Wired logic relies on programmable connections to perform operations, offering greater flexibility and adaptability in circuit design, while hardwired logic uses fixed connections and dedicated hardware paths for faster processing speeds and lower latency. Explore the rest of the article to understand how these differences impact your electronic system's performance and applications.
Table of Comparison
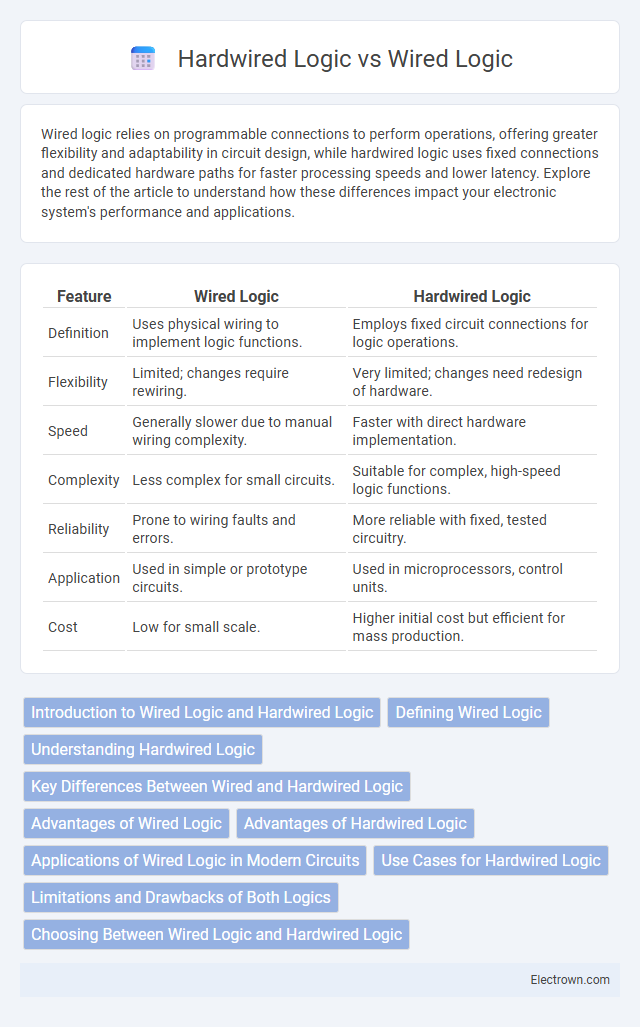
| Feature | Wired Logic | Hardwired Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses physical wiring to implement logic functions. | Employs fixed circuit connections for logic operations. |
| Flexibility | Limited; changes require rewiring. | Very limited; changes need redesign of hardware. |
| Speed | Generally slower due to manual wiring complexity. | Faster with direct hardware implementation. |
| Complexity | Less complex for small circuits. | Suitable for complex, high-speed logic functions. |
| Reliability | Prone to wiring faults and errors. | More reliable with fixed, tested circuitry. |
| Application | Used in simple or prototype circuits. | Used in microprocessors, control units. |
| Cost | Low for small scale. | Higher initial cost but efficient for mass production. |
Introduction to Wired Logic and Hardwired Logic
Wired logic relies on fixed physical connections using wiring to implement logical functions, making it simple but less flexible for complex operations. Hardwired logic uses dedicated hardware circuits designed to perform specific functions, offering faster execution and higher efficiency in digital systems. Both approaches differ fundamentally in design and application, where wired logic suits small-scale tasks and hardwired logic is optimized for speed and reliability in larger systems.
Defining Wired Logic
Wired Logic refers to the design approach where logic functions are implemented using physical wiring and hardware components, such as gates and switches, directly connected to perform specific tasks. Unlike Hardwired Logic, which relies on fixed, unchangeable circuitry, Wired Logic offers flexible interconnections that can be modified by altering the wiring scheme. Your understanding of Wired Logic is crucial for designing systems requiring customizable logic paths without the complexity of programmable devices.
Understanding Hardwired Logic
Hardwired logic uses fixed wiring connections and predefined circuit pathways to implement specific logical functions, providing fast and deterministic processing ideal for control systems. Unlike wired logic, which can be more flexible or reconfigurable, hardwired logic offers high reliability and low latency by eliminating the need for software interpretation. Your system's performance in real-time applications greatly benefits from the simplicity and stability inherent in hardwired logic designs.
Key Differences Between Wired and Hardwired Logic
Wired logic refers to logic circuits created through physical connections using wiring, allowing reconfigurability, while hardwired logic involves fixed, non-modifiable circuits etched or embedded into hardware. Key differences include flexibility, as wired logic can be easily altered or reconfigured for different functions, whereas hardwired logic offers faster operation and higher efficiency due to its permanent structure. Wired logic is commonly used in programmable devices like FPGAs, while hardwired logic is prevalent in application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) for optimized performance.
Advantages of Wired Logic
Wired logic offers faster processing speeds due to direct hardware connections, minimizing signal delay and improving overall system efficiency. It provides higher reliability and stability as it is less susceptible to software errors or bugs common in programmable systems. Your application benefits from reduced power consumption and enhanced performance in real-time processing environments with wired logic.
Advantages of Hardwired Logic
Hardwired logic offers advantages such as faster processing speeds due to direct electrical pathways and simpler control circuitry, making it ideal for time-critical applications. It consumes less power and provides increased reliability by minimizing the likelihood of logic errors from software bugs. Your system benefits from the efficiency and robustness of hardwired logic in environments requiring consistent and predictable performance.
Applications of Wired Logic in Modern Circuits
Wired logic finds significant applications in modern circuits, particularly in programmable logic devices such as PALs and PLAs, where customizable interconnections enable flexible logic functions. It is extensively used in embedded systems and microcontroller designs to implement specific combinational logic without the complexity of full gate-level programming. Wired logic's simplicity and efficiency make it ideal for low-power, high-speed applications where fixed logic paths optimize performance and reduce propagation delay.
Use Cases for Hardwired Logic
Hardwired logic is commonly used in applications requiring high-speed, deterministic performance, such as embedded systems, real-time processing, and hardware controllers. It excels in scenarios where tasks are fixed and predictable, like microprocessor control units and digital signal processors, where low latency and minimal power consumption are critical. This logic type supports efficient implementation of critical path functions in complex integrated circuits and custom ASIC designs.
Limitations and Drawbacks of Both Logics
Wired logic faces limitations such as inflexibility and difficulty in reprogramming since connections are physically fixed, leading to high costs and time-consuming modifications. Hardwired logic, while faster in operation due to dedicated pathways, suffers from complexity and scalability issues as increasing circuit size results in bulky and intricate designs. Both approaches lack adaptability, with wired logic being less efficient in handling dynamic tasks and hardwired logic constrained by irreversible hardware configurations.
Choosing Between Wired Logic and Hardwired Logic
Choosing between wired logic and hardwired logic depends on your project's complexity and flexibility needs. Wired logic offers easier modifications and scalability through configurable wiring, making it ideal for prototyping and variable applications, while hardwired logic provides faster performance and greater reliability due to its fixed circuit design. Evaluate your requirements for speed, adaptability, and cost to determine the most efficient logic implementation for your system.
Wired Logic vs Hardwired Logic Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com