T flip-flops toggle their output on each clock pulse, making them ideal for counting applications, while SR flip-flops set or reset the output based on input signals, suitable for simple memory storage. Explore the differences in functionality and use cases to enhance Your understanding of flip-flop types in digital circuits.
Table of Comparison
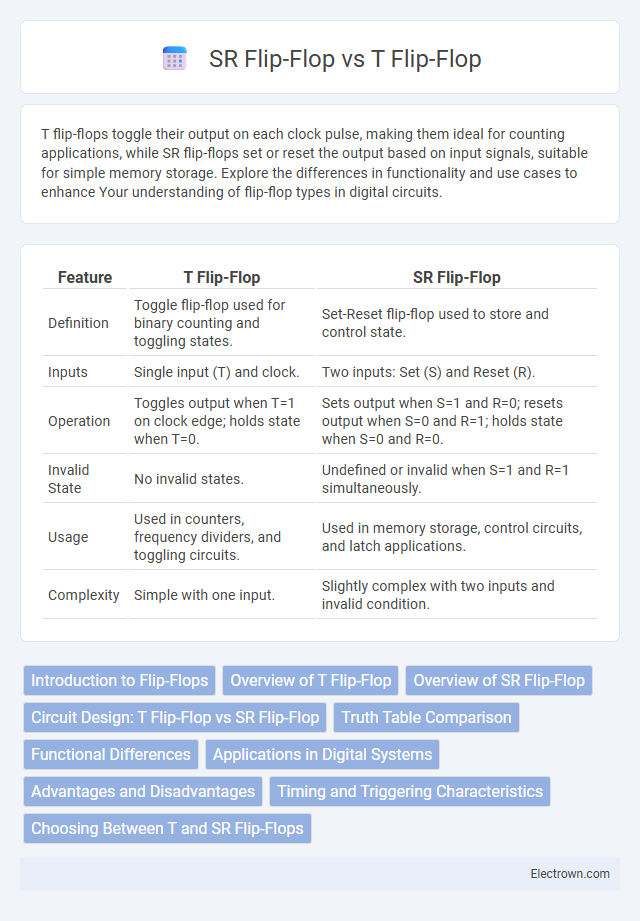
| Feature | T Flip-Flop | SR Flip-Flop |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Toggle flip-flop used for binary counting and toggling states. | Set-Reset flip-flop used to store and control state. |
| Inputs | Single input (T) and clock. | Two inputs: Set (S) and Reset (R). |
| Operation | Toggles output when T=1 on clock edge; holds state when T=0. | Sets output when S=1 and R=0; resets output when S=0 and R=1; holds state when S=0 and R=0. |
| Invalid State | No invalid states. | Undefined or invalid when S=1 and R=1 simultaneously. |
| Usage | Used in counters, frequency dividers, and toggling circuits. | Used in memory storage, control circuits, and latch applications. |
| Complexity | Simple with one input. | Slightly complex with two inputs and invalid condition. |
Introduction to Flip-Flops
Flip-flops are fundamental bistable devices used in digital circuits for storing binary information, essential in sequential logic systems. The T flip-flop toggles its output state with each clock pulse when the input is high, making it suitable for counters and toggling applications. The SR flip-flop uses Set (S) and Reset (R) inputs to control its output, allowing direct setting or clearing of the stored bit, widely employed in memory storage and control circuits.
Overview of T Flip-Flop
The T flip-flop, or toggle flip-flop, changes its output state on every clock pulse if the T input is high, making it ideal for counting applications and binary division. Unlike the SR flip-flop, which uses Set and Reset inputs for direct state control, the T flip-flop simplifies design by using a single input to toggle between states. Its characteristic equation Q(next) = T XOR Q(current) highlights its utility in sequential logic circuits and frequency division tasks.
Overview of SR Flip-Flop
The SR flip-flop, or Set-Reset flip-flop, is a fundamental bistable circuit used for storing binary information by toggling between two stable states based on its S (set) and R (reset) inputs. It operates by setting the output Q to 1 when the S input is activated and resetting Q to 0 when the R input is triggered, with the state retained until an input change occurs. This flip-flop is widely used in storage registers, memory devices, and digital logic circuits for basic state holding and switching functions.
Circuit Design: T Flip-Flop vs SR Flip-Flop
The T flip-flop circuit design features a single input toggling its output state on each clock pulse, making it simpler and more efficient for binary counting applications. In contrast, the SR flip-flop utilizes two inputs, Set (S) and Reset (R), which require careful handling to avoid invalid states and provide direct control of the output. Your choice between these depends on the desired complexity and functionality within sequential logic circuits.
Truth Table Comparison
The T flip-flop toggles its output state when the input T is high, as shown in its truth table: T = 0 maintains the current state (Qn+1 = Qn), while T = 1 inverts it (Qn+1 = Qn'). In contrast, the SR flip-flop's truth table includes Set (S) and Reset (R) inputs, where S = 1 and R = 0 sets the output to high, S = 0 and R = 1 resets it to low, and S = R = 0 retains the previous state; the combination S = R = 1 is typically undefined. Understanding these differences in truth tables helps you select the appropriate flip-flop for toggling or setting/resetting operations in sequential logic circuits.
Functional Differences
T flip-flops toggle their output state with each clock pulse when the T input is high, making them ideal for counters and frequency dividers. SR flip-flops have separate Set and Reset inputs, allowing explicit control to set or reset the output, useful for memory storage and control circuits. Your choice between these depends on whether toggling or definitive state setting is required in the application.
Applications in Digital Systems
T flip-flops are widely used in digital counters and toggle operations due to their ability to change state on each clock pulse, making them ideal for frequency division and state machine design. SR flip-flops find applications in simple storage elements and as basic memory units for setting and resetting binary states in asynchronous control circuits. Both flip-flop types are fundamental in designing sequential logic circuits, but T flip-flops excel in timing and counting applications, while SR flip-flops are preferred for direct state control and latch implementations.
Advantages and Disadvantages
T flip-flops offer simplicity in toggling operations, making them ideal for counters and frequency dividers, while SR flip-flops provide more control with separate set and reset inputs, useful in memory storage applications. However, T flip-flops lack direct control over individual set or reset states, limiting their flexibility compared to SR flip-flops which can face invalid states when both inputs are active simultaneously. The choice depends on the required application, where T flip-flops excel in sequential logic but SR flip-flops are preferred for precise state control despite potential instability.
Timing and Triggering Characteristics
T flip-flops toggle their output on each clock pulse, making their timing closely tied to the clock's rising or falling edge, ensuring precise synchronization in sequential circuits. SR flip-flops respond immediately to changes in the Set and Reset inputs, exhibiting asynchronous behavior that can cause unpredictable timing if inputs change near clock edges. The edge-triggered nature of T flip-flops provides more stable and controlled timing characteristics compared to the level-sensitive and potentially metastable states of SR flip-flops.
Choosing Between T and SR Flip-Flops
Choosing between T and SR flip-flops depends on your circuit requirements and functionality. T flip-flops simplify toggling operations with a single input, making them ideal for counters and frequency dividers, while SR flip-flops offer more control with separate set and reset inputs, useful in level-sensitive storage and memory applications. Understanding your design's need for either toggle behavior or explicit set/reset control will guide you in selecting the most efficient flip-flop.
T flip-flop vs SR flip-flop Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com