Fixed Priority Arbitration assigns priority levels to requests in a consistent manner, ensuring predictable access but potentially causing lower-priority tasks to experience starvation. Understanding the differences helps optimize your system's performance and fairness--continue reading to explore which method suits your needs best.
Table of Comparison
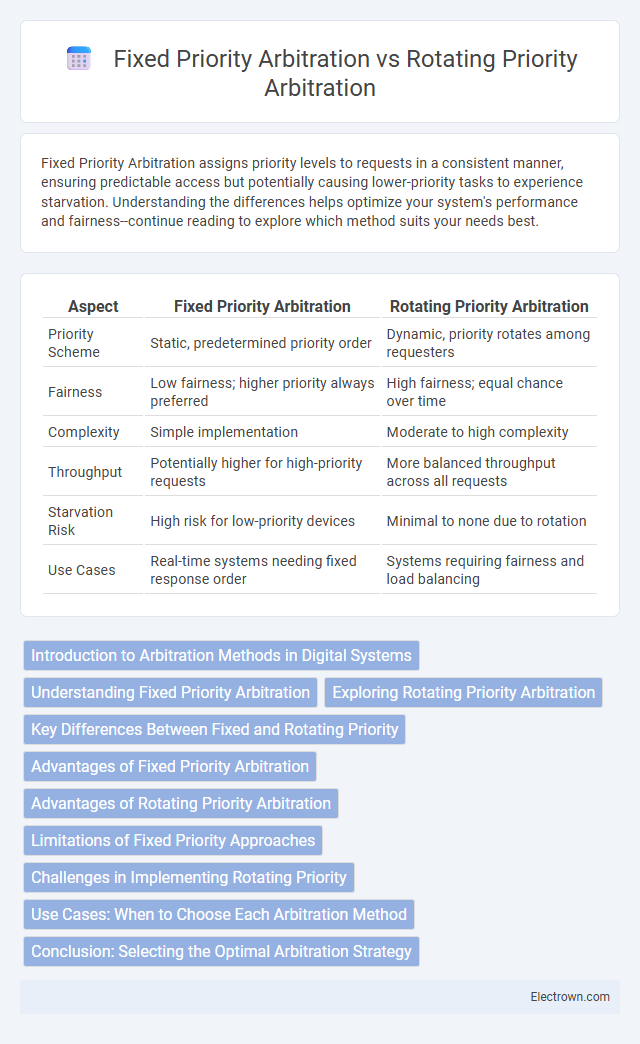
| Aspect | Fixed Priority Arbitration | Rotating Priority Arbitration |
|---|---|---|
| Priority Scheme | Static, predetermined priority order | Dynamic, priority rotates among requesters |
| Fairness | Low fairness; higher priority always preferred | High fairness; equal chance over time |
| Complexity | Simple implementation | Moderate to high complexity |
| Throughput | Potentially higher for high-priority requests | More balanced throughput across all requests |
| Starvation Risk | High risk for low-priority devices | Minimal to none due to rotation |
| Use Cases | Real-time systems needing fixed response order | Systems requiring fairness and load balancing |
Introduction to Arbitration Methods in Digital Systems
Fixed Priority Arbitration assigns a constant priority level to each device in digital systems, ensuring predictable and straightforward conflict resolution but risking lower-priority device starvation. Rotating Priority Arbitration cyclically changes device priorities, promoting fairness by distributing access opportunities more evenly across all devices. These arbitration methods are crucial in managing resource access in multiplexers, bus controllers, and shared communication channels, optimizing system performance and avoiding data collisions.
Understanding Fixed Priority Arbitration
Fixed Priority Arbitration assigns static priority levels to requests, ensuring that higher-priority signals are always granted access before lower-priority ones. This method simplifies decision-making and guarantees predictable response times but can lead to starvation of lower-priority requests under heavy load. Understanding Fixed Priority Arbitration helps you design systems that require consistent and deterministic access control without the complexity of dynamic prioritization.
Exploring Rotating Priority Arbitration
Rotating Priority Arbitration enhances fairness in resource allocation by dynamically changing the priority order among competing requests, preventing starvation of lower-priority agents. This method contrasts with Fixed Priority Arbitration, which always favors higher-priority requests, potentially causing indefinite delays for lower-priority ones. Implementing rotating priority schemes improves system responsiveness and balances access in multi-agent environments, especially in shared bus or memory arbitration contexts.
Key Differences Between Fixed and Rotating Priority
Fixed Priority Arbitration assigns a permanent priority order to requests, ensuring higher-priority signals are always granted access first, which can cause lower-priority requests to experience starvation. Rotating Priority Arbitration cycles the priority among requests in a round-robin fashion, promoting fairness and preventing any single request from being consistently delayed. Your system's performance and fairness requirements dictate which arbitration method optimally balances response time and equitable resource access.
Advantages of Fixed Priority Arbitration
Fixed Priority Arbitration offers predictable and consistent access to shared resources by assigning static priority levels, ensuring time-critical tasks receive immediate attention. This method minimizes latency for high-priority requests and simplifies hardware implementation, reducing design complexity and cost. Your system benefits from guaranteed response times, making it ideal for real-time applications where reliability and determinism are crucial.
Advantages of Rotating Priority Arbitration
Rotating Priority Arbitration offers fairer access to shared resources by preventing any single requester from monopolizing the system, which enhances overall system throughput. This method reduces starvation risks by cyclically adjusting priority levels, ensuring your requests are serviced over time. The dynamic allocation improves responsiveness and load balancing, particularly in complex, multi-requester environments.
Limitations of Fixed Priority Approaches
Fixed Priority Arbitration suffers from inherent limitations such as starvation, where lower-priority tasks may never get access to shared resources under heavy load conditions. This approach lacks fairness since higher-priority requests continuously preempt lower-priority ones, leading to potential system inefficiency. In contrast, Rotating Priority Arbitration enhances resource allocation fairness by cyclically adjusting priorities, mitigating the starvation problem found in fixed priority systems.
Challenges in Implementing Rotating Priority
Implementing rotating priority arbitration poses challenges such as increased complexity in hardware design to maintain a fair and dynamic priority scheme, which can lead to higher latency compared to fixed priority arbitration. Ensuring synchronization and preventing starvation requires sophisticated control logic and careful timing considerations. Your system might face trade-offs between fairness and real-time responsiveness when choosing rotating priority over fixed priority arbitration.
Use Cases: When to Choose Each Arbitration Method
Fixed Priority Arbitration is ideal for systems requiring deterministic response times, such as safety-critical embedded applications, where high-priority tasks must consistently preempt lower-priority ones to ensure reliability. Rotating Priority Arbitration suits fair resource sharing environments like time-shared processors or network routers, preventing starvation by cyclically adjusting priority levels. Your choice depends on whether predictable task precedence or equitable access is paramount for system performance and fairness.
Conclusion: Selecting the Optimal Arbitration Strategy
Fixed Priority Arbitration offers predictable latency by assigning static priority levels, ideal for systems with critical real-time requirements. Rotating Priority Arbitration ensures fairness by cyclically adjusting priorities, reducing starvation risks in multi-requester environments. Choosing the optimal arbitration strategy depends on balancing latency guarantees with fairness needs, where fixed priority suits deterministic tasks and rotating priority benefits dynamic or evenly distributed workloads.
Fixed Priority Arbitration vs Rotating Priority Arbitration Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com