A 7-segment decoder directly converts binary input into signals that light up specific segments on a 7-segment display to show numbers, while a BCD to decimal decoder translates Binary-Coded Decimal inputs into one of ten outputs representing the decimal digits 0-9. Understanding the differences between these decoders can enhance your knowledge of digital display systems, so continue reading to explore their functionalities and applications in detail.
Table of Comparison
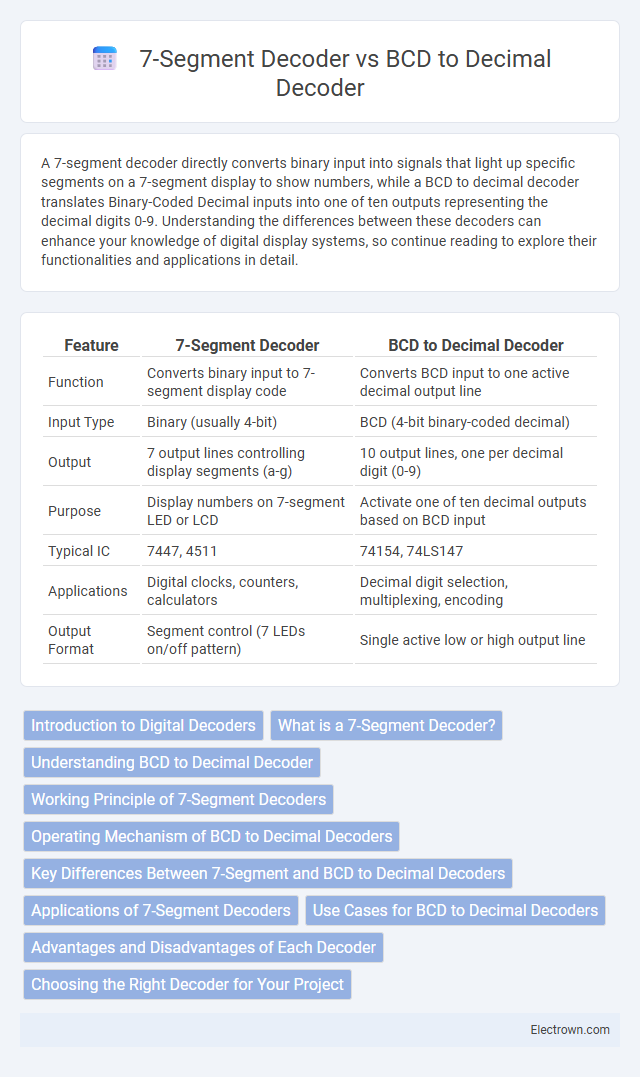
| Feature | 7-Segment Decoder | BCD to Decimal Decoder |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts binary input to 7-segment display code | Converts BCD input to one active decimal output line |
| Input Type | Binary (usually 4-bit) | BCD (4-bit binary-coded decimal) |
| Output | 7 output lines controlling display segments (a-g) | 10 output lines, one per decimal digit (0-9) |
| Purpose | Display numbers on 7-segment LED or LCD | Activate one of ten decimal outputs based on BCD input |
| Typical IC | 7447, 4511 | 74154, 74LS147 |
| Applications | Digital clocks, counters, calculators | Decimal digit selection, multiplexing, encoding |
| Output Format | Segment control (7 LEDs on/off pattern) | Single active low or high output line |
Introduction to Digital Decoders
Digital decoders convert coded inputs into a set of outputs, enabling interpretable numerical displays and system controls. A 7-segment decoder specifically translates binary-coded decimal (BCD) inputs into signals that drive LED segments to form decimal digits on a 7-segment display. In contrast, a BCD to decimal decoder converts BCD input into a one-hot output, activating only a single output line corresponding to the decimal digit, making it suitable for applications like display drivers and binary-to-decimal conversion circuits.
What is a 7-Segment Decoder?
A 7-segment decoder is a digital circuit that converts binary-coded inputs into signals that control a 7-segment display, enabling the visual representation of decimal digits from 0 to 9. It receives a 4-bit binary input and activates specific segments in the display to form the corresponding numeral. Unlike a BCD to decimal decoder, which outputs a single active line for each digit, the 7-segment decoder directly drives the display segments for numeric visualization.
Understanding BCD to Decimal Decoder
A BCD to Decimal Decoder converts Binary-Coded Decimal inputs into a one-out-of-ten output, activating a single line corresponding to the decimal digit. It simplifies digital circuits by translating 4-bit BCD inputs into decimal form, enabling devices like digital displays and keypads to interpret binary numbers correctly. Understanding this decoder is crucial for designing systems that require accurate decimal representation from BCD-coded data.
Working Principle of 7-Segment Decoders
A 7-segment decoder converts binary-coded decimal (BCD) inputs into signals that illuminate the appropriate segments of a 7-segment display to represent decimal digits accurately. Its working principle involves interpreting 4-bit BCD inputs and activating specific combinations of the seven LED segments to display numbers from 0 to 9 clearly. Understanding this process helps you effectively interface digital systems with visual numeric displays for precise data representation.
Operating Mechanism of BCD to Decimal Decoders
BCD to decimal decoders operate by translating binary-coded decimal inputs into a single active output line corresponding to the decimal digit represented, enabling clear numerical display interpretation. These decoders employ combinational logic circuits such as AND, OR, and NOT gates to accurately convert 4-bit BCD inputs into 10 unique output signals. The mechanism enhances digital systems by simplifying the interface between binary data and human-readable decimal displays, crucial in applications like digital clocks and calculators.
Key Differences Between 7-Segment and BCD to Decimal Decoders
7-segment decoders convert binary inputs directly into signals that drive a 7-segment display for numeric representation, while BCD to decimal decoders translate a 4-bit binary-coded decimal input into one of ten outputs corresponding to decimal digits 0-9. The 7-segment decoder controls LED segments individually to form digits, whereas the BCD to decimal decoder activates a single output line for each decimal digit, often used for driving other types of display or control circuits. Key differences lie in output format--segment activation versus decimal line selection--and application focus, with 7-segment decoders tailored for visual digit displays and BCD to decimal decoders optimized for digital logic interfacing.
Applications of 7-Segment Decoders
7-segment decoders are primarily used in digital clocks, electronic meters, and basic display systems to translate binary-coded inputs into corresponding illuminated segments, enabling clear numerical output. They simplify the interface between microcontrollers and LED or LCD display units, ensuring efficient and accurate visual representation of digits. Unlike BCD to decimal decoders, which focus on converting binary-coded decimal signals into seven discrete outputs, 7-segment decoders directly drive the segments to form numbers and some alphabets for user-readable electronics.
Use Cases for BCD to Decimal Decoders
BCD to decimal decoders are primarily used in digital display systems to convert binary-coded decimal input into its corresponding decimal output, enabling easy interfacing with seven-segment displays and other numerical indicators. They are essential in applications like electronic calculators, digital clocks, and measurement devices where numerical data visualization is crucial. Their precise conversion capability simplifies circuit design by directly driving decimal output devices from BCD-coded inputs without additional processing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Decoder
7-segment decoders simplify display driving by directly converting binary inputs into seven-segment signals, making them ideal for simple numeric displays but limited to basic digit representation. BCD to decimal decoders provide precise binary-coded decimal inputs translating into individual decimal outputs, offering greater accuracy for digital systems but requiring more complex wiring and increased hardware size. While 7-segment decoders excel in compactness and ease of use, BCD to decimal decoders offer enhanced functionality at the cost of circuit complexity and space.
Choosing the Right Decoder for Your Project
Choosing the right decoder for your project involves understanding the specific functions of a 7-segment decoder versus a BCD to decimal decoder. A 7-segment decoder converts binary-coded decimal input into signals that directly drive a 7-segment display, ideal for visual numeric output, while a BCD to decimal decoder converts BCD input into a one-hot decimal output, perfect for applications requiring individual decimal line activation. Your selection should depend on whether you need to control a display or activate separate digital circuits to optimize performance and functionality.
7-Segment Decoder vs BCD to Decimal Decoder Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com