ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) performs fundamental arithmetic and logical operations essential to processor function, while CU (Control Unit) directs the operation of the processor by managing the execution of instructions and coordinating the activities of ALU and other components. Discover how understanding the differences between ALU and CU can enhance your grasp of computer architecture in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
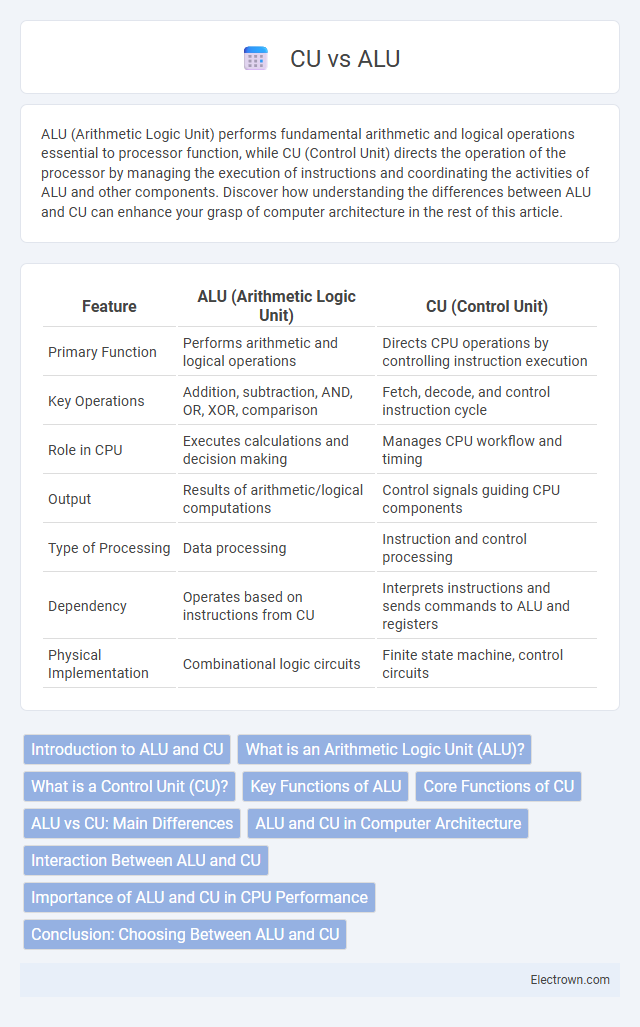
| Feature | ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) | CU (Control Unit) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Performs arithmetic and logical operations | Directs CPU operations by controlling instruction execution |
| Key Operations | Addition, subtraction, AND, OR, XOR, comparison | Fetch, decode, and control instruction cycle |
| Role in CPU | Executes calculations and decision making | Manages CPU workflow and timing |
| Output | Results of arithmetic/logical computations | Control signals guiding CPU components |
| Type of Processing | Data processing | Instruction and control processing |
| Dependency | Operates based on instructions from CU | Interprets instructions and sends commands to ALU and registers |
| Physical Implementation | Combinational logic circuits | Finite state machine, control circuits |
Introduction to ALU and CU
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) performs critical mathematical and logical operations within the CPU, handling tasks such as addition, subtraction, and comparison. The Control Unit (CU) directs the flow of data between the CPU, memory, and input/output devices by decoding instructions and generating control signals. Together, the ALU and CU form the core components of the central processing unit, enabling efficient data processing and execution of instructions.
What is an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)?
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) is a critical component of a computer's central processing unit (CPU) responsible for performing arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, as well as logical operations such as AND, OR, XOR, and NOT. It processes binary data inputs and generates results that are essential for executing instructions and enabling decision-making in computing systems. The ALU works closely with the Control Unit (CU), which directs its operations by decoding instructions and managing data flow within the CPU.
What is a Control Unit (CU)?
The Control Unit (CU) directs the operation of the processor by decoding instructions and managing the flow of data between the CPU, memory, and input/output devices. It generates control signals that orchestrate the execution of instructions by the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and other components. Unlike the ALU, which performs arithmetic and logical operations, the CU acts as the brain of the CPU, ensuring each instruction is carried out precisely and in sequence.
Key Functions of ALU
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) performs crucial operations such as arithmetic calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) and logical operations (AND, OR, NOT, XOR) essential for processing data. It handles binary integer operations and bitwise operations, enabling efficient decision-making and data manipulation within the CPU. Your computer's speed and ability to execute instructions heavily rely on the ALU's performance in these fundamental tasks.
Core Functions of CU
The Control Unit (CU) orchestrates the execution of instructions by directing the operation of the ALU, memory, and input/output devices within the CPU. It interprets instruction codes, generates control signals, and manages the flow of data between the processor and other components. Your computer relies on the CU to ensure organized and timely processing of tasks, enabling efficient overall system performance.
ALU vs CU: Main Differences
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) performs all arithmetic and logical operations within a CPU, such as addition, subtraction, and comparison, while the Control Unit (CU) directs the execution of instructions by managing the flow of data between the CPU and other components. The ALU processes data and executes mathematical and logical tasks, whereas the CU interprets program instructions and generates control signals to coordinate hardware activity. ALU's primary function is data manipulation, contrasting with CU's role in instruction decoding and controlling the timing of operations.
ALU and CU in Computer Architecture
In computer architecture, the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) performs core mathematical and logical operations essential for processing data, while the Control Unit (CU) directs the flow of instructions by interpreting and executing control signals. The ALU handles tasks such as addition, subtraction, and logical comparisons, directly impacting your computer's ability to perform calculations efficiently. The CU coordinates the operations of the ALU and other components, ensuring seamless execution of programs by managing instruction cycles and data paths.
Interaction Between ALU and CU
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) executes all arithmetic and logical operations while the Control Unit (CU) manages and coordinates the sequence of these operations by directing data flow and instruction execution within the CPU. Your processor relies on the CU to fetch, decode, and control instructions, signaling the ALU when specific calculations or logical decisions must occur. This seamless interaction ensures efficient processing and the correct execution of complex instructions.
Importance of ALU and CU in CPU Performance
The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) executes essential mathematical and logical operations that directly impact the speed and efficiency of data processing within the CPU. The Control Unit (CU) coordinates instruction decoding and orchestrates the flow of data between the ALU, registers, and memory, ensuring proper execution of programs. Your computer's overall performance hinges on the seamless interaction between the ALU's computation power and the CU's control precision.
Conclusion: Choosing Between ALU and CU
Choosing between an Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and a Control Unit (CU) depends on your system's computational and control needs. The ALU excels in performing arithmetic and logical operations essential for data processing, while the CU directs instruction execution and manages the flow of data within the CPU. For optimizing your processor design, prioritize the ALU for intensive calculations and select the CU to enhance overall system coordination and instruction management.
ALU vs CU Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com