NAND and NOR gates are fundamental building blocks in digital circuits, with NAND implementing the NOT-AND function and NOR implementing the NOT-OR function, each playing a crucial role in logic design and optimization. Understanding the differences between these gates helps you choose the right type for efficient circuit performance; continue reading to explore their characteristics and applications in detail.
Table of Comparison
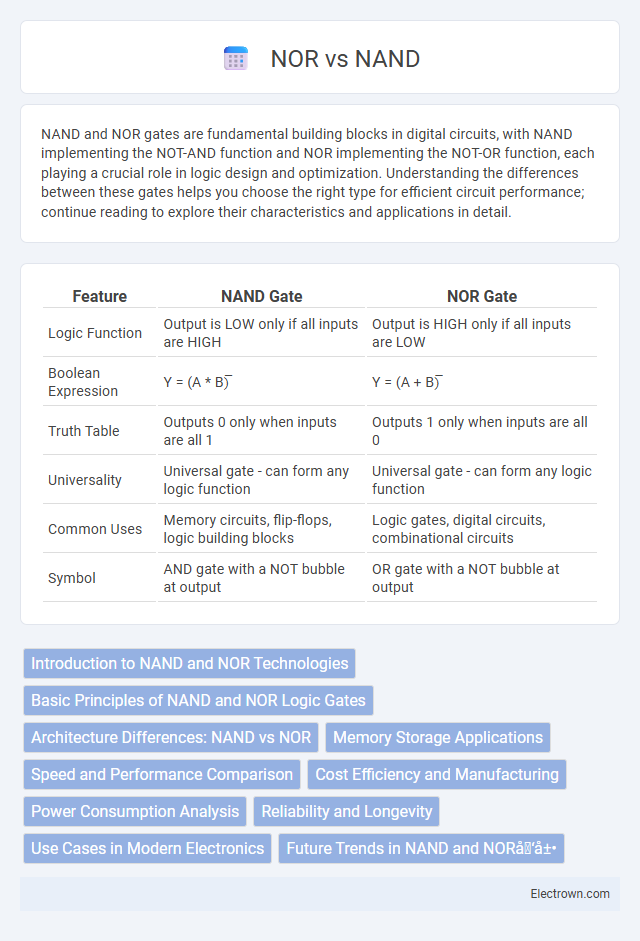
| Feature | NAND Gate | NOR Gate |
|---|---|---|
| Logic Function | Output is LOW only if all inputs are HIGH | Output is HIGH only if all inputs are LOW |
| Boolean Expression | Y = (A * B)̅ | Y = (A + B)̅ |
| Truth Table | Outputs 0 only when inputs are all 1 | Outputs 1 only when inputs are all 0 |
| Universality | Universal gate - can form any logic function | Universal gate - can form any logic function |
| Common Uses | Memory circuits, flip-flops, logic building blocks | Logic gates, digital circuits, combinational circuits |
| Symbol | AND gate with a NOT bubble at output | OR gate with a NOT bubble at output |
Introduction to NAND and NOR Technologies
NAND and NOR technologies are fundamental building blocks in digital logic circuits, characterized by their distinct gate structures and logic functions. NAND gates output a low signal only when all inputs are high, making them essential in creating programmable logic arrays and memory cells like flash memory. NOR gates produce a high output only when all inputs are low, commonly utilized in logic circuits requiring simple OR functionality combined with inversion, such as in combinational logic and certain types of latches.
Basic Principles of NAND and NOR Logic Gates
NAND and NOR gates are fundamental digital logic gates used to perform basic Boolean operations. A NAND gate outputs false only when all its inputs are true, implementing the negation of the AND function, while a NOR gate outputs true only when all its inputs are false, representing the negation of the OR function. These gates serve as universal gates since any Boolean function can be constructed exclusively using either NAND or NOR gates.
Architecture Differences: NAND vs NOR
NAND architecture features parallel-connected transistors in series, resulting in faster switching speeds and lower power consumption compared to NOR. NOR architecture consists of transistors connected in parallel, providing faster read times and better signal integrity but generally higher power usage and slower write speeds. These structural differences make NAND ideal for high-density storage applications, while NOR is preferred for read-intensive tasks requiring quick access.
Memory Storage Applications
NAND and NOR flash memory both play crucial roles in memory storage applications, with NAND being the preferred choice for high-density data storage due to its faster write and erase speeds and lower cost per bit. NOR flash memory excels in read-intensive tasks such as code execution in embedded systems, offering faster random access and better reliability for boot code storage. Your decision between NAND and NOR depends on whether you prioritize storage capacity and speed or fast, reliable read performance for code execution.
Speed and Performance Comparison
NAND gates typically offer faster switching speeds compared to NOR gates due to their simpler transistor configurations, resulting in lower propagation delays. In digital circuits, NAND gate-based designs often achieve higher performance and efficiency, particularly in CMOS technology where NAND gates exhibit reduced power consumption and improved speed. Your choice between NAND and NOR should consider these speed advantages to optimize overall circuit responsiveness and functionality.
Cost Efficiency and Manufacturing
NAND gates are more cost-efficient to manufacture due to their simpler design and higher density integration on silicon wafers, resulting in lower production costs compared to NOR gates. NAND technology benefits from widespread industry adoption, driving economies of scale and reducing expenses in large-scale manufacturing processes. Your choice between NAND and NOR should consider the balance of cost constraints and circuit requirements, as NAND typically offers superior cost efficiency.
Power Consumption Analysis
NAND gates typically consume less power than NOR gates due to their transistor configurations, which allow faster switching and lower static power dissipation. The difference in power consumption becomes more significant in high-speed and low-voltage circuits, where NAND gates enhance energy efficiency. Optimizing your design by selecting NAND over NOR can significantly reduce overall power usage, improving battery life in portable devices.
Reliability and Longevity
NAND flash memory typically offers higher reliability and longer lifespan compared to NOR flash due to its architecture optimized for frequent write and erase cycles, making it ideal for storage-intensive applications. NOR flash, while providing faster read speeds and better random access, tends to have lower endurance and shorter longevity, limiting its use in scenarios where durability is critical. Understanding these reliability differences helps you choose the most suitable flash memory type for your device's operational demands.
Use Cases in Modern Electronics
NAND gates serve as fundamental building blocks in digital memory storage such as SRAM and flash memory due to their high speed and reliability. NOR gates are predominantly used in digital logic circuits for implementing simple combinational functions and in microprocessor control logic because of their straightforward design and fast switching. Both gates are crucial in programmable logic arrays (PLAs) and field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) to create complex logic functions efficiently.
Future Trends in NAND and NOR发展
Future trends in NAND and NOR technologies emphasize increasing storage density and improved speed to meet growing data demands. NAND flash memory advances with 3D stacking and QLC (Quad-Level Cell) architectures, significantly enhancing capacity and cost-efficiency for SSDs and mobile devices. NOR flash continues evolving with faster read speeds and lower power consumption, making it ideal for code storage and embedded systems; your choice depends on balancing performance needs with cost and application requirements.
NAND vs NOR Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com