A bus driver controls data flow and timing on a communication bus, ensuring signals reach the correct destination without conflict, while a bus transceiver facilitates bidirectional data transmission by enabling communication between devices on the bus. Understanding how these components interact can improve your grasp of electronic communication systems; read on to explore their roles and differences in detail.
Table of Comparison
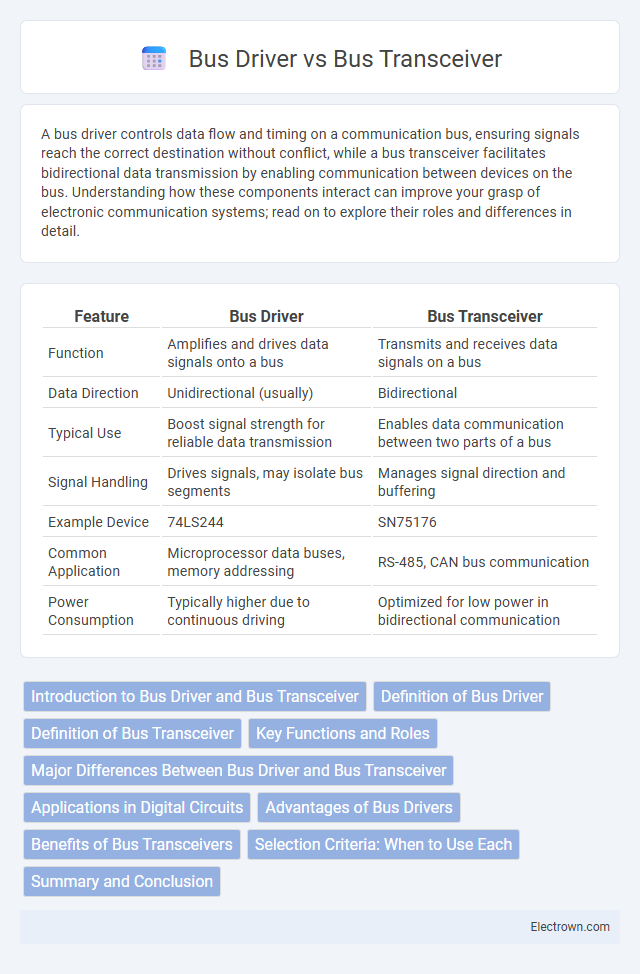
| Feature | Bus Driver | Bus Transceiver |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Amplifies and drives data signals onto a bus | Transmits and receives data signals on a bus |
| Data Direction | Unidirectional (usually) | Bidirectional |
| Typical Use | Boost signal strength for reliable data transmission | Enables data communication between two parts of a bus |
| Signal Handling | Drives signals, may isolate bus segments | Manages signal direction and buffering |
| Example Device | 74LS244 | SN75176 |
| Common Application | Microprocessor data buses, memory addressing | RS-485, CAN bus communication |
| Power Consumption | Typically higher due to continuous driving | Optimized for low power in bidirectional communication |
Introduction to Bus Driver and Bus Transceiver
A bus driver is an electronic component designed to control and amplify signals on a data bus, ensuring proper communication between multiple devices. A bus transceiver, on the other hand, functions as a bidirectional device that allows data to flow in both directions between different sections of the bus, facilitating efficient data exchange. Understanding the distinct roles of bus drivers and bus transceivers is essential for optimizing signal integrity and bus communication in digital circuits.
Definition of Bus Driver
A bus driver is an electronic device or circuit responsible for transmitting data signals from a microcontroller or processor to a communication bus, ensuring proper voltage levels and signal integrity for reliable data transfer. It acts as a source that drives the bus lines, enabling multiple devices to share the communication medium without signal degradation. In contrast, a bus transceiver facilitates bidirectional data flow by both driving and receiving signals on the bus, allowing devices to switch between sending and receiving modes.
Definition of Bus Transceiver
A bus transceiver is an electronic device that functions as a bidirectional data buffer, enabling communication between different parts of a digital system by controlling data flow on a shared bus. Unlike bus drivers, which are primarily used to drive signals in one direction, bus transceivers can transmit and receive signals, facilitating two-way data exchange. The primary role of a bus transceiver is to ensure proper signal integrity and synchronization when data is transferred between buses or peripherals.
Key Functions and Roles
Bus drivers manage data transmission by controlling the flow of signals between devices on a communication bus, ensuring accurate timing and synchronization for effective data transfer. Bus transceivers act as bidirectional interface components that facilitate signal conversion and amplification, enabling proper voltage levels and signal integrity between the bus and connected devices. Your system's performance depends on the coordinated operation of bus drivers and transceivers to maintain reliable and efficient communication.
Major Differences Between Bus Driver and Bus Transceiver
A bus driver is an integrated circuit responsible for controlling data flow and driving signals along a digital bus, ensuring proper voltage levels and timing for communication between components. In contrast, a bus transceiver facilitates bidirectional data transmission, allowing data to be sent and received on the bus while isolating components to prevent signal interference. Key differences include the bus driver's unidirectional control role versus the bus transceiver's ability to manage bidirectional data flow and signal direction switching.
Applications in Digital Circuits
Bus drivers amplify and buffer digital signals to ensure reliable communication across bus lines in digital circuits, especially where signal integrity and driving capability are critical. Bus transceivers facilitate bidirectional data flow on a shared bus, enabling efficient communication in systems requiring data transmission and reception, such as microcontroller interfaces or memory buses. Your choice depends on whether unidirectional drive or bidirectional communication is needed for optimal circuit performance.
Advantages of Bus Drivers
Bus drivers enhance signal integrity by providing strong drive capability and reducing signal degradation over long distances in data communication systems. They facilitate the effective management of multiple devices on a shared bus by isolating loading effects, which improves overall system reliability and performance. Their ability to boost signals ensures accurate data transmission and minimizes errors in complex bus architectures.
Benefits of Bus Transceivers
Bus transceivers offer enhanced bidirectional communication on data buses, improving signal integrity and reducing transmission errors compared to basic bus drivers. Their ability to manage direction control and enable multiple device interfacing boosts system efficiency and flexibility in complex circuits. You benefit from streamlined data flow and increased reliability in applications requiring robust communication protocols.
Selection Criteria: When to Use Each
Bus drivers are essential for controlling data flow in digital communication systems where signal integrity and timing are critical, especially in parallel bus architectures requiring precise synchronization. Bus transceivers are preferred in applications demanding bidirectional data transfer between two separate buses, such as in microprocessors with external memory interfaces or data buses needing isolation and direction control. Selecting between the two depends on system requirements: choose bus drivers for uni-directional, high-drive scenarios and bus transceivers for flexible, bidirectional data communication with isolation capabilities.
Summary and Conclusion
Bus drivers manage control signals and data flow within a system to ensure proper communication timing and coordination, while bus transceivers facilitate two-way data transmission between devices on a shared bus. The bus driver primarily handles driving signals to maintain signal integrity, whereas transceivers enable bidirectional data exchange by switching between sending and receiving modes. Understanding the distinct roles of bus drivers and transceivers is essential for designing efficient and reliable communication systems.
Bus Driver vs Bus Transceiver Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com