Dual-core MCUs offer enhanced processing power and multitasking capabilities by distributing workloads between two cores, improving real-time performance and energy efficiency compared to single-core MCUs. Explore the rest of the article to understand how choosing the right MCU can optimize Your embedded system's performance.
Table of Comparison
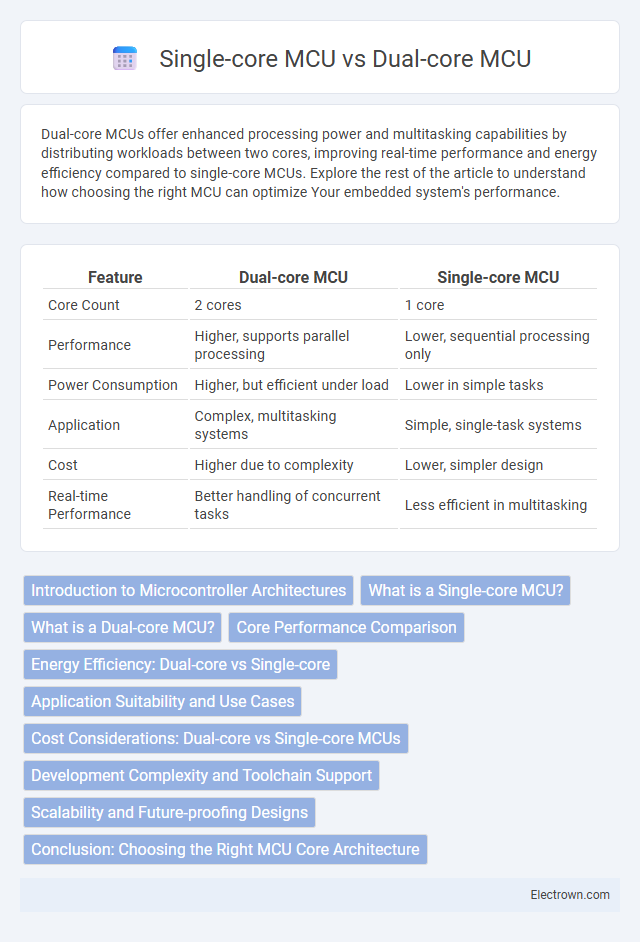
| Feature | Dual-core MCU | Single-core MCU |
|---|---|---|
| Core Count | 2 cores | 1 core |
| Performance | Higher, supports parallel processing | Lower, sequential processing only |
| Power Consumption | Higher, but efficient under load | Lower in simple tasks |
| Application | Complex, multitasking systems | Simple, single-task systems |
| Cost | Higher due to complexity | Lower, simpler design |
| Real-time Performance | Better handling of concurrent tasks | Less efficient in multitasking |
Introduction to Microcontroller Architectures
Dual-core MCUs feature two processing units enabling simultaneous task execution, enhancing performance and efficiency compared to single-core MCUs, which rely on one processor handling tasks sequentially. Your application demands and real-time processing requirements determine the optimal microcontroller architecture, as dual-core MCUs excel in multitasking and complex computations while single-core MCUs offer simplicity and lower power consumption. Advances in dual-core MCU architectures integrate shared memory and inter-core communication to streamline parallel processing and improve overall system responsiveness.
What is a Single-core MCU?
A Single-core MCU (Microcontroller Unit) integrates one central processing unit (CPU) core, executing instructions sequentially and managing tasks independently. It offers simpler architecture, lower power consumption, and cost-effectiveness ideal for basic embedded applications. Single-core MCUs are widely used in devices requiring straightforward control and limited processing capabilities, such as home appliances and sensor monitoring systems.
What is a Dual-core MCU?
A Dual-core MCU features two independent processing cores within a single microcontroller unit, enabling parallel processing and improved multitasking capabilities. This architecture enhances performance by allowing simultaneous execution of different tasks or threads, which is critical in real-time applications and complex embedded systems. Your projects can benefit from increased efficiency and faster response times compared to Single-core MCUs, which rely on a single processing unit to handle all operations sequentially.
Core Performance Comparison
Dual-core MCUs typically deliver enhanced core performance compared to single-core MCUs by enabling parallel processing and multitasking, which increases throughput and reduces latency in complex applications. Each core in a dual-core MCU can handle separate tasks or threads simultaneously, resulting in improved efficiency and faster execution of compute-intensive operations. Single-core MCUs may offer lower latency for single-threaded tasks but generally lack the scalability and performance advantage introduced by dual-core architectures.
Energy Efficiency: Dual-core vs Single-core
Dual-core MCUs typically offer superior energy efficiency by dynamically distributing tasks between cores, allowing one core to run at lower power states while the other handles intensive processing. Single-core MCUs often operate at higher frequencies continuously, leading to increased power consumption for complex tasks. Your choice should consider workload patterns where dual-core architectures can optimize energy use without sacrificing performance.
Application Suitability and Use Cases
Dual-core MCUs excel in applications requiring concurrent processing, such as industrial automation, automotive systems, and advanced IoT devices, where real-time performance and multitasking are critical. Single-core MCUs are suitable for simpler control tasks like home appliances and basic consumer electronics, offering cost efficiency and lower power consumption. The choice between dual-core and single-core MCUs depends on the complexity of the application, processing demands, and power budget constraints.
Cost Considerations: Dual-core vs Single-core MCUs
Single-core MCUs generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to dual-core MCUs, making them ideal for budget-sensitive projects with simpler processing requirements. Dual-core MCUs, while more expensive, provide enhanced performance and multitasking capabilities that can justify the higher investment in applications demanding real-time processing or parallel task execution. Your choice should balance cost against performance needs, considering overall system complexity and long-term scalability.
Development Complexity and Toolchain Support
Dual-core MCUs increase development complexity due to the need for managing inter-core communication, synchronization, and parallel processing, requiring more sophisticated software design and debugging techniques. Toolchain support for dual-core MCUs often includes specialized multi-core debugging tools, real-time operating system (RTOS) support, and enhanced compilers tailored for concurrent execution. Single-core MCUs benefit from simpler development workflows and broader toolchain compatibility, with mature, well-documented software stacks and debugging environments.
Scalability and Future-proofing Designs
Dual-core MCUs offer superior scalability for complex applications by distributing tasks across two processing units, enhancing performance and enabling smoother multitasking compared to single-core MCUs. Your designs become more future-proof with dual-core architectures, as they can handle increasing software demands and integration of advanced features without significant hardware changes. Single-core MCUs may suffice for simpler, cost-sensitive applications but lack the flexibility needed for evolving technology requirements and expanding functionalities.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right MCU Core Architecture
Selecting between dual-core and single-core MCUs depends on specific application requirements, such as processing power, energy efficiency, and real-time performance. Dual-core MCUs offer enhanced multitasking capabilities and higher throughput for complex applications, while single-core MCUs provide simpler designs with lower power consumption ideal for straightforward tasks. Considering factors like workload complexity, cost constraints, and power budgets ensures the optimal MCU core architecture for embedded system design.
Dual-core MCU vs Single-core MCU Infographic
 electrown.com
electrown.com