MUX (Multiplexer) combines multiple input signals into a single output line, optimizing data transmission by reducing the number of required pathways. DEMUX (Demultiplexer) performs the reverse operation by distributing a single input signal to one of many output lines, making it essential for decoding data streams; explore the rest of the article to understand how these components can enhance Your communication systems.
Table of Comparison
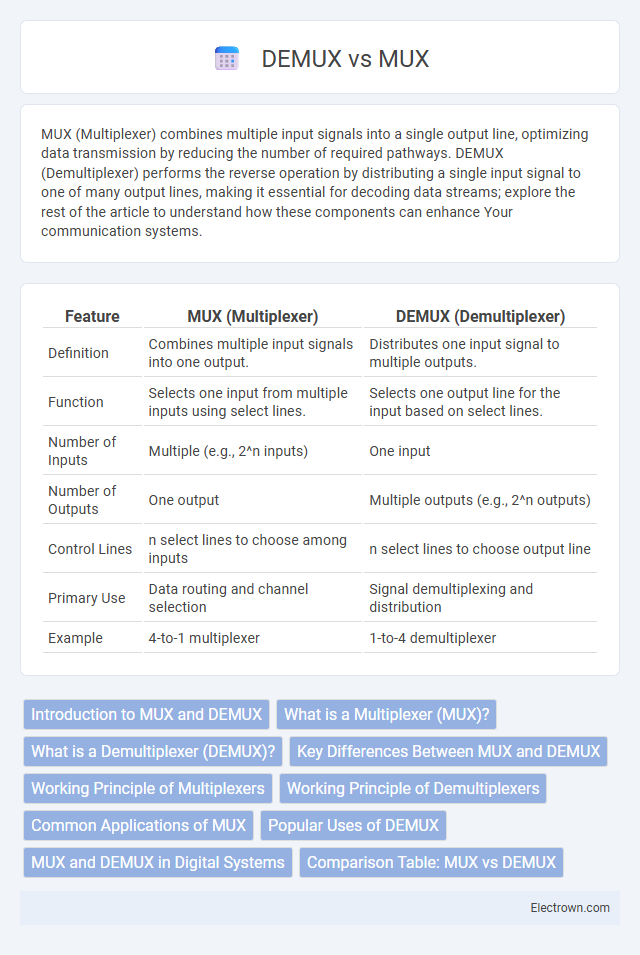
| Feature | MUX (Multiplexer) | DEMUX (Demultiplexer) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines multiple input signals into one output. | Distributes one input signal to multiple outputs. |
| Function | Selects one input from multiple inputs using select lines. | Selects one output line for the input based on select lines. |
| Number of Inputs | Multiple (e.g., 2^n inputs) | One input |
| Number of Outputs | One output | Multiple outputs (e.g., 2^n outputs) |
| Control Lines | n select lines to choose among inputs | n select lines to choose output line |
| Primary Use | Data routing and channel selection | Signal demultiplexing and distribution |
| Example | 4-to-1 multiplexer | 1-to-4 demultiplexer |
Introduction to MUX and DEMUX
A multiplexer (MUX) is a digital switch that selects one input from multiple inputs and forwards it to a single output line, optimizing channel usage and data routing in communication systems. A demultiplexer (DEMUX) performs the inverse function by taking a single input and distributing it to one of many output lines, used extensively in digital signal processing and data distribution. Both components are fundamental in circuit design for efficient data management and transmission.
What is a Multiplexer (MUX)?
A Multiplexer (MUX) is a digital switch that selects one input line from several data inputs and forwards it to a single output line, effectively reducing multiple signals into one. It plays a crucial role in communication systems and data routing by efficiently managing bandwidth and minimizing the number of physical connections. Understanding your MUX can optimize signal transmission by ensuring accurate data selection and transfer within electronic circuits.
What is a Demultiplexer (DEMUX)?
A Demultiplexer (DEMUX) is a digital circuit that takes a single input signal and routes it to one of several output lines based on select inputs, effectively performing the reverse operation of a multiplexer (MUX). DEMUX is essential in communication systems for data routing, enabling one data source to be distributed to multiple destinations. Common applications include digital signal processing, data distribution in memory systems, and channel selection in telecommunications.
Key Differences Between MUX and DEMUX
MUX (Multiplexer) selects one input from multiple inputs and forwards it to a single output line, optimizing data transmission by reducing the number of data lines needed. DEMUX (Demultiplexer) takes a single input signal and channels it to one of several output lines, effectively distributing data to multiple destinations. The key difference lies in their direction of data flow: MUX compresses multiple inputs into one output, while DEMUX expands one input into multiple outputs.
Working Principle of Multiplexers
Multiplexers (MUX) work by selecting one input line from multiple data inputs and forwarding it to a single output line based on control signals or select lines. The number of select lines determines how many inputs the multiplexer can handle, following the logic 2^n inputs for n select lines. Your digital system benefits from multiplexers by efficiently managing multiple data signals into one output pathway, simplifying circuit design and conserving resources.
Working Principle of Demultiplexers
Demultiplexers (DEMUX) operate by taking a single input signal and distributing it to one of many output lines based on select inputs, enabling efficient data routing within communication systems. The working principle involves using control signals to determine which output channel receives the input, effectively reversing the operation of a multiplexer (MUX). Understanding DEMUX functionality is essential for designing digital circuits that require signal separation and routing.
Common Applications of MUX
MUX devices are widely used in communication systems to combine multiple data signals into a single transmission line, optimizing bandwidth usage and reducing hardware complexity. Common applications include data routing in telecommunication networks, signal selection in digital circuits, and resource sharing in computer memory systems. Your ability to efficiently manage multiple inputs through a multiplexer enhances system performance and simplifies circuit design.
Popular Uses of DEMUX
DEMUX, or demultiplexer, is widely used in communication systems to route a single input signal to one of many output lines, making it essential for data distribution and signal processing. Its popular applications include digital circuit design, where it directs data from one source to multiple destinations, and memory management in computers to select storage locations. Your systems benefit from DEMUX implementation in scenarios like network switching and multiplexed signal decoding, enhancing efficient data handling.
MUX and DEMUX in Digital Systems
MUX and DEMUX are essential components in digital systems designed for data routing and signal management. A multiplexer (MUX) selects one input from multiple data lines and forwards it to a single output line, optimizing data transmission efficiency and reducing the number of required communication channels. Conversely, a demultiplexer (DEMUX) takes a single input and distributes it to one of many output lines, enabling precise data routing in communication and digital signal processing applications to enhance system performance.
Comparison Table: MUX vs DEMUX
A MUX (multiplexer) combines multiple input signals into a single output line, while a DEMUX (demultiplexer) takes one input signal and distributes it to multiple output lines. Key parameters in the comparison table include the number of inputs and outputs, control signals used, and primary function--MUX serves for data selection and routing, whereas DEMUX handles data distribution. Understanding these differences helps you design efficient digital circuits by selecting the appropriate device based on signal direction and application needs.
MUX vs DEMUX Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com