected devices. Prioritize Wi-Fi 6 if you need enhanced security and future-proofing for your wireless network.
Wi-Fi 5 vs Wi-Fi 6 Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com