A Schmitt Trigger Inverter offers improved noise immunity and a clearer, more defined switching threshold compared to a Standard Inverter, which can result in better performance in noisy environments or with slowly changing input signals. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Your choice between these inverters impacts circuit stability and efficiency.
Table of Comparison
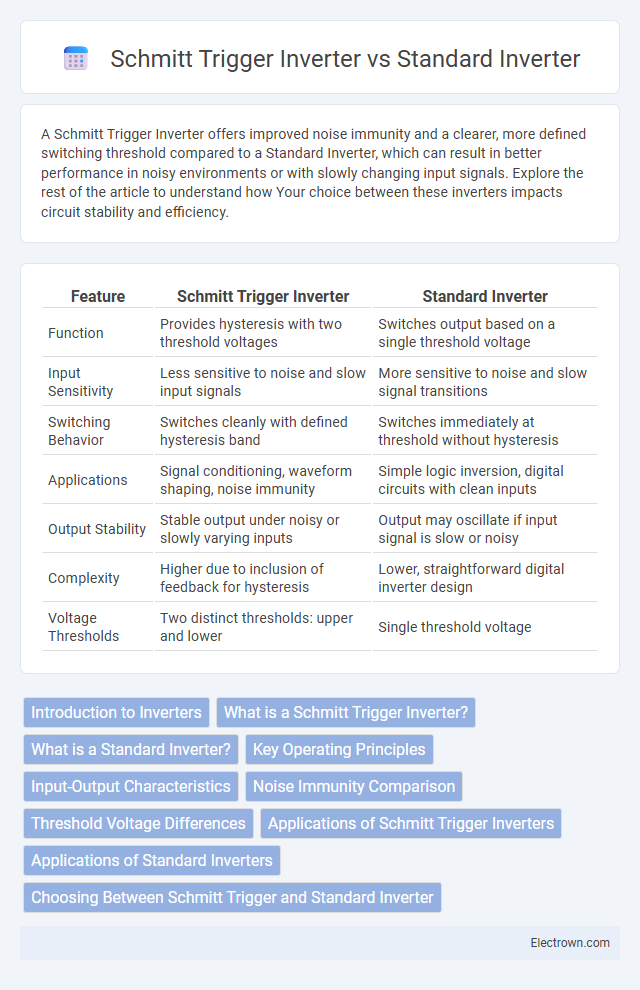
| Feature | Schmitt Trigger Inverter | Standard Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Provides hysteresis with two threshold voltages | Switches output based on a single threshold voltage |
| Input Sensitivity | Less sensitive to noise and slow input signals | More sensitive to noise and slow signal transitions |
| Switching Behavior | Switches cleanly with defined hysteresis band | Switches immediately at threshold without hysteresis |
| Applications | Signal conditioning, waveform shaping, noise immunity | Simple logic inversion, digital circuits with clean inputs |
| Output Stability | Stable output under noisy or slowly varying inputs | Output may oscillate if input signal is slow or noisy |
| Complexity | Higher due to inclusion of feedback for hysteresis | Lower, straightforward digital inverter design |
| Voltage Thresholds | Two distinct thresholds: upper and lower | Single threshold voltage |
Introduction to Inverters
Inverters convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) for powering various electronic devices. A Schmitt trigger inverter incorporates a hysteresis characteristic to improve noise immunity and provide cleaner, more stable switching compared to a standard inverter, which lacks hysteresis and can produce noisy, less reliable output signals. This makes Schmitt trigger inverters especially useful in digital circuits requiring precise signal transitions and reduced signal distortion.
What is a Schmitt Trigger Inverter?
A Schmitt Trigger Inverter is a digital logic circuit that incorporates hysteresis to provide noise immunity and a clean, stable output signal by converting a noisy input waveform into a well-defined square output. Unlike a Standard Inverter, which switches output states strictly based on a single threshold voltage, the Schmitt Trigger Inverter uses two distinct threshold voltage levels--upper and lower--to control transitions, preventing rapid toggling caused by input noise or slow signal changes. This characteristic makes Schmitt Trigger Inverters ideal for applications involving analog signals or noisy environments where precise and stable digital output is critical.
What is a Standard Inverter?
A Standard Inverter converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) with a straightforward output waveform, often a square or modified sine wave. It is commonly used in applications requiring basic AC power conversion but may suffer from noise and signal distortion. Your choice between a standard inverter and a Schmitt Trigger Inverter depends on the need for signal stability and noise immunity.
Key Operating Principles
A Schmitt Trigger Inverter operates with a hysteresis effect, featuring two distinct threshold voltage levels for switching, which enhances noise immunity and stabilizes the output signal in the presence of slow or noisy input transitions. Standard Inverters switch output states precisely at a single threshold voltage, making them more susceptible to noise and fluctuating input signals. The key operating principle difference lies in the Schmitt Trigger's use of positive feedback to create a clean, noise-resistant transition compared to the standard inverter's single-threshold-switching behavior.
Input-Output Characteristics
The Schmitt Trigger Inverter features a distinct hysteresis curve in its input-output characteristics, producing two switching thresholds that mitigate noise and ensure stable transitions between logic states. In contrast, a Standard Inverter exhibits a single threshold voltage without hysteresis, making it more susceptible to input noise and signal fluctuations near the switching point. The Schmitt Trigger's dual-threshold operation enhances noise immunity and signal integrity in digital circuits compared to the Standard Inverter's simpler, noise-sensitive input-output response.
Noise Immunity Comparison
Schmitt Trigger Inverters exhibit superior noise immunity compared to Standard Inverters due to their hysteresis characteristic, which allows them to ignore small fluctuations in input voltage and prevent false switching. This enhanced noise rejection is crucial in environments with electrical noise, ensuring more stable and reliable signal processing in your digital circuits. The distinct threshold voltages in Schmitt Triggers reduce susceptibility to glitches, making them ideal for applications requiring robust noise tolerance.
Threshold Voltage Differences
Schmitt Trigger inverters exhibit hysteresis with two distinct threshold voltages--an upper threshold (V_UT) and a lower threshold (V_LT)--which improves noise immunity and signal stability by preventing rapid switching near the threshold region. Standard inverters have a single, fixed threshold voltage (V_T) where the output transitions, making them more susceptible to noise-induced oscillations. The dual threshold nature of Schmitt Trigger inverters ensures cleaner signal propagation in noisy environments compared to the single threshold operation of standard inverters.
Applications of Schmitt Trigger Inverters
Schmitt Trigger Inverters are widely used in signal conditioning applications where noise immunity and clean switching are crucial, such as waveform shaping, oscillator circuits, and debounce circuits for mechanical switches. They excel in digital circuits that require precise threshold detection and hysteresis to prevent false triggering in noisy environments. Unlike standard inverters, Schmitt Trigger Inverters stabilize input transitions, making them ideal for use in sensors, pulse generators, and timing circuits.
Applications of Standard Inverters
Standard inverters are widely used in applications requiring simple signal inversion without noise immunity, such as basic logic circuits, signal processing, and waveform generation. They are suitable for systems where input signals are clean and do not require hysteresis to prevent output oscillations. Your choice of a standard inverter is ideal for cost-sensitive projects prioritizing straightforward voltage level shifting without the complexity of Schmitt trigger functionality.
Choosing Between Schmitt Trigger and Standard Inverter
Choosing between a Schmitt Trigger inverter and a standard inverter depends on the specific application requirements such as noise immunity, switching speed, and signal stability. Schmitt Trigger inverters offer hysteresis, making them ideal for noisy environments and slow or noisy input signals by preventing false triggering and providing a clean digital output. Standard inverters are suitable for high-speed switching where input signals are clean and well-defined, typically found in digital logic circuits without significant noise interference.
Schmitt Trigger Inverter vs Standard Inverter Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com