Hardwired control units use fixed logic circuits for instruction execution, offering faster operation but limited flexibility, while microprogrammed control units rely on programmable control memory for greater adaptability and easier updates. Explore the article to understand how these differences impact your computer system's performance and design choices.
Table of Comparison
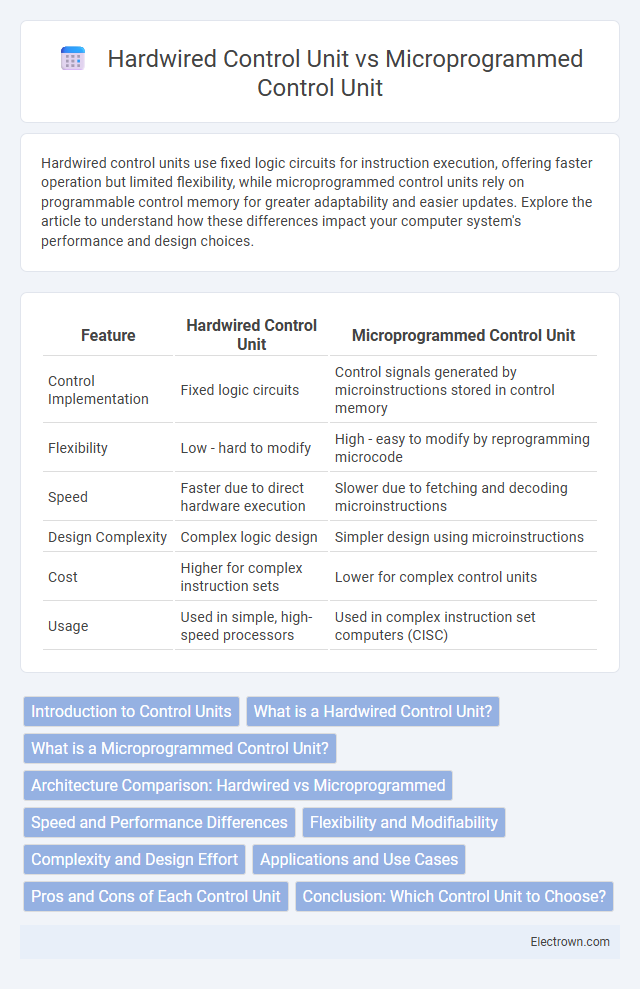
| Feature | Hardwired Control Unit | Microprogrammed Control Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Control Implementation | Fixed logic circuits | Control signals generated by microinstructions stored in control memory |
| Flexibility | Low - hard to modify | High - easy to modify by reprogramming microcode |
| Speed | Faster due to direct hardware execution | Slower due to fetching and decoding microinstructions |
| Design Complexity | Complex logic design | Simpler design using microinstructions |
| Cost | Higher for complex instruction sets | Lower for complex control units |
| Usage | Used in simple, high-speed processors | Used in complex instruction set computers (CISC) |
Introduction to Control Units
Control units manage the execution of instructions in a CPU by generating control signals. Hardwired control units use fixed logic circuits to produce these signals rapidly and efficiently, offering high speed and low instruction set flexibility. Microprogrammed control units store control signals in memory as microinstructions, enabling easier modification and support for complex instruction sets at the cost of slower execution.
What is a Hardwired Control Unit?
A Hardwired Control Unit is a digital circuit that generates control signals through fixed logic gates, flip-flops, and combinational circuits to manage the execution of instructions in a CPU. Its design enables faster instruction processing due to direct signal generation but lacks flexibility for modifications or complex instruction sets. Your system's performance depends on this unit's speed and efficiency, making it ideal for simple, high-speed applications.
What is a Microprogrammed Control Unit?
A microprogrammed control unit uses a set of stored microinstructions in control memory to generate control signals, enabling flexible and easily modifiable instruction execution. This design contrasts with a hardwired control unit, which relies on fixed logic circuits for control signal generation, offering faster but less adaptable operation. Microprogramming facilitates complex instruction sets and simplifies the implementation of new instructions or control sequences.
Architecture Comparison: Hardwired vs Microprogrammed
Hardwired control units utilize fixed logic circuits for control signal generation, offering faster instruction execution due to direct hardware implementation, while microprogrammed control units rely on a stored sequence of microinstructions in control memory, providing greater flexibility and easier modification. The architecture of a hardwired control unit is typically simpler and more compact but less adaptable to instruction set changes, whereas microprogrammed control units feature a control memory and a microinstruction decoder, enabling complex instruction sets and easier updates. Understanding these architectural differences helps you select the appropriate control unit design based on performance needs and system flexibility.
Speed and Performance Differences
Hardwired control units offer faster speed and higher performance due to their fixed, dedicated circuitry, enabling rapid instruction execution with minimal delay. Microprogrammed control units, while more flexible and easier to modify, typically experience slower operation because they rely on microinstruction sequencing stored in memory. Consequently, hardwired designs excel in applications demanding high-speed processing, whereas microprogrammed units prioritize adaptability and complexity management.
Flexibility and Modifiability
Hardwired control units offer fast and efficient instruction execution but lack flexibility and are difficult to modify once designed. In contrast, microprogrammed control units provide greater flexibility and ease of modification because control signals are generated by microinstructions stored in control memory, allowing quick updates or changes to the instruction set. Your choice between these control units depends on whether you prioritize speed or adaptability in your processor design.
Complexity and Design Effort
Hardwired control units feature simpler designs with faster execution due to fixed logic circuits but require significant expertise and effort to develop and modify, making them less flexible. Microprogrammed control units rely on a set of microinstructions stored in control memory, increasing initial design complexity yet offering easier updates and greater adaptability to instruction set changes. Your choice depends on balancing design effort against flexibility needs, with hardwired units favoring performance and microprogrammed units enhancing maintainability.
Applications and Use Cases
Hardwired control units are ideal for applications requiring high-speed processing and simple control logic, such as embedded systems in real-time devices and microcontrollers in automotive electronics. Microprogrammed control units excel in complex instruction set computing (CISC) architectures, making them suitable for general-purpose processors and systems needing easy updates or modifications, like desktop CPUs and sophisticated communication systems. Both control units find use in specialized domains where either rapid execution or flexible control logic adaptation is prioritized.
Pros and Cons of Each Control Unit
Hardwired control units offer faster instruction execution due to their fixed logic design, making them suitable for simple, high-speed applications but lack flexibility and are difficult to modify or expand. Microprogrammed control units provide greater flexibility and easier implementation of complex instructions through microinstructions stored in control memory, though they typically exhibit slower performance and require more hardware resources. Choosing between the two depends on balancing speed requirements and the need for adaptability in control logic design.
Conclusion: Which Control Unit to Choose?
Hardwired control units offer faster execution and lower hardware complexity, making them ideal for simple, performance-critical applications. Microprogrammed control units provide greater flexibility, easier debugging, and simpler design modifications, suitable for complex instruction sets and evolving architectures. Your choice depends on the specific requirements of speed, flexibility, and design scalability in your computing system.
Hardwired control unit vs microprogrammed control unit Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com