Micro USB ports are commonly found on older devices and offer slower data transfer speeds and limited power delivery compared to USB-C, which supports faster charging, higher data rates, and reversible plug orientation for easier use. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these differences impact your device compatibility and overall performance.
Table of Comparison
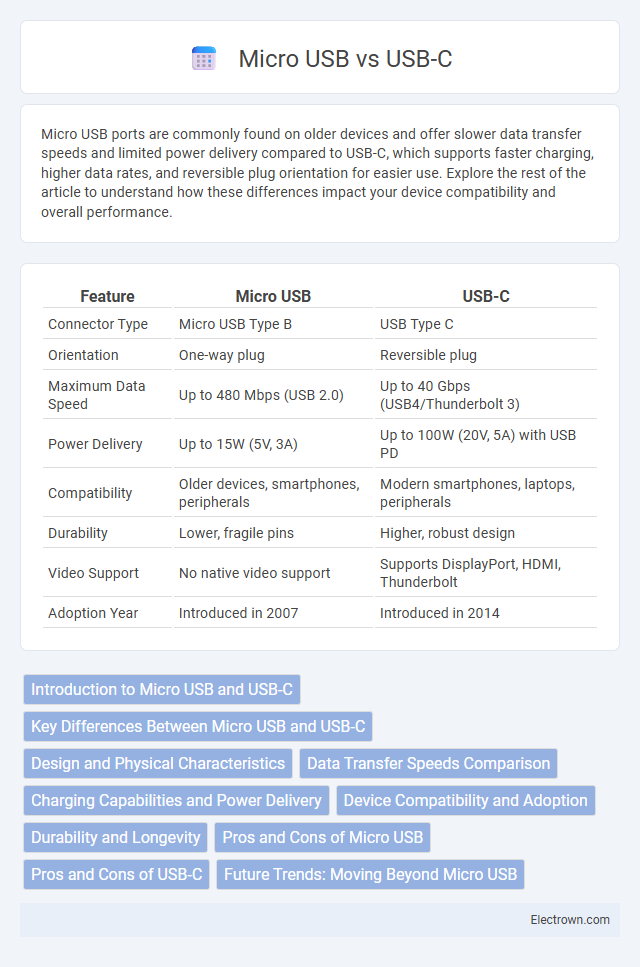
| Feature | Micro USB | USB-C |
|---|---|---|
| Connector Type | Micro USB Type B | USB Type C |
| Orientation | One-way plug | Reversible plug |
| Maximum Data Speed | Up to 480 Mbps (USB 2.0) | Up to 40 Gbps (USB4/Thunderbolt 3) |
| Power Delivery | Up to 15W (5V, 3A) | Up to 100W (20V, 5A) with USB PD |
| Compatibility | Older devices, smartphones, peripherals | Modern smartphones, laptops, peripherals |
| Durability | Lower, fragile pins | Higher, robust design |
| Video Support | No native video support | Supports DisplayPort, HDMI, Thunderbolt |
| Adoption Year | Introduced in 2007 | Introduced in 2014 |
Introduction to Micro USB and USB-C
Micro USB is a widely used connector standard for charging and data transfer in older smartphones, tablets, and other portable devices, characterized by its small, flat, and asymmetrical shape. USB-C, introduced to replace previous USB types, features a reversible, oval design that supports faster data transfer rates up to 10 Gbps, higher power delivery up to 100 watts, and improved versatility across devices including laptops, smartphones, and peripherals. The shift from Micro USB to USB-C enhances connectivity efficiency and device compatibility in modern electronic ecosystems.
Key Differences Between Micro USB and USB-C
Micro USB connectors have a smaller, asymmetrical design and support slower data transfer speeds up to 480 Mbps, while USB-C features a reversible, symmetrical design with faster data rates reaching 10 Gbps or higher and the ability to deliver more power for charging. USB-C offers enhanced compatibility with modern devices, supporting features like video output and faster charging protocols that Micro USB lacks. Understanding these key differences helps you choose the right cable for efficient connectivity and device compatibility.
Design and Physical Characteristics
Micro USB features a smaller, asymmetrical design with a tapered edge, making it less convenient to plug in due to its one-way orientation. USB-C offers a symmetrical, oval shape that is reversible, allowing you to connect your devices effortlessly without worrying about orientation. The USB-C design also supports higher durability and efficient data transfer compared to the more fragile Micro USB connectors.
Data Transfer Speeds Comparison
Micro USB supports data transfer speeds up to USB 2.0 standards at 480 Mbps, while USB-C often utilizes USB 3.1 or higher protocols, enabling speeds up to 10 Gbps or more. Your choice between Micro USB and USB-C impacts how quickly files, videos, and other data move between devices, especially for high-volume transfers. USB-C's advanced capabilities make it the superior option for faster, more efficient data transmission in modern electronics.
Charging Capabilities and Power Delivery
USB-C offers significantly higher charging capabilities and power delivery compared to Micro USB, supporting up to 100 watts with USB Power Delivery (PD) technology, ideal for fast charging laptops, smartphones, and other devices. Micro USB typically maxes out around 15 watts, making it suitable only for slower charging of older smartphones and accessories. Your devices will charge more efficiently and quickly with USB-C, benefiting from reversible connectors and enhanced power management protocols.
Device Compatibility and Adoption
Micro USB remains widely compatible with older devices such as smartphones, tablets, and peripherals released before 2015, making it a reliable choice for maintaining connections with legacy hardware. USB-C is rapidly adopted across newer devices including laptops, smartphones, and gaming consoles due to its reversible connector, higher power delivery, and faster data transfer speeds. You should consider USB-C for future-proofing and broader compatibility with modern technology ecosystems.
Durability and Longevity
USB-C connectors offer superior durability and longevity compared to Micro USB, with a robust design rated for approximately 10,000 connection cycles, whereas Micro USB typically supports around 1,500 to 5,000 cycles. The symmetrical and reversible shape of USB-C reduces wear and tear from incorrect plugging, enhancing its lifespan in everyday use. Choosing USB-C ensures your device maintains reliable charging and data transfer over an extended period, minimizing the need for frequent replacements.
Pros and Cons of Micro USB
Micro USB offers widespread compatibility with many older devices and chargers, making it a cost-effective option for users with legacy electronics. However, its slower data transfer speeds and limited power delivery capacity lag behind the capabilities of USB-C. The physical design of Micro USB is less durable and reversible compared to USB-C's symmetrical connector, leading to potential wear and user inconvenience.
Pros and Cons of USB-C
USB-C offers faster data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps and supports higher power delivery, enabling quicker device charging compared to Micro USB. Its reversible design improves user convenience by eliminating orientation issues during connection. However, USB-C cables and chargers are typically more expensive and not universally compatible with older devices relying on Micro USB ports.
Future Trends: Moving Beyond Micro USB
USB-C is rapidly replacing Micro USB due to its reversible design, faster data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps, and higher power delivery of up to 100 watts, supporting rapid charging and powering larger devices. Future trends emphasize broader adoption of USB-C in smartphones, laptops, and peripherals, driven by universal compatibility and regulatory mandates such as the EU's standardized charging port directive. Advances in USB4 and Power Delivery 3.1 protocols will further enhance USB-C's capabilities, reinforcing its position as the future standard beyond Micro USB.
Micro USB vs USB-C Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com