ROM stores permanent data essential for your computer's startup, while RAM temporarily holds data your system actively uses for faster access and processing. To understand how these vital memory types impact your device's performance, continue reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
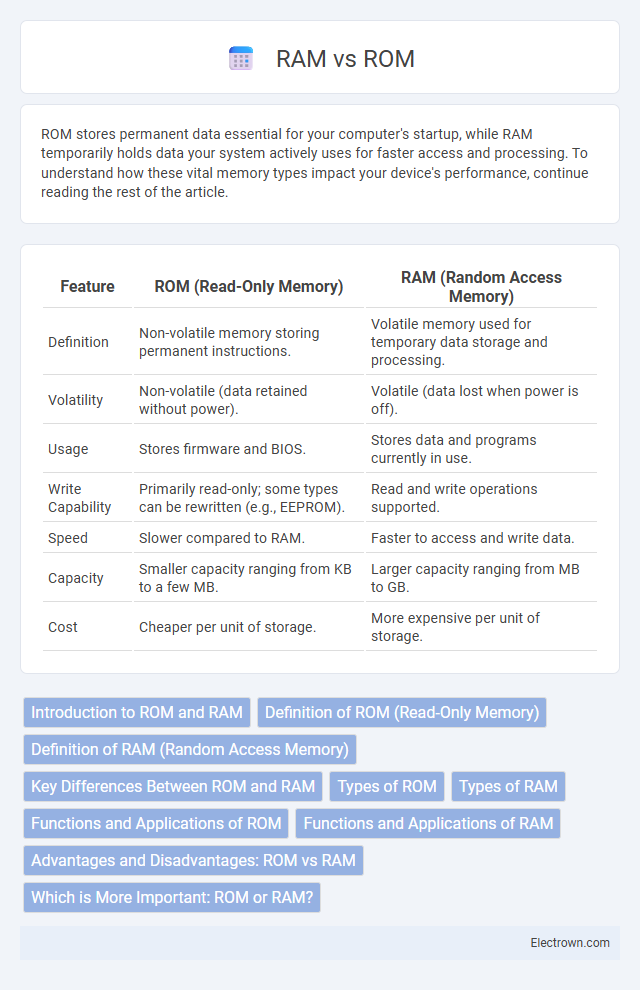
| Feature | ROM (Read-Only Memory) | RAM (Random Access Memory) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Non-volatile memory storing permanent instructions. | Volatile memory used for temporary data storage and processing. |
| Volatility | Non-volatile (data retained without power). | Volatile (data lost when power is off). |
| Usage | Stores firmware and BIOS. | Stores data and programs currently in use. |
| Write Capability | Primarily read-only; some types can be rewritten (e.g., EEPROM). | Read and write operations supported. |
| Speed | Slower compared to RAM. | Faster to access and write data. |
| Capacity | Smaller capacity ranging from KB to a few MB. | Larger capacity ranging from MB to GB. |
| Cost | Cheaper per unit of storage. | More expensive per unit of storage. |
Introduction to ROM and RAM
ROM (Read-Only Memory) is non-volatile storage that retains data even when the computer is powered off, primarily used for firmware and system boot processes. RAM (Random Access Memory) is volatile memory providing fast, temporary data access essential for running applications and processing tasks in real-time. Understanding the differences between ROM and RAM helps optimize Your device's performance and storage capabilities.
Definition of ROM (Read-Only Memory)
ROM (Read-Only Memory) is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers and electronic devices to store firmware or permanent software instructions essential for booting and hardware initialization. Unlike RAM (Random Access Memory), ROM retains data even when the device is powered off, ensuring reliable storage of critical system code. Common ROM types include PROM, EPROM, and EEPROM, each varying in reusability and data modification capabilities.
Definition of RAM (Random Access Memory)
RAM (Random Access Memory) is a type of volatile memory that stores data and machine code currently being used by the computer, enabling quick read and write access to improve processing speed and multitasking efficiency. Unlike ROM, which contains permanent instructions, RAM temporarily holds data your system needs to actively access and manipulate. This rapid access memory is essential for running applications smoothly and managing multiple tasks simultaneously on your device.
Key Differences Between ROM and RAM
ROM (Read-Only Memory) is non-volatile storage that retains data even when the power is off, primarily used to store firmware and system boot instructions. RAM (Random Access Memory) is volatile memory that temporarily holds data and programs currently in use for quick access by the CPU, significantly impacting system performance and multitasking capabilities. ROM is read-only and cannot be easily modified, whereas RAM is read-write and allows for constant updates during operation.
Types of ROM
Read-Only Memory (ROM) includes various types such as Mask ROM, Programmable ROM (PROM), Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM), and Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM), each differing in programmability and erasability. Mask ROM is pre-written during manufacturing and cannot be modified, while PROM allows one-time programming by the user. EPROM and EEPROM can be erased and reprogrammed, with EEPROM enabling electrical erasure and modification without removing the chip from the device.
Types of RAM
RAM (Random Access Memory) primarily includes Dynamic RAM (DRAM) and Static RAM (SRAM), with DRAM being the most common type used in computers due to its cost-effectiveness and higher density, while SRAM offers faster performance and is typically used for cache memory. Other types of RAM include Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), which synchronizes with the system clock for improved speed, and Double Data Rate SDRAM (DDR SDRAM), which doubles data transfer rates by transferring data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. Understanding these types helps you optimize system performance for specific applications and workloads.
Functions and Applications of ROM
ROM (Read-Only Memory) stores essential firmware and system software that remains intact even when your device is powered off, ensuring reliable boot-up and core operation. It is primarily used to hold the BIOS in computers, embedded system instructions, and firmware in appliances, providing permanent, non-volatile storage for critical functions. Unlike RAM, which is volatile and used for temporary data processing, ROM's function centers on maintaining fixed data required for hardware initialization and system stability.
Functions and Applications of RAM
RAM (Random Access Memory) is a volatile memory used to store data and instructions that a computer's processor needs in real time, enabling fast read and write access for active applications and processes. It plays a crucial role in system performance, supporting multitasking by temporarily holding operating system files, application programs, and currently processed data. RAM is essential in gaming, video editing, and running complex software, where rapid access to data significantly enhances user experience and system responsiveness.
Advantages and Disadvantages: ROM vs RAM
ROM provides permanent data storage essential for firmware, ensuring stability and security, but lacks flexibility since its content cannot be modified easily. RAM offers fast, volatile memory critical for running applications and multitasking, enhancing Your system's performance, yet it loses data when power is off. Choosing between ROM and RAM depends on whether You prioritize data permanence or speed and adaptability.
Which is More Important: ROM or RAM?
RAM is more important for your device's performance because it temporarily stores data and applications in active use, enabling faster processing and multitasking. ROM, on the other hand, contains essential firmware and system instructions that remain unchanged and are crucial for booting your device. While both serve vital roles, RAM's impact on speed and responsiveness often makes it the key factor in your device's overall efficiency.
ROM vs RAM Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com